ORGANIZATION CULTURE
Introduction
Culture is shared meaning, understanding and sense making .Culture sums up the dominant values visions, perspectives ,standards and models of behaviour that are in organizations. The shared beliefs, values and expectations held by individual also constitute organization culture.
Definitions:
- Organization culture is defined as a pattern of basic assumptions invented , discovered or developed by a group as it learns to cope with its problems of external adaptation and internal integration that has worked well enough to be considered valuable and therefore to be taught to new members as the correct way to perceive ,think and feel in relation to these problems.( Edgar
Schein) - Organization culture can therefore said to be the essential collection of shared values which provide both explicit and implicit sign post to preferred behaviour in the organizations.
- Organization culture refers to a system of shared meaning held by members that distinguishes the organization from other organizations.
Functions of cultures
- It creates distinction between one organization and others.
- It conveys a sense of identity for organizations members.
- It facilities the generation of commitment to something larger than one’s individual interest.
- It enhances the stability of social system.
Characteristics of Organization Culture
- Innovation and risk taking
The degree to which employees are encouraged to be innovative and take risk. - Attention to detail
The degree to which employees are expected to exhibit precision ,analysis and attention to detail . - Outcome orientation
The degree to which management focuses on result or outcomes rather than on the techniques and processes used to achieve those outcomes. - People orientation
The degree to which management decisions take into consideration the effect of outcomes on people within organization. - Team orientation
The degree to which work activities are organized around teams rather than individuals. - Aggressiveness
The degree to which people are aggressive and competitive rather than easy going - Stability
The degree to which organizational activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in contrast to growth. - Norms
Standard to behavior exist including guidelines on how much work to do . - Dominant values
These are those values that the organizations advocates and expects from the participants in an organization e.g. High quality, low absenteeism and high efficiency. - Rules
These are strict guidelines related to getting along in the organization.
Creating an Ethical Organization Culture
1. Be a visible role model
Employees will look to top management behaviour as bench mark for defining appropriate behavior.
2. Communicate ethical expectations
Ethnical ambiguities can be minimized by creating and disseminating an organizational code of ethics. It should state the organization’s primary values and ethical rules that employees are expected to follow.
3. Provide ethical training
Set up seminars ,workshops and ethical training programs .Use the training sessions to reinforce the organization’s primary values, rules and standard of conduct .
4. Visibility rewards to ethical acts and punish unethical ones
Performance appraisals of managers should include a point by point evaluation of how his or her decisions measure up against the organization code of ethics .People who act ethically should be visibly rewarded for their behavior and unethical acts should be punished .
5. Provide protective mechanisms
The organization needs to provide formal mechanisms so that employees can discuss ethical dilemmas and report unethical behaviour without fear of reprimand.
Creating a Culture
A culture is created basically by a founder or top-level manager who forms a core group that shares a common vision .
Stage I
- Recruitment of like minded individuals
These people will be attracted instinctively to the founder’s visions and aims. - The development of groups norms
These are likely to be strongly influenced by founders in the formative stages - Statement of espoused values
The founders or initiators will have the greatest influence on these values in the early stages , subsequently, the organizations leadership must demonstrate to other stakeholders that what is saying truly believes and not accordingly . - Production of mission statement
These provides visible evidence of espoused values and norms and the platform for the organization’s relationships with various stakeholders.
Stage 2
These comprise of habit and tradition building activities, aimed at embedding the culture in the day to day activities of the organizations by means of procedural and ritualistic measures such as:
- The introduction of appropriate communication systems and decision making to assist integration
- The installation of organizational procedures and rules which promotes integration by setting standards for members to follow.
- Promotion of organization symbols
Battle flags national emblems demonstrates the unity of the organization which come to embody a certain reputation e.g. Red Cross. - Development of key rituals, helps to establish the organizations ethos’s i.e.- the part of culture to do with organization climate.
- The production of policy statements on the key issues .These lay the basis for relations with stakeholders.
