- In project identification, potential set of interventions arising from ideas crystallized in the conception stage are determined and individual or communication representative to an agency capable of identifying on institution to provide the necessary support to realize the expectation may submit the in information in the proposal for project conception.
- Usually some objective judgment is applied to assess the proposal or set or proposals to establish if the proposal can proceed to the next stage in the cycle.
Problem identification
- This is a very crucial process in the formative stages of any project development undertaking and it forms the basis of project justification and rational i.e. the core of the project existence and definition.
- Problem identification refers to the process of assessing the problems people encounter in the community and prioritizing them.
- Projects grow out of problems or opposite. Problem identification can also refer to finding out those issues affecting people and those that limit them to function maximamlly.
- These issues are summed up into a problem statement. It specifies the problem at hand that need to be addressed, ideas to solve the problem are generated and produced as a document describing the project in sufficient details coveting all aspects necessary for consideration by project team.
- The problem to be solved becomes the objective of the project
Sources of Project Ideas
- These ideas are usually hatched through discussion by local leaders in a community and specialists as need based issues are crystallized into a proposal.
The projects can therefore be conceived based on:-
- Market demand – either domestic or overseas
- Resource availability – opposite to make profitable use of available resources
- Technology – i.e. to make use of available technology
- Natural calamity – in order to address the adverse effects of natural events i.e drought, floods etc
- Political consideration
Project Ideas Can Also Originate From Other Sources
- National level – these are projects with form part of a broad national program
- Sectoral level – various sectors may decide to concentrate on development projects in one area because of the potential in that area
- NGO`s – there are many NGO`s operating in local areas, they can come up with profit ideas aimed at benefiting the people.
- Leaders – politicians as people’s representatives also come up with profit ideas
- Local people – the local people are the intended beneficiaries of the proposed project. The projects initiated by the people themselves have strong support from them and stand a better chance of success.
Factors influencing the selection of community projects
- The project ideas generated from the community level are many but the available financial resources and the staff do not allow for implementation of more than a few projects at a time.
- These projects are sorted out and only those given the highest priority are submitted for implementation.
- Projects are selected with a particular objective, project selection should not be assumed as an easy task.
- In essence, the basis of selecting a project is determined by the objective it should fulfill the objectives or the problem it is meant to solve among other things.
- Project selection therefore is the process of evaluating individual projects or group of projects and choosing to implement some of them so that the objectives of the organization are achieved.
These factors include:-
Policy framework
- This s the main guide to all matters involved in the project. it clarifies the overall principles for the project attitude towards handling management work.
- Policy framework involves statements that have the backing and resources necessary for its achievement.
- A project policy framework incorporates all stages of the project from completion to operation stems until decommissioning.
- It also serves the purpose of coordinating the project activities. The policy framework should be based on the following activities i.e. planning, execution.
- All the activities and tasks affecting the project require well laid down policies describing all requirements and stakeholders.
To achieve the objectives of the project, the policy framework should:-
- Determine the size of the project, the project team and the location of the project
- Identify the status of the existing document and determine whether or not the existing document is compatible and the proposed project activities
- Determine the range of project activities within the specific project.
- Identify the level of activities within the project and the method of work allocation
- Determine the responsibilities and the commitment of the project management team.
- The policy framework should take into account structure to avoid overlapping and duplication design to provide a uniform simple format and facility for documentation of changes.
- Policy framework also ensures that all members of the project team have a job description and that they comprehend and understand their job well.
Criteria
- These are procedures organization use to decide with creative idea to support. This is because projects have different costs, benefits and risks. Project selection is usually a task of senior management as it’s the crucial part of project life because the success meets its goals.
Relevance
- Project selection is one of the many decisions closely associated without project management. Decision aiding models are used to deal with all problems of relevance. Such models are needed because they abstract the relevant issues about a problem. It is said that realist cannot solve a problem but idealists can do. An idealist strips away almost all the reality from a problem leaving only the aspects of “real” situation without he/she wants to deal with. Reality is too far complex to deal with. The process of carrying away the unwanted reality from the bones of a problem is called modeling the problem.
- The model represents the problem structure i.e. the modeling foam.
