- Planning refers to what is to be done, how it is to be done and who is to do it.
- In its expanding role, the planning process should refer to making decisions in a forecasted evaluation.
- Planning involve the determination of future course of actions i.e. how it is to be done, why an action is to be taken, what is to be done, when it is to be done etc
- Project planning means an activity in which human, material and financial resources are organized in a better way to undertake a unique work within a specified time, cost and quality to achieve objectives. Anyone planning a project of significant size will soon find that, there are a number of factors both inside and outside the project organization that can have a profound effect on the planer’s intentions.
External factors that can affect or wretch attempts at project planning include:-
- Act of god e.g earthquakes, floods, slides
- Fiscal policy – the policy of a national government in respect of taxation and other financial measures
- Corporate strategy – i.e. decisions made by managers outside and above the project organization
- Statutory regulations – legislations by national and regional government can impose extra burdens on project designers and contractors that have to be taken into account at the planning stage.
Characteristics of Planning
- Planning is closely associated with the objectives of the organization
- Planning is concerned with looking into the future. It requires forecasting of future situation in that organization has to function
- planning involves the selection of the best alternatives i.e. To achieve objectives
- Planning is comprehensive and includes every course of action in the organization
- Planning is an interdependent process i.e. It coordinates activities of various departments, sections and subjections
- Planning is flexible as its based on future conditions that are dynamic.
Importance of Planning
- All managerial actions depends on planning
- It provides a guideline to all functions
- Better planning ensures better utilization of the organization’s resources
- It helps to focus attention on objectives thus all activities are performed to meet these objectives within a specified time.
- It minimizes cost because of the emphasis on efficient operations and consistency.
- It reduces risks and uncertainties and prepares for any eventuality
- It helps in identifying situations that may impact negatively in implementation of the project.
- It helps to determine available resources for the project implementation
- It helps in control – control involves measurement of accomplishment of events against plans and correction of deviations to assure attainment of objectives according to plan.
- It increases organization effectiveness – proper use of resources to accomplish objectives.
Causes of Poor Project Planning
- Lack of accurate information
- Problems of changer in technology, business conditions, consumer taste and desires
- Poor project management discipline
- Lack of knowledge and skills in planning
- Inadequate time for planning
- Wrong team members of the project
- Inflexibility in planning (inability to change)
- Absence of risk management – a good project must have a well defined risk plan
Components of a comprehensive Plan for a project
- Planning the project work – this spells out the activities related to the organization or the project in a detailed schedule and sequential way
- Manpower and organization planning – i.e. determining human resource, work force and labor required
- Planning for funds – this establishes the overall cost i.e. sources and uses of funds within the project
- Planning the information system – i.e. ensuring to update and keep the data or information catalogue for the project.
Project planning guidelines
- The project team should have a detailed project plan. The plan includes the following:-
- Work schedule and guidelines
- Budgets, cost account and control system
- Detailed work breakdown structures and work packages
- Quality plans
- Areas if high risk, uncertainty and contingency plans
- Documentation plans
- Change, control and work review plans
- Personnel plans and resources utilization plans
Project guidelines involves
- Project identification – this involves needs assessment in order to determine the most felt need. The project identified should be the priority of the target group.
- Verification of feasibility report – after a need assessment report is completed, which summarizes the problems and needs of the area, the strength and weaknesses in terms of resources and opportunities available for development are also identified.
- Identification of project objectives- once the project has been selected, the objectives is stated clearly in measurable terms.
- Project team is identifies – these are people who are going to work in the project and they need to possess relevant qualifications and experience.
- Identify the project stakeholders – these are groups/individuals that have interest for the project to be initiated.
- Establish the scope of work – these involves, knowing the nature of work to be performed.
- Draw the standard of work or specification – this involves specifying the quality of work that is expected to be performed. This information would be used to be performed. This information would be used during monitoring and evaluation.
- Identify the project key stages – these are vital activities for the project that must be performed at different times and their completion affect the entire project.
- Prepare the project bar chart – a bar chart is a diagrammatic representation of the project implementation. It is a tool used to show how the project is to be implemented from the start to end of the project.
