WEDNESDAY: 23 May 2018. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
Answer ALL questions. Marks allocated to each question are shown at the end of the question. Show ALL your workings.
QUESTION ONE
1. Describe four limitations of management accounting. (4 marks)
2. XYZ Ltd. manufactures a component branded “zed” at the rate of 4,000 units per week. Demand for the component is 2,000 units per week while the production set up cost is Sh.50 per batch. The accountant has provided the holding cost per unit per annum as Sh.0.001.
Assume a 50-week year.
Required:
Economic Batch Quantity (EBQ) for the company. (3 marks)
Determine the relevant costs for the EBQ in (b) (i) above. (3 marks)
3. Louise Njambi has taken a lease on a stall from the county government at a down payment of Sh.50,000. The annual rental payment amounts to Sh.50,000. If the lease is cancelled, the initial payment of Sh.50,000 is forfeited. Louise plans to use the stall in selling women’s clothes and the estimated operation costs for the next 12 months are as follows:
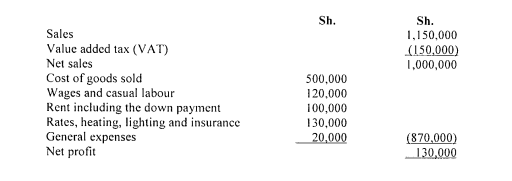
Additional information:
No provision has been made for Louise Njambi’s salary but it is estimated that half of her time will be devoted to the business.
- She has an option of subletting the stall to a friend at a monthly rent of Sh.5,500 if she does not use the stall herself.
Required:
Explain using relevant examples from the situation depicted above; sunk costs and opportunity costs. (4 marks)
Using a cost analysis statement, advise Louise Njambi on whether to use the stall herself or sublet it. (6 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION TWO
1. Classification of cost based on function involves classifying costs on the basis of the purpose for which costs are incurred.
With reference to the above statement, explain three types of costs classified by function. (6 marks)
2. The administrator of Chebatok Hills Hospital would like to establish a cost formula linking the administrative costs involved in admitting patients to the number of patients admitted during the month. The admissions department’s costs and the number of patients admitted during the last eight months for the year 2017 are given below:
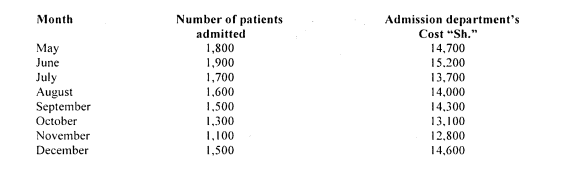
Required:
Using the high-low method, estimate the fixed and variable components of admission costs. (4 marks)
Using the least squares ,method, estimate the relationship between number of patients admitted and the admission costs in the form of Y = a + bx. (8 marks)
Using the relationship obtained in (ii) above, estimate the admission costs incurred in January 2018 if admission was 2,000 patients. (2 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION THREE
1. Savanah Company is highly automated and uses computers to control manufacturing operations. The company uses job order costing system and applies manufacturing overhead costs to products on the basis of computer hours. The following estimates were used in preparing predetermined overhead rates at the beginning of the financial year ended 31 March 2018.
Computer hours 85,000
Fixed manufacturing overhead costs Sh.1,275.000
Variable manufacturing overhead per computer-hour Sh.3.0
During the year, a severe economic recession resulted in cutting back production and a buildup of inventory in the company’s warehouse. The company’s cost records disclosed the following actual costs and operating data for the year ended 31 March 2018:
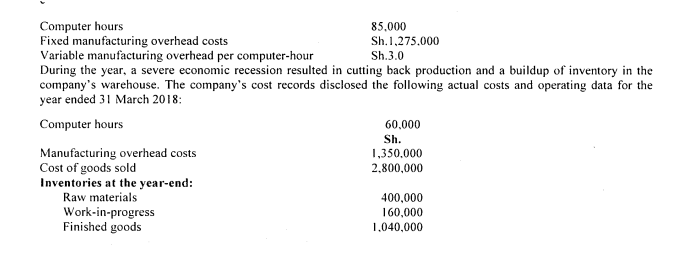
Required:
Compute the company’s predetermined overhead absorption rate for the year. (3 marks)
Compute under-applied or over-applied overhead cost for the year. (4 marks)
It is the policy of the company to allocate any under or over-applied overheads to cost of goods sold.
Determine the cost of goods sold to be charged to the income statement. (3 marks)
2. Better Designs Ltd. manufactures a single product using a single grade of labour. Its sales budget and finished goods inventory budget for the third quarter of the year 2018 are as follows:
Units
Sales 7,000
Opening inventories finished goods 500
Closing inventories finished goods 700
Additional information:
- The goods are inspected only when production work is completed and it is budgeted that 10% of finished work will be scrapped.
- Standard direct labour hours per unit is 3.
- The budgeted productivity ratio for the direct labour is only 80% (which means that labour is working at 80% efficiency).
- The company employs 18 direct employees who are expected to average 1,440 working hours each for the quarter.
Required:
Production budget for the quarter. (4 marks)
Direct labour budget. (4 marks)
Calculate the shortfall in direct labour hours. (2 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION FOUR
1. Summarise four advantages of value chain analysis in cost management. (8 marks)
2. Karibu Cottages Ltd. operates three types of suites for its customers namely; Standard, Deluxe and Luxury.
The following information is provided:
- The number of suites of each type are:
Standard 100
Deluxe 30
Luxury 20
- The rent of Deluxe suite is to be fixed as 11/2 times the standard suite and that of Luxury as twice the standard suite.
- The occupancy level for each suite is as follows:
Peak season Off peak season
Standard suites 90% 50%
Deluxe suites 80% 20%
Luxury suites 60% 20%
- The expenses are as follows:
- Room attendant wages per day when occupied:
Suite Peak season Off peak season
Sh. Sh.
Standard 20 30
Deluxe 30 45
Luxury 40 60
o Lighting, heating and power for full month, when occupied is as follows:
Suite Lighting (Sh.) Power (Sh.)
Standard 400 200
Deluxe 600 300
Luxury 800 400
Other costs (annual): Sh.
Staff salaries 2,200,000
Repairs and renovations 420,000
Linen and laundry 450,000
Interior decorations 500,000
Sundries 315,500
O Annual depreciation is charged on a straight