- Projects are selected according to their relevance to the needs of the people or community. It is imperative to consider that the projects are relevant based on the situation on ground.
Feasibility
- In project selection, a feasibility report is inevitable as it covers important areas in any report.
- The feasibility report covers
- The technical configuration of the project
- The performance requirement for the project
- Lost estimate for the project
- Techno-economic viability of the project
- An overall schedule implementation
- A feasibility report shows how possible it is to carry out a project
- The project manger may update and validate it before proceeding with the project.
- He is responsible for the completion of the project according to what is laid down in the feasibility report
- According to the guidelines published by the planning feasibility
A feasibility report should include the following:-
- Raw material survey
- Demand study
- Technical study
- Product pattern
- Planted size
- Raw material requirement
- Location study
- Project capital cost estimate and source of finance
- Profitability and cash flow analysis
- Cost benefit analysis
- Process selection
Project feasibility study takes into account the following areas
- Need for the project
- Availability of resources
- Available technology and use
- Location of the project
- Infrastructural facilities and services
- Financial and economic benefit
PROJECT AREA ANALYSIS
- This is a comprehensive and a quality study of the area where a project is to be initiated.
- The study is aimed at finding out whether an area is fit for a particular project.
- Projects are analysis is inevitable in the pre-feasibility study of any project.
- Pre-feasibility study is the initial process of deciding what kind of project is most needed given the development requirement at a particular time and place corresponding to this stage; the series of document is usually prepared with a report referred to as an identification report.
- Project area analysis involves
- Mapping out the area of the project relating all the details with the type of desired project, coming up with statistics bearing data including that of demographic.
- Locate your project by providing specific co-ordinates using the nearest big town, the distance between the largest city/town must be given in km and in annex and maps to give the result location.
- Provide historical background for the area
- Append information that will clarify certain issues i.e. National HIV charts on bar graphs
- Give details of legitimacy on land ownership.
The pre-feasibility study is aimed at finding out-
Resources
- In project area analysis, we analyze the resources that are found in an area whether they can be used in the project. In this case we analyze:-
- Human resources – this seeks to find out whether there are personnel qualified to work or contribute to the project.
- Natural resources – these are God given resources i.e. water, trees, stones etc
- It is important to find their source and availability.
- Material resources – these are man-made resources. They include raw materials and others resources i.e. money and equipment. It is necessary to find out whether local resources are available to be used in the project, their sources and transportation requirement.
Administrative infrastructure
- This involves analysis of administrative units in an area I.e. divisions, locations and villages
- The types of local leaders and their roles are also studied
- The need to interact with the government and representatives of government is probably inevitable.
- The project manager can expect to deal with bureaucracy at several district levels.
Economic infrastructure
- It is concerned with the process of production, distribution and consumption of goods and services in the project area.
- It examines existing industries and other economic activities. Although there is a great need for new projects in the developing countries, there is also lack of funds from the normal sources expected in the developed countries.
- Many projects are funded externally. Project managers involved in the identification preparation and appraisal stages of a funded project need to be fully aware of the requirement of the grants or a warding agency to which they are making application for funding.
Land use patterns
- In project area analysis you can’t ignore the question of land use patterns. This can be tackled in project location studied.
- To meet targets relating to time and cost, it is necessary that the site has been properly selected and cost. It is necessary that the site has been, properly selected and the position taken care of before zero date.
- Normally the donors will dispatch a team of experts to inspect the site before they sanction any money.
- Uncertainties associated with the land use patterns and particularly that of sub soil conditions must also be removed before the zero date.
- Understanding of the land use patterns of a potential project site is very important that’s why project sites are selected on several considerations that include:-
- Availability of land, soil characteristics and cost of land
- Sources of raw materials and transportation requirements
- Transportation and marketing
- Source and availability of water
- Availability of power/source and skilled manpower
- Social amenities in the area
- Availability of tax incentives
- Facilities of engineering and maintenance facilities
- Acceptance of project by local bodies
Social infrastructure
- Social infrastructure is amenities or facilities that support people in an area. They include:-
- Hospitals, churches, cinema halls, schools, play grounds etc. You need to find out whether they are available and their use.