- Draw the project network critically – a project network is a diagrammatic representation showing how much time the project is going to take on each activity from the start to the end of the project.
Project Planning Process
1. Problem identification
- This is the 1st step in project planning. It involves identifying the problem that interferes with the development in the communication.
- All projects are intended to solve or reduce some problems thus the need to identify the problems and they should be felt needs.
2. Setting objectives
- Objectives are positive statements of the goals we want to achieve by carrying out the project. These are general and specific objectives.
- General objective – is a statement about what we wish to success of the general objective.
Objectives should be
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Reachable
- Time bound
1. formulating alternative course of action and selecting the most appropriate.
At this stage, various alternative course of action are identified the various alternatives are evaluated in the lights of objectives and other factors that can affect planning e.g politics, demand, resources, government controls.
2. Feasibility analysis.
This is examining the feasibility report, examining each area and comparing it with the alternative selected. it meant to ensure that the project selected is relevant to the needs. It is at this stage that the plan is formulated.
3. Writing the plan
A plan is a skill drawn before an action takes place so as to meet the same goals and objectives. It shows what has to be done, who will do it and when it will be done. It is used during project implementation.
4. Project budget
A budget is a financial statement of a given period of time. It is a qualitative and quantitative statement for the income for a given activity.
During the planning process, it is important to bear in mind that a project plan must be:-
Clear
- The over driving goals for all units of projects are clear enough to give continuity and conditions to all of the tactical choices made during the life time of the strategy.
Keep the initiative
- A good plan reserves freedom of activities or actions, support the empowerment and enhances commitments.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN PROJECT PLANNING
1. Length of the project. Too lengthy projects need adequate resources and time allocation. The overall end result must be considered.
2. Availability of resources
- These include both human and financial resources available. Quality delivery is determined by the availability of adequate resources, time and finance.
3. Objectives/user requirements
- The overall needs to be met have to be identified. This helps in formulating the project objective and intention.
- A project officer examines the requirements deemed useful by the intended target.
4. Fiscal policy and government policy
- The plans must be coordinated with the policies on land. Aspect i.e. taxation must be considered to ensure the right amount is budgeted for a given procurable goods.
5. Initial planning for proceeding project
- This gives an evaluation tool to justify the success of a given project. Consider the reasons for success or failure of previous projects in order to prepare for any risk of danger ahead.
Project Planning Techniques
- This is the process through which the project activities are allocated specific time for their completion. It shows all activities of the project in a logical order as they will be implemented and the time to be spent in each stage.
- Project management has a special set of techniques. However project management like any other functional management is not a technique only. The techniques are the scientific but they are also the act of politics manager.
- For quite sometime project management was equated to project evaluation review technique, pert. But it did not take long for them to get disillusioned. This does not mean that pert has failed. It only reflects that it is a mixture of techniques.
- In project scheduling and coordinating techniques pert plays a key in networking techniques
Project Evaluation Review Technique (PERT)
- Pert is a model for project management designed to analyze and represent the task involved in completing a given project .it is commonly used in conjunction with critical pert method. Pert is a method used to analyze the involved task in completing a project, especially the time needed to complete each task and identify the minimum time needed to complete the total project
- In project scheduling pert plays a key role in networking techniques. In network analysis we try to establish the activities and the time each activity will take.
- It is a representation of project activities and the specific time period they need to be implemented. Pert is also a network by itself.
Critical Path Analysis Method
- Well planned projects have a critical path that key project activities fall in. If these activities are delayed the will delay the whole project.
- CPA Is the longest time period that important activity of the project is going to take. The activities that lie on the longest path of the project from the time of starting to the completion are known as critical activities.
- These activities must be carried out and completed on time in order to operate within the required period of time.
- Analysis of these activities is known as critical path analysis. It is important for project managers to conduct a proper analysis to project requirement before specifying a solution and writing a programme before testing it.
- To understand dependencies, is important in both simple and complex project i.e. If activity can begin only when another activity is complete then we have a dependency but with multiple teams operating dependencies become more complex, this is because we still need to know exactly that components from one team are required before another team can start on something else.
