WEDNESDAY: 3 August 2022. Morning paper. Time Allowed: 2 hours.
The paper is made up of fifty (50) multiple choice questions. Answer ALL questions by indicating the letter (A, B, C or D) that represents the correct answer. Each question is allocated two (2) marks.
1. Which of the following is NOT a potential advantage of using good project management?
A. Shorter development times
B. Higher worker morale
C. Lower cost of capital
D. Higher profit margins (2 marks)
2. A _______________________ is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service or result.
A. Program
B. Process
C. Project
D. Portfolio (2 marks)
3. Which of the following is NOT an attribute of an IT project?
A. Projects are unique
B. Projects are developed using progressive elaboration
C. Projects have a primary customer or sponsor
D. Projects involve little uncertainty (2 marks)
4. Which of the following is NOT part of the triple constraint of project management?
A. Meeting scope goals
B. Meeting time goals
C. Meeting communication goals
D. Meeting cost goals (2 marks)
5. ____________________ is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements.
A. Project management
B. Program management
C. Project portfolio management
D. Requirements management (2 marks)
6. Project portfolio management addresses ___________________ goals of an organisation, while project management addresses _______________ goals.
A. Strategic, tactical
B. Tactical, strategic
C. Internal, external
D. External, internal (2 marks)
7. Several application development projects done for the same functional group might BEST be managed as a part of
____________________.
A. Portfolio
B. Program
C. Investment
D. Collaborative (2 marks)
8. Which of the following is NOT part of the three-sphere model for systems management?
A. Business
B. Information
C. Technology
D. Organisation (2 marks)
9. In IT project management, which process group normally requires the MOST resources and time? (2 marks)
A. Initiating
B. Planning
C. Executing
D. Monitoring and controlling
10. Farida is the project manager of a project, and she is planning responses to a set of risks. As a direct result of implementing these risk responses, she anticipates certain other risks to arise. These are:
A. Primary risks
B. Secondary risks
C. Planned risks
D. Workaround (2 marks)
11. As an experienced project manager, you have found that running a work breakdown structure (WBS) meeting is tricky because you need to find a balance between insufficient decomposition and excessive decomposition. When items are excessively decomposed, it leads to all the following EXCEPT?
A. Inefficient use of resources
B. Nonproductive management effort
C. Decreased efficiency when performing work
D. Breaking the 100 percent rule (2 marks)
12. What is the last step in the four-stage planning process for selecting IT projects?
A. IT strategy planning
B. Resource allocation
C. Business area analysis
D. Mind mapping (2 marks)
13. Scope _________________ is often achieved by a customer inspection and then sign-off on key deliverables.
A. Acceptance
B. Completion
C. Validation
D. Close-out (2 marks)
14. Predecessors, successors, logical relationships, leads and lags, resources requirements, constraints, imposed dates, and assumptions are ALL examples of __________________________.
A. Items in an activity list
B. Items on a Gantt chart
C. Milestone attributes
D. Activity attributes (2 marks)
15. Which of the following is NOT an output of the project cost management process called estimating costs?
A. Activity cost estimates
B. A cost baseline
C. Basis of estimates
D. Project documents updates (2 marks)
16. What tool can you use to determine whether a process is in control or out of control?
A. A cause-and-effect diagram
B. A control chart
C. A run chart
D. A control panel diagram (2 marks)
17. A ___________________ maps the work of a project, as described in the work breakdown structure (WBS), to the people responsible for performing the work.
A. Project organisational chart
B. Work definition and assignment process
C. Resource histogram
D. Responsibility assignment matrix (2 marks)
18. Which risk management process involves prioritizing risks based on their probability and impact of occurrence?
A. Planning risk management
B. Identifying risks
C. Performing qualitative risk analysis
D. Performing quantitative risk analysis (2 marks)
19. The ___________________ is the point at which the contractor assumes total responsibility for each additional dollar of contract cost.
A. Breakeven point
B. Share Ratio Point
C. Point of Reconciliation
D. Point of Total Assumption (2 marks)
20. What methodology was developed in the United Kingdom, defines 45 separate sub processes, and organises them into eight process groups?
A. Six Sigma
B. PRINCE2
C. Kaizen
D. TQM (2 marks)
21. Which of the following is NOT a typical reason that project teams would use a predictive approach versus an agile approach to managing a project?
A. The project has unclear up-front requirements
B. The project team is inexperienced and dispersed.
C. Large risks are involved
D. The completion date is fairly rigid. (2 marks)
22. What is the last step in the four-stage planning process for selecting IT projects?
A. IT strategy planning
B. Business area analysis
C. Mind mapping
D. Resource allocation (2 marks)
23. Which of the following is NOT a BEST practice that can help in avoiding scope problems on IT projects?
A. Don’t involve too many users in the scope management
B. Keep the scope realistic
C. Use off-the-shelf hardware and software whenever possible.
D. Follow good project management processes. (2 marks)
24. Which of the following processes involves determining the policies, procedures, and documentation that will be used for planning, executing, and controlling the project schedule?
A. Planning schedule management
B. Defining activities
C. Estimating activity resources
D. Activity sequencing (2 marks)
25. An IT project is halfway completed, its schedule performance index is 110 percent, and its cost is performance index is 95 percent, how is it progressing?