Creating a Customer Responsive Culture
Customer responsive cultures hire service oriented employees with good listening skills and willingness to go beyond the constraints of their job description to do what’s necessary to please the customer.
Managerial Actions to Be Taken
- Selection
Customer responsive culture begins by service; contact people with the personality and attitudes consistent with a high service orientation. - Training and socialization
The training programs vary according to the organization but they focus on product knowledge, active listening , showing patience and displaying emotions. - Structural design
Organization structure need to give employee more control by reducing rules and regulations. Employers are better able to satisfy customers when they are in control. - Empowerment
These involves consistent empowering employees with discretion to make day to day decisions about job related activities. - Leadership
Effective leaders in customer responsive cultures deliver by conveying a customer focused vision and demonstrating by their continual behaviour that they are committed to customers. - Performance
A customer responsive culture will be fostered by using evaluations that include, input from customers - Reward systems
Provision of ongoing recognition to employees who have demonstrated extra – ordinary effort to please customers,i.e. the management promotes good service.
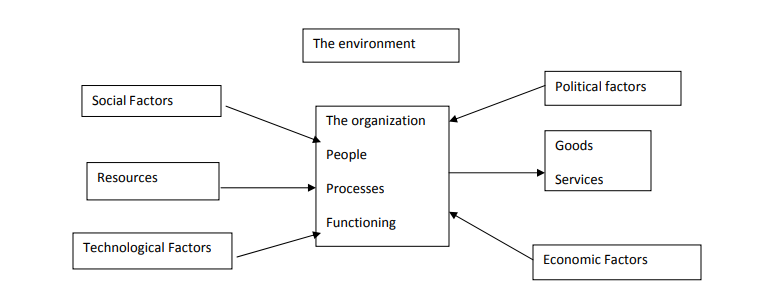
THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS ENVIRONMENT
Organization does not exist in isolation .There are part of wider fabric of society in general which constitute the environment within which they operate . Environment is analyses using an acronym PEST as follows:
- Political
These are factors affecting the requirements placed on the organizations arising from actions of national (and international ) governments and its agencies, including legislation and general political dimension which issues and activities may assume. - Economic
These are factors affecting financial functioning of the organization such as potential for growth , market for organizations products ,or the views of money as it impacts on reward system . - Social
These are factors affecting the supply of labour such as demographic changes in terms of age , profile of the working population , numbers of people in the Job market and changing cultural norms of behavior and attitudes in society at large which influences people’s expectations and behavior at work. - Technology
These are factors affecting processes of production , such as changes in computer technology and communication and the implications of new manufacturing processes.
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
This is the arrangement and inter-relationship of the components parts and positions of organizations. Organization structure defines how tasks are formally divided, grouped and coordinated. Organization structure is divided into two;
- Formal Structure
These comprises of allocation and organization of individual and group responsibilities in pursuit of organizational goals . - The Informal Structure
These comprises of patterns of social interaction within the organization which are separate from those derived from the formal structure.
Key Elements to Consider When Designing Organization Structure
- Work specification
This is division of labour which describes the degree to which activities in organization are subdivided into separate jobs .These increases productivity and reduces boredom and promote employee satisfaction . - Departmentalization
These is grouping jobs which involve common tasks or by functions performed .These enhances smooth running and defines job description . - Chain of command
These is unbroken line of authority that extends from the top of organization to the lowest echelon and clarifies who reports to whom. - Span of control
These is the number of subordinates of manager can efficiency and effectively direct. The wider the span, the more efficient the organization. - Centralization and decentralization
Centralization refers to the degree to which decision making is concentrated at a single point in the organizations with little or no allocation to lower subordinates levels .Decentralization refers to the systematic devolution of responsibility and authority
within structure of organization .These means certain levels or parts of organizations are given responsibility or authority to discharge responsibility. - Formalization: Formalization refers to the degree to which jobs within organizations are standardized .The degree of formalization vary widely between organizations and within organizations .If a job is highly formalized , then the job incumbent has minimum amount of discretion over what is to be done, when it is to be done , and how it is to be done .