- Dependencies are developed by asking what can start once. This activity has started: the conception is that dependencies run from the finish of one activity to the start of succeeding activity.
- An activity network is therefore important as it shows the inter dependencies between the tasks needed to develop the product and a critical path through the project.
The Ganty Chart/Bar Chart
- This is another planning tool named after H.L Ganty, an industrial engineer who pioneered their used.
- They provide a visual way of illustrating the sequence of activity in a project. They show planned and actual progress for a number of activities displayed against the horizontal time skill.
Advantages of Gant Chart
- Helps to keep truck on how things are doing
- It is easier to make re-allocation of resources among the activities faster
- It can also be easily understood
- It can be easily maintained
- It provides a clear picture of current state of the project
Disadvantages
- They do not show dependencies very easily i.e. that activity has to be completed before another one start.
- They are less useful for managing progress on a project.
Work Breakdown Structure (W.B.S)
- It is a traditional approach and has been used in many projects the basic idea is to take the overall work of the project and break it down progressively into smaller and smaller until we end up with individual tasks or work packages that we can estimate equal.
- The work can probably be sub-divided into smaller work packages e.g a day’s work.
- The idea is to breakdown each activity until we arrive at tasks that are:-
- Fairly atomic i.e. Not readily lie themselves to further subdivision or assignment to more than one person.
- Small enough to estimate with reasonable accuracy e.g half a day or 2 days duration
- The danger of using a standard WBS is that each project has got some distinctive features and it is not important has not ready to fit the project to a standardized approach.
- If anything the standardized approach must be customized in each project.
IMPORTANCE OF WBS
- There is thorough implementation leading to efficiency and effectiveness
- There is reduced work load
- It is time saving
- It enhances specialization
- It helps to reduce conflict
- Priority areas are identified
Duty Specification
This refers to the process of identification of individuals and specialized groups who will perform duties as well as assigning them various responsibilities.
Advantages
- Reduces workload during project implementation
- Promotes project efficiency and effectiveness
- Saves time
- It leads to applying and development of expertise
Disadvantages
- It leads to failure of communication because different specialists do not mix due to lack of social common interest and understanding.
Time specification and management
- Time specification refers to scheduling that determines when activities are to be done and how much is to be done. The period within that the project is to be done must be specified and followed during implementation stage. In ideal situation, a project will be considered very successful if it is completed in time, within budget and performs exactly the way it was designed.
- Time estimate is made by making a work breakdown of the project, estimating the time schedule for each work, putting them in proper sequence or series or any other logical manner and matching them with available resources.
- There should be correct estimate of time taken by each activity.
Disadvantages
- Unrealistic time estimate
- Late deliveries by contractors
- Defective design and subsequent modifications to suit the project requirement increases time and cost
- Problems of resources
NB:-
The estimated time for the completion of a project is dependent only on the work content or sequence. Resources and constrains will also influence it.
There are several approaches for estimating time duration
- Time study
- Previous project data
- Estimating approach
- Range estimates
- Time taken versus time required
- Estimates from contractors
- Allocated and committed time
Project logical framework
- It is a tool to aid projects and programs planning and management especially at strategic and institutional level.
- Project logical framework consist of a 4 x 4 matrix with that summarizes the project records their sanctions that under pins the strategy adopted and outlines how the project may be monitored or arranged according to the hierarchy of objectives or an ends means continuum logical framework approach is a set of interlocking concept that must be used together in a dynamic fashion to permit elaboration of a well designed, objectively described and valuable project.
EXAMPLE
We carry out all the activities necessary to support the family planning clinic then they will provide family planning services to the community. If they have access to FP services then they will use FP methods effectively. If they use FP methods increases, then the population growth rate will fall.