Food path
- This is the study of the process of food preparation, harvesting, and storage in an area. It involves how cultivation of land is done, planting, weeding, harvesting and storing
Population (demography)
Occupation
METHODS USED IN PROJECT IDENTIFICATION
- Projects that eventually end up succeeding and making an impact in transformational agenda are those that are built on definite purpose and established on attained goals and objectives.
- These projects are need driven i.e. they set out to address a given problem.
- To identity such a project or set of projects activities, it is imperative that the project promoter considers the use of methods that are all inclusive i.e. involving all people who will be involved and benefit from the project activities (stakeholders)
Some of these methods include:-
- Brainstorming
- Focus group discussion
- Cost versus benefit analysis
- Transact walk
- Problem three analysis
Problem Analysis
- Problem analysis brings out ideas on particular problems to be solved or specific needs to be met.
- It is a tool for understanding the problem in details by trying to identify the route causes and the effects of the problem. The purpose is to organize the disintegrated data into manageable.
Structures for the communication to assess and rank
The following methods can be used
Preference ranking – here the group members can discuss and agree on the ranking from the most to the lease processing pressing problem. It helps to determine quickly the main problems or preferences of individuals and enable the priority of individuals to be easily compared.
Voting is a form of preference ranking
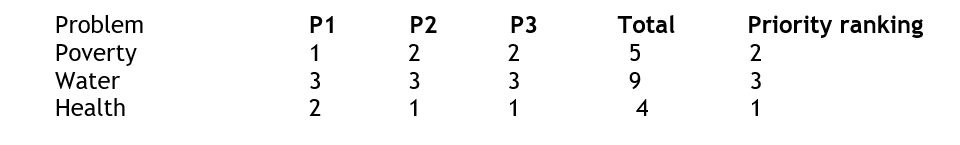
The table shows that health is the most serious problem.
Pair – wise ranking – this is whereby 2 problems are compared at ago to find out with one is pressing to the development in an area. All the problems are compared against each other to establish the most felt need.
Ranking provides a visual impression of whether development projects are addressing the community need or not. It can be used to identify conflict of interest between individuals or groups and how they perceive issues.
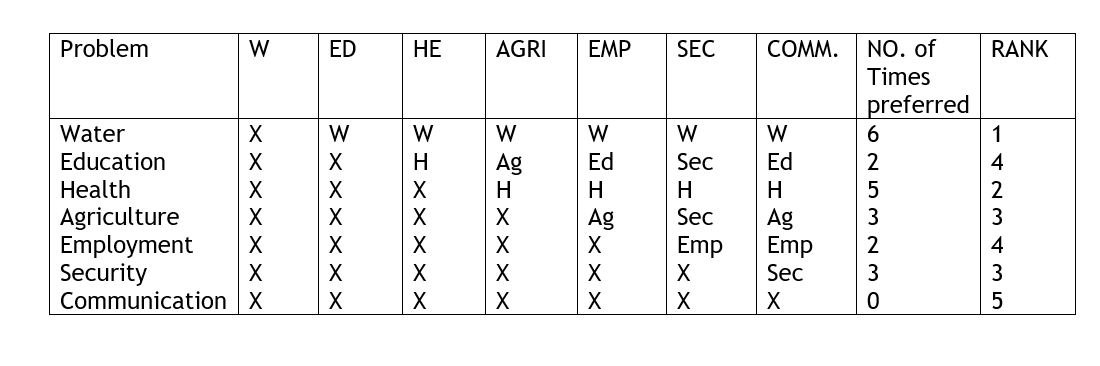
Matrix scoring/Ranking – this is used to compare problems/solutions against selected criteria. It is used to identify local criteria used in making choices for the ranking of problems as well as understanding local preferences.
Some of the criteria can be:-
- Cost which is the least expensive
- Time which can be achieved in the shortest time
- Resources which can be accomplished with little or no outside support
- Sustainability which can the community manage on their own
- Effectiveness which is the most effective in achieving the objective
Flow diagram – they are used to explore impacts, cause effect and relationships on problems or solutions. They are used to illustrate casual flows, impacts and linkages between problems and solutions.
Problem three – once a problem has been identified, it can be analyzed using problem tree. This is where the causes and effects of problems are analyzed.