A. It is ahead of schedule and under budget
B. It is ahead of schedule and over budget
C. It is behind schedule and under budget
D. It is behind schedule and over budget (2 marks)
26. Which of the following statements BEST explains the purpose of IT project management?
A. To produce the highest – quality products and services possible
B. To ensure that appropriate quality standards are met
C. To ensure that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken
D. To ensure that the project will be executed at a low cost (2 marks)
27. The figure below shows an extract of a network diagram. What is the name given to the path named W?
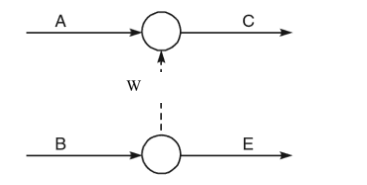
A. Dummy activity
B. Precedence activity
C. Successor activity
D. Event activity (2 marks)
28. Which of the following is NOT a tool or technique for managing IT project teams?
A. Observation and conversion
B. Project performance appraisals
C. Conflict management
D. Social styles profile (2 marks)
29. Which risk identification tool involves deriving a consensus among a panel of experts by using anonymous input regarding future events?
A. Risk breakdown structure
B. Brainstorming
C. Interviewing
D. Delphi technique (2 marks)
30. An IT project team has decided NOT to use an upcoming release of software because it might cause your schedule to slip. Which negative risk response strategy are you using?
A. Avoidance
B. Acceptance
C. Transference
D. Mitigation (2 marks)
31. An IT company wants to get information from potential sellers for providing new computers. What type of document would be required of the potential sellers?
A. Request for proposal
B. Request for quote
C. Proposal
D. Quote (2 marks)
32. Which of the following outputs is often completed before initiating an IT project?
A. Stakeholder register
B. Business case
C. Project charter
D. Kick-off-meeting (2 marks)
33. Which of the following is NOT a scope of an IT support office?
A. Supervisory services
B. Provision of expertise in Planning, Business Case, Risk Management and Issue Management
C. Central conduit for communications for the project environment
D. Audit and guidance on processes, tools and techniques (2 marks)
34. _____________________is the analysis done to consider the profitability of an investment over the life of an asset alongside considerations of affordability and strategic fit.
A. Profitability appraisal
B. Return on investment
C. Investment appraisal
D. Viability analysis (2 marks)
35. Which of the following is NOT an IT Project Selection Model?
A. Comparative Benefit
B. Scarcity Necessity
C. Product Line Extension
D. Sacred Cow (2 marks)
36. What tool and technique is used for all processes of project integration management?
A. Project management software
B. Templates
C. Expert judgement
D. Intuition (2 marks)
37. One of your project stakeholders has a high amount of authority and a high amount of interest. How should you manage that relationship?
A. Manage closely
B. Keep informed
C. Keep satisfied
D. Monitor (2 marks)
38. Use the table below to determine the critical path and its duration?
Activity Predecessor Estimate in Weeks
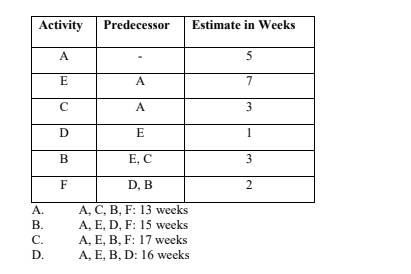
(2 marks)
39. Suppliers and concerned citizens are examples of which type of stakeholders.
A. Internal
B. External
C. Supportive
D. Immediate (2 marks)
40. Which type of matrix can help clarify which knowledge areas are MOST important to stakeholders on an IT project?
A. A knowledge area matrix
B. A stakeholder management matrix
C. A prioritisation matrix
D. An expectations management matrix (2 marks)
41. In undertaking an IT project, who should identify risks?
A. Those invited to the risk identification process only
B. Key project stakeholders only
C. The project manager only
D. All project personnel (2 marks)
42. Which of the following is not a project competing constraint?
A. Budget
B. Procurement
C. Risk
D. Resource (2 marks)
43. Change control tool selection should be based on the needs of the project stakeholders, including organisational and environmental considerations and/or constraints. Which of the following is NOT a key change management consideration while selecting an appropriate change control tool for a project?
A. Identifying and selecting a change item
B. Documenting the change into a proper change request
C. Configuration item verification and audit
D. Tracking change requests (2 marks)
44. On-demand scheduling is one of the techniques used in agile projects. This type of scheduling relies on:
A. A schedule that was developed previously for the development of the project increments.
B. Discretionary dependencies that cannot be changed by the project team.
C. Skills of the project manager rather than the skills of the team.
D. A backlog or intermediate queue of work to be done. (2 marks)
45. The project management team has determined that there are some changes to the scope of the project. Suggest who may be responsible for reviewing, evaluating, and approving documented changes to the project?
A. Change Control Board
B. Change Configuration Board
C. Scope Control Board
D. Configuration Control Board (2 marks)
46. A project manager estimates the work to be accomplished in the near term in detail at a low level of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). He estimates work far in the future as WBS components that are at a relatively high level of the WBS. What is this technique called?
A. Decomposition
B. Rolling wave planning
C. Scope Creep
D. Earned value planning (2 marks)
47. Most project management software packages use a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram known as:
A. Waterfall Method
B. Agile Method
C. Just-in-time Method
D. Precedence Diagramming Method (2 marks)
48. As a project manager, you are analysing the costs incurred in a project. Which of the following costs cannot be classified under cost of nonconformance?
A. Quality Assurance Costs
B. Warranty costs
C. Costs due to loss of reputation
D. Rework costs (2 marks)
49. A technical team can begin to edit a large document 15 days after it begins writing it. What kind of dependency would this represent?
A. Start-to-start with a 15-day lead
B. Finish-to-finish with a 15-day lead
C. Start-to-start with a 15-day lag
D. Finish-to-start with a 15-day lag (2 marks)
50. Analogous Estimating is an estimation technique that uses the values of parameters such as scope, cost, budget, and duration from a previous similar activity as the basis of activity. It is frequently used for estimation when there is a limited amount of information about the project. This is a form of:
A. Gross value estimation
B. Function point estimation
C. Fixed point estimation
D. Precision Estimation (2 marks)