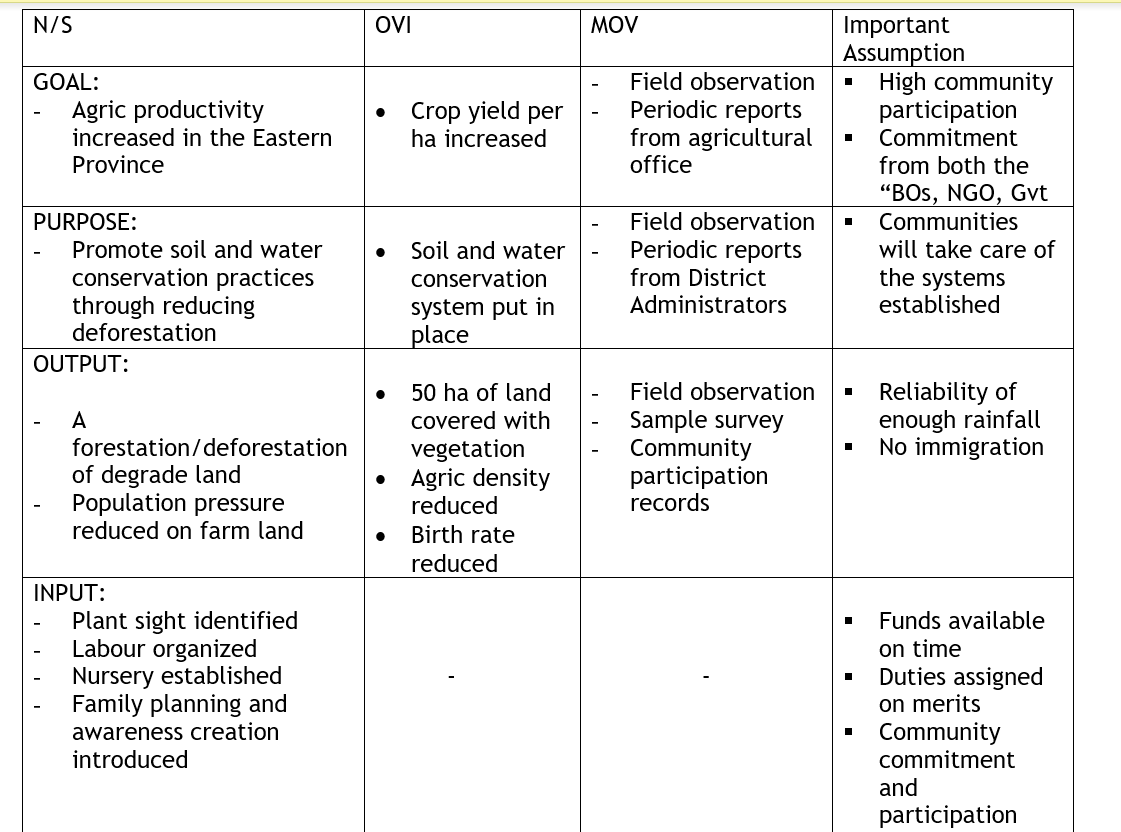
Column I Nutritive Summary
- The narrative summary defines the project structure; care should be taken to distinguish between project activities, inputs, outputs purposes and goals
- Goal/overall objective – is the ultimate objective of the project to that specific project will contribute.
- It may not necessarily be reach till end of project implementation
- Purpose
- This is what the project is expected to achieve. It is the intended effect or impact of project on target population.
- Output
- Are the likely results achieved i.e. the results of completed project activities
- Activities
- This are what we actually do e.g in a road project, the inputs might be the materials, machinery and labour. The output might be the number of kilometers of the finished road; purpose might be to enable easy transportation of products and goals to enhance economic development.
Column II Objectively Verifiable Indicators
- It shows the achievement of objectives applying at each level. In the hierarchy, OVI should show that the project is successful in the purpose column; we need indicators to show the purpose of a project
- At the output level, the indicators should be measurable
- At the activity level, we have means/inputs but no indicators
Column III Means Of Verification
- There must be a way of measuring or collecting information about each of the indicators.
- It is important to identify the sources from that information to verify indicators can be gathered e.g reports, documents.
Column IV Important Assumptions
Project may fail not because of the project structure was necessarily bad or illogical but because of external or evolutional factors outside control of the project i.e. Natural calamities. They are external to the project and those responsible for the project have little or no control over them.