Steps in Project Identification
Problem definition – starts with a more thorough exercise of collection of data and information on the proposed project. In this stage personnel conduct the exercise with technical and analytical skills in consultation with the target and beneficiary community.
Formulation of specific policies – the objectives of the project are defined and alternative solutions described.
The identification contains the design of a set of operational proposals that is technically, finally and economically feasible.
Decision – is made on the scope of the project location, size among others.
- The detail of feasibility study depends on the complexity of the project and on how much is already known about the proposals. in fact a succession of increasingly detailed feasibility studies is sometimes called for in complex projects.
- The feasibility study provides opportunity to shape the projects to fit its physical and social evaluated and exclude relatively poor alternative ways of achieving the project goals.
Approaches Used In Project Identification
- Methods of data collection, project ideas, and sources of information for project identification must be considered. This process is referred to as need assessment method or approaches.
In Need Assessment, A Planner Must Ask the Following Questions
- Who are the beneficiaries of the project to be implemented?
- Who are the stakeholders of the project?
- What are their needs?
The various approaches used to identify projects include:-
- Felt need approach – here the needs are articulated by the people to benefit from the project. These are the actual needs of the people e.g the Kamba people need water and food while in Kitale people require security.
- Nomadic need approach – this implies those needs that are established by the society or the community and below with no individual should go. It is the planner’s role to identify these minimum requirements and to solve these problems. The people’s requirements should be identified and the nomadic needs should be solved according to the society’s commission, needs and expectations.
- Expressed need approach – it is the same as the felt need; they are expressed by the people or the target group. The only difference from the felt need approach is that the planner is the one who identifies the problem.
- Comparative need approach – here the community may have a comparison of their needs with other communities. These are needs with axe relative in that they are not exactly important or they arise in the community.
Challenges in Project Identification
- The technical nature of project identification stage requires a lot of technical analysis and review to determine the most workable and feasible of the project alternatives, some of the related challenges include:-
- Lack of technical expertise to conceptualize and deapher the specification of parameters that would measure feasibility.
- Subjectivity consideration for establishing the site, length and even coverage of the project.
- Conflict: – in the issue of project ownership and conflict of interests
- Legal impediments
- Poor government policies
- Inadequate resources
- Norms, beliefs and traditions of the people
- Community participation
- Insecurity
- Lack of community awareness (ignorance or illiteracy)
Factors That Assist In Problem Identification
- Symptom of the problem i.e. Invisible signs of a problem
- Impact of the problem: – the felt effect of the problem
- Contributing factors – factors contributing to the existence of the problem
- Affected persons – victims of the problem
- Relationship with other problems
PROJECT APPRAISAL
- The implication of the project on the study and the evaluation are more thoroughly investigated, clarified and documented in project appraisal. Project appraisal involves a further analysis of the proposed project. At this stage, a critical review of the proposal is undertaken.
- The systematic and comprehensive review is usually undertaken by an independent team of experts in consultation with the stakeholders of the project. This provides an opportunity to re-examine every aspect of the project plan to assess whether the proposal is justified before large sums are committed.
Components of project appraisal
- Environment: The focus of project appraisal will revolve around technical assessment and determination of how the intended project will affect and be affected by the immediate physical and social evaluation.
- The impact of the project on overall evaluation has to be as positive as possible i.e. preserving and conserving at best.
- Economic and financial appraisal seeks to determine the feasibility and validity of the project based on its overall cost as measured against its benefits (whether monetary or not)
- A systematic and comprehensive review of cost implication is undertaken and this is compared to other financial analysis of the projects activities are weighed with the view of answering the question. Is the project worthy the cost?social, cultural and political
- Project appraisal looks at the extent to which the social, cultural and political aspects of people’s lives will be affected by the implementation of the project.
- A development project should as far as possible work towards the enhancement.
Technical Methods Used In Project Appraisal
- The appraisal process builds on the project plan be may involve new information if the appraisal team feels that some of the data used at preparation or some assumptions are faulty.
- Similarly, the technical design, financial measures, commercial aspects, incentives, economic parameters, managerial skills, organizational arrangements are thoroughly scrutinized.
- Based on appraisal report, decisions are made about whether to go ahead with the project or not. The appraisal may also change the project plan or develop a new plan.
