
1. (a) Steel Limited stocks chemical K3 which is used in the manufacturing process. The following information relates to the chemical:
Cost of placing the order
Annual stock cost per unit
Annual demand
Delivery time after placing an order
Ksh. 75
Ksh. 10
96,000 units
2 weeks
(i) Prepare a schedule of costs for orders of 40,60,80 and 100 showing:
(I) order size;
(II) annual ordering costs;
(III) average stock holding;
(IV) annual holding costs;
(V) total costs.
(ii) Advise the management on the optimal number of orders. (12 marks)
(b) Explain the financial needs of each of the following stakeholders:
(i) shareholders;
(ii) government;
(iii) lenders;
(iv) employees.
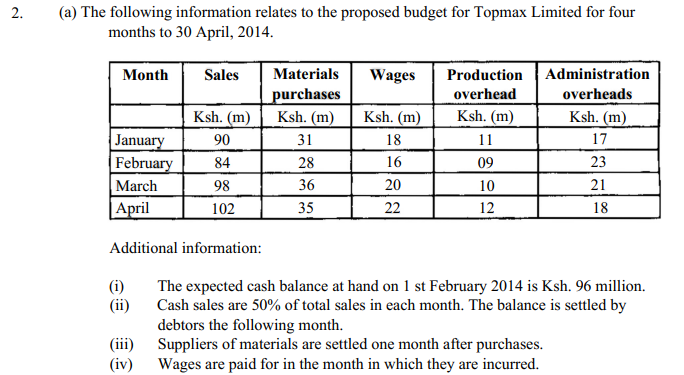
(v) Production and administration overheads are settled one month after they have been incurred.
(vi) Production overheads include a depreciation change of Ksh. 1 million per month.
(vii) Machinery is to be acquired and paid for in the month of February, 2014 at
Ksh. 12 million.
(viii) A dividend of Ksh. 66 million will be paid in April 2014.
(ix) A bank loan of Ksh. 28 million will be received in March, 2014.
(x) A sales commission of 2% on sales is paid in the month of sale. Prepare a cash budget for February, March and April, 2014. (12 marks)
(b) Explain four limitations of financial accounting.
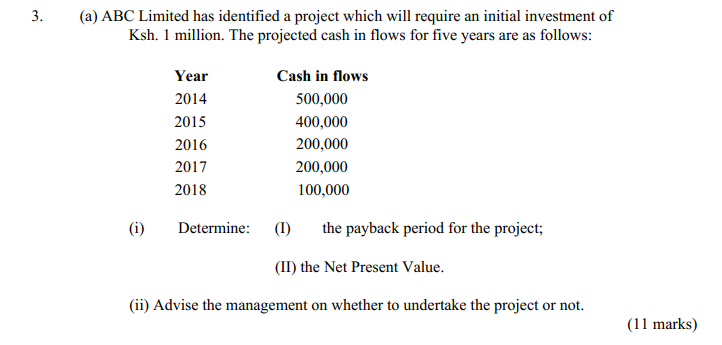
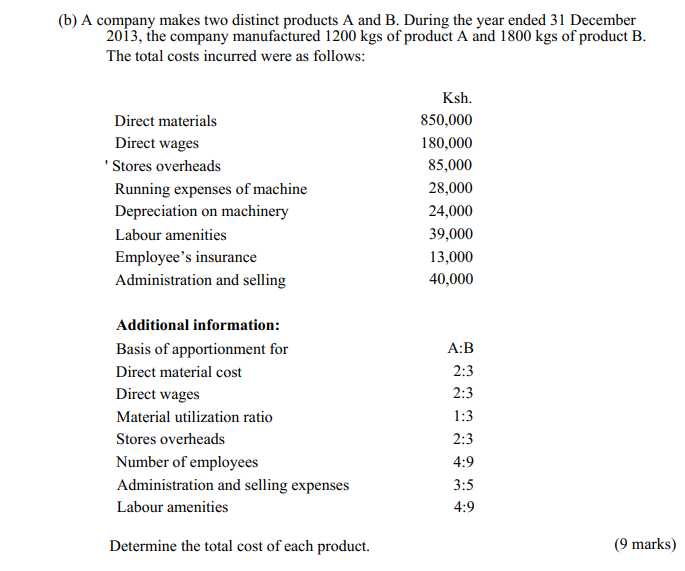
4, (a) Explain four advantages of Equity finance as compared to Debt finance to businesses. (8 marks)
(b) In process A 1000 units of raw materials were introduced at Ksh. 10,000. The other
expenditures incurred by the process were labour Ksh. 3000 and overheads Ksh. 2,500.
Of the units introduced 10% are normally lost in the course of manufacture. Losses
have a scrap value of Ksh. 20 per unit. The output of process A was 750 units.
Prepare:
(i) process A account;
(ii) normal loss account;
(iii) abnormal loss account.
5. (a) On 1st January, 2014 John started business with Ksh. 1,960,000 in the bank.
Jan 4lh
Purchased goods cm credit from Kamwa Limited for Ksh. 500,000
Jan 8,h Sold goods on credit to Tumi Limited for Ksh. 400,000
Jan 15th Paid Ksh. 40,000 to Kamwa Limited by cheque
Jan 20th Tumi paid John Ksh. 300,000 by cash
Jan 25th Purchased goods worth Ksh. 400,000 by cheque
Jan 26th Sold goods and received a cheque of Kshs. 700,000
Jan 31st Paid salaries and wages by cash Ksh. 200,000
(i) Prepare the ledger accounts to record the transactions above.
(ii) Balance off the ledger accounts as at 31s’ January, 2014.
(12 marks)
(b) Explain the causes of each of the following adverse variances:
(i) Purchase price variances;
(ii) material usage variance;
(iii) labour efficiency variance;
(iv) overhead variance.
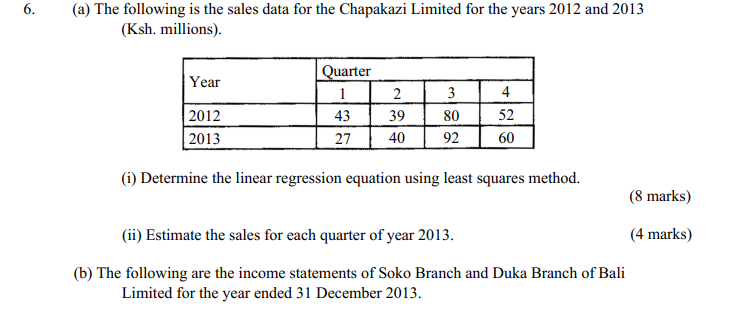
7. (a) The following information relates to Pewa Limited for the year ended 30 June 2013. Sales Ksh.
3,600,000
Materials 1,080,000
Labour 810,000
Variable overheads 360.000
Fixed overheads 210,000
During the year the factory operated at 50%capacity with an output of 180,000 units. The marketing manager has projected that the sales could double in the next financial year if the selling price could be reduced to Ksh. 17 per unit. This will increase the
fixed overheads by Ksh. 50,000.
(i) Prepare:
(I) the income statement for the year ended 30 June 2013.
(II) the projected income statement for the year to 30 June 2014.
(ii) Advise the management on whether the selling price should be reduced as proposed.
(12 marks)
(b) Outline four disadvantages of excessive working capital in a business.