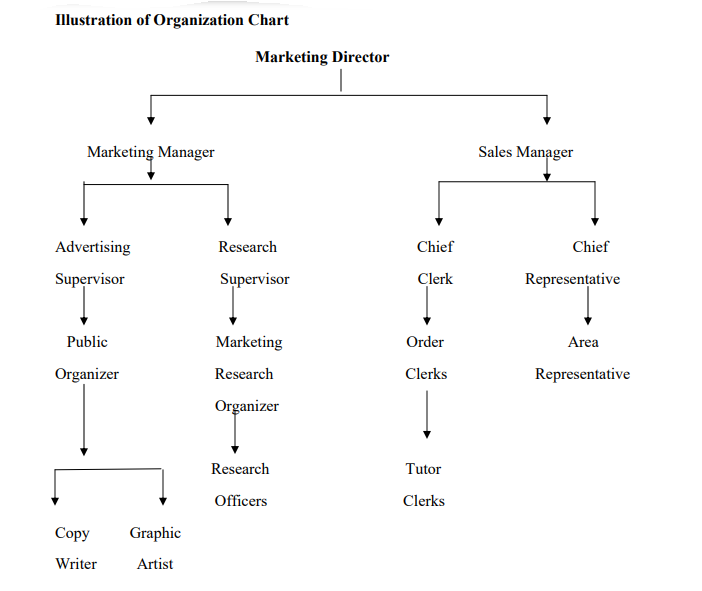
Organizational Charts
Organization’s chart is a diagrammatic representation of the organization structure. Organization charts vary in the level of detail displayed but they all invariably display three elements of the organizations structure:
- The division of organizations into departments section ,unit e.t.c
- The major positions in each divisions
- The interrelationships between positions and division , including the management reporting lines and channels of communication .
Types of Organizational Structures
1. The simple structure
These is characterized by what is not rather by when it is .It is not elaborate. The simple structure is a flat organization .It tends to be associated with broad span of control but in larger organizations broad span control The major advantage is that there is provision , for more flexible work and greater devolution of authority and autonomy .
2. The Bureaucracy
These structure has highly routine operating task achieved through specialization, very formularized rules and regulations .Tasks that are grouped into functional development , centralized authority ,narrow Spans of control and decision making that follows chain
command
3. The team structure
Team structure breaks down departmental barriers and decentralizes decision making to the level of work team. It requires employees to be generalist as well as specialist.
4. The virtual structure
This is where the organizations out sources major business functions. The virtual structure is highly centralized with little or no departmentalization .
5. The bounder less structured organization
These organization seeks to eliminate the chain of command ,have limitless span of control , and replace departments with empowered teams by removing vertical boundaries ,management flattens the hierarchy status and rank are minimized .
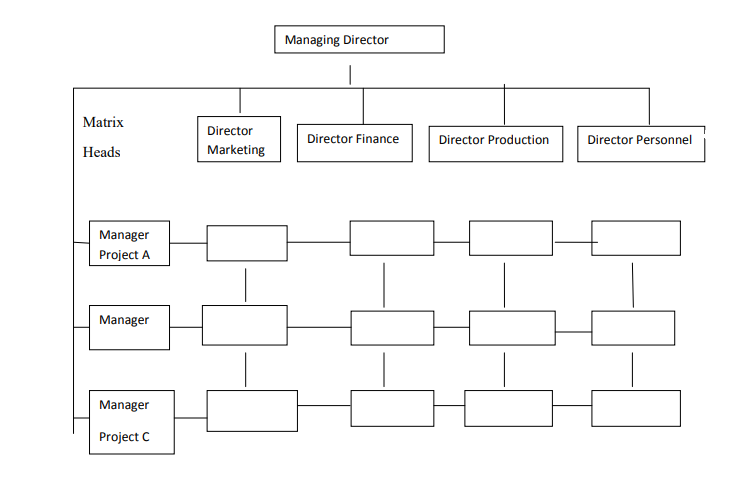
6. The Matrix Structure
These structure creates dual lines of authority and members functional and product departmentalization .