Meaning of Natural Resource
Natural resources (economically referred to as land or raw materials) occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity existent in various ecosystems. Natural resources are derived from the environment. This is currently restricted to the environment of Earth yet the theoretical possibility remains of extracting them from outside the planet, such as the asteroid belt. Many of them are essential for our survival while others are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Different Types of Natural Resources
Natural resources are simply the resources that human beings use for their protection, shelter, comfort, etc. Earth is abundant in natural resources, but they should be used judiciously.
Natural resources are naturally occurring resources in the environment that have not been disturbed by mankind. By resource is meant any physical entity, which has limited availability. These resources occur in their natural form. Few examples of natural resources are:
- Air, wind and atmosphere
- Plants (Flora)
- Animals (Fauna)
- Agronomy (the science of using plants for food, fuel, feed and fiber)
- Wildlife
- Forestry and Agroforestry
- Coal and fossil fuels
- Range and pasture
- Soils
- Water, oceans, lakes and rivers
Something that people generally aren’t aware of, is that everything we use in everyday life are derived from natural resources, for example, milk which comes from cows – animals are a natural resource. We use water, food and vegetables that come from plants, salt which is a mineral are some of the other natural resources. Wood that we get from tree is a natural resource. It can be used to build a house, make paper, burn in fireplaces and in stoves for cooking, etc.
Man utilizes these resources in various ways. These resources are processed further so as to be made suitable for our needs. The table below is an example that shows in what way the resources have been utilized;
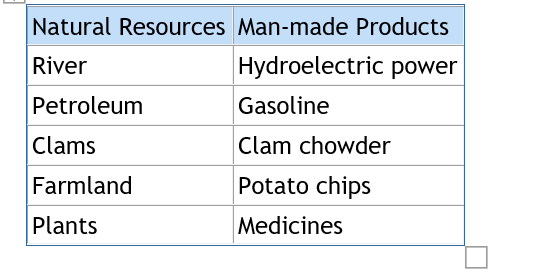
Here are few natural resources and their uses.
Soil
- Used for growing crops (only 10% of the Earth’s surface).
- Soil can be used for shelter. Many tribal people all around the world make shelter with the help of soil.
Water
- Used for drinking (only 0.0007% of Earth’s water is suitable for drinking. The rest is salt water, water trapped in glaciers or polluted water.
- Fresh water is used for irrigation of crops.
- Water bodies such as oceans, lakes and rivers of the world can be used for transportation.
- Fishing is a valuable source of food that is provided by water.
- Water in rivers is be used to generate hydro-electricity.
Minerals
Minerals can be defined as naturally occurring substances obtained from the ground. They are coal, petroleum, natural gas, iron, copper, gold, etc. They are also absorbed up by plants from the Earth’s surface and transferred to humans through food.
- They (coal, natural gas and fossil fuels) are a source of energy.
- Used as ingredients to make other materials like iron ore, is used to make steel and petroleum is used to make a variety of products like gasoline, plastics, etc.
- Can be used as they are in natural form like salt.
Vegetation
- Land is used for farming from which vegetables and fruits are grown.
- Wood from trees is cut and processed to make furniture and home
- Wood is used for cooking and also as fuel to produce heat for warmth.
- Clothing – clothes are made from cotton.
- Plants are used as an ingredient in medicines.
Animals
- Animals are used as a food, and their waste is used as fertilizers for crops.
- We get fur and hides from animals which are used for making clothes.
- Used for transportation.
Natural resources can further be defined as renewable and nonrenewable. Renewable resources are those that can be produced again, for example, plants and animals whereas, nonrenewable resources are those which cannot be produced again, for example, fossil fuels.
We need to make serious attempts to use natural resources in an efficient manner because in recent years, natural resources have depleted as a result of their careless use. The seriousness of the problem can be understood from the words of former American president Theodore Roosevelt, “The conservation of natural resources is the fundamental problem. Unless we solve that problem, it will avail us little to solve all others.”
Management
Natural resource management is a discipline in the management of natural resources such as land, water, soil, plants and animals, with a particular focus on how management affects the quality of life for both present and future generations. Natural resource management is interrelated with the concept of sustainable development, a principle that forms a basis for land management and environmental governance throughout the world.
In contrast to the policy emphases of urban planning and the broader concept of environmental management, Natural resource management specifically focuses on a scientific and technical understanding of resources and ecology and the life-supporting capacity of those resources.
Depletion
In recent years, the depletion of natural resources and attempts to move to sustainable development has been a major focus of development agencies. This is a particular concern in rainforest regions, which hold most of the Earth’s natural biodiversity – irreplaceable genetic natural capital. Conservation of natural resources is the major focus of natural capitalism, environmentalism, the ecology movement, and green politics. Some view this depletion as a major source of social unrest and conflicts in developing nations.
Mining, petroleum extraction, fishing, hunting, and forestry are generally considered natural-resource industries. Agriculture is considered a man-made resource. Theodore Roosevelt, a well-known conservationist and former United States president, was opposed to unregulated natural resource extraction. The term is defined by the United States Geological Survey as “The Nation’s natural resources include its minerals, energy, land, water, and biota.”
Protection
Conservation biology is the scientific study of the nature and status of Earth’s biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction. It is an interdisciplinary subject drawing on sciences, economics, and the practice of natural resource management.
Habitat conservation is a land management practice that seeks to conserve, protect and restore, habitat areas for wild plants and animals, especially conservation reliant species, and prevent their extinction, fragmentation or reduction in range.