- After appraisal, the viable project proposals are chosen for implementation based on the priorities of the stakeholders and the available resources.
Techniques used in project (appraisal)
Project appraisal is a comparative tool for project selection. They are either
- Financial methods
- Non-financial methods
Financial method is variously known as financial analysis, business case or project It include:-
-
- Net present value. It deals with how much money these projects make
- Internal rate of return
- It is how rapidly money will be repaid
- Its calculation of the percentage rate of that project will be yield, wealth of saving account.
Pay back period
- This is when the original investment in project will be received to benefits.
Non – financial method EIA (environmental impact assessment analysis)
- Whenever the process of getting financial data is difficult, expensive or time consuming, using a weighted factor scoring method may be a reasonable option for selecting the best alternative solution.
- I.A is a logical method of examining the actions of people and the effects of the project and policies on the evaluation in order to help ensured the long term sustainability of the earth as a habitual planet.
Steps In The Process Of EIA
- screening
- scoping (define issues or identify major impact)
- baseline studies/survey
- impact prediction (if project will succeed/benefit)
- prepare environmental impact statement
- monitoring and audit
Project appraisal and risk management
- Project appraisal or feasibility study is an important stage in the evolution of a project.
- It is important to consider alternatives, identify and assess risks at a time when data is uncertain or unavailable. It does not concentrate on mathematical analysis but rather on the purpose and objectives of using a logical process of managing project risks.
Investment
- The individual project however significance and potentially beneficial to the promoting organization will only constituter part of corporate business. It is also likely that, in the early stages of the project cycle, several alternative projects will be competing for available resources.
Particular finance
- The progress of any project will therefore be subject to investment decision by the parent organization that may allow the project to proceed.
Sanctions
- When a project is sanction, the investing organization is committing itself to major expenditure and is assuming the associated risks. This is the key decision in the life cycle of the project in order to make a well researched decision, the promoter will require:-
Clear objectives
- The promoters objectives in pursuing this investment must be clearly stated and agreed by senior management early in the appraisal phase, for all that follows is directed at achievement of these objectives in the most effective manner.
- The primary objectives of quality, time and cost may well conflict and it is particularly important that the project team know whether minimum time for completion or minimum cost is the priority.
Market intelligence
- This relates to the commercial evaluation in which the project will be developed and later operated. It is necessary to study and predict trends in the market and the economy anticipate technological developments and the actions of competitors.
Realistic estimates/predictions
- It is easy to be over optimistic when promoting a new project. Estimates and predictions made during appraisal will extend over the whole life cycle of implementation and operation of the project.
- Consequently, single figure estimates are likely to be misleading and due allowance for uncertainty and exclusion should be included.
Assessment of risk
- A thorough study of uncertainties associated with investment will help to establish confidence in the estimate and allocate appropriate contingencies.
Project execution plan
- This should give guidance on the most effective way to implement the project and to achieve the project objectives, taking account of all constraints and risks. Ideally, this plan will define the likely contract strategy and include a program showing the timing of key decisions to awards of contracts.
Project Appraisal and Selection
- With an understanding that project proposal is a process of investigation, review and evaluation undertaken as the project or alternative concepts of project are defined.
- This study is designed to assist the promoter to reach informed and rational choices concerning the nature and scale of investment. The core of the process is an economic evaluation, based on a cash flow analysis of all costs and benefits that can be valued in terms of money.
- The consequences of inadequate or unrealistic appraisal can be very expensive to the project. Ideally, all alternative concepts and ways of achieving the project objectives should be considered.
- The resulting proposal prepared for sanction must define the major parameters of the project. The location, the technology to be used, the size of the facility, the sources of finance, raw materials, forecasts in the market and predictions of the cost benefit of the investment.
Program
- It will be necessary to decide when it’s the best time to start the project based on the previous considerations. Normally this means as soon as possible because no profit can be made until a project is completed. In deed may be that market conditions or other commitment impose a program deadline.
Challenges in Project Appraisal
- Personal qualifications – those appraising should be skilled
- Finance – funds required to carry out impact assessment
- Time – requires a lot of time in visiting the field
- Government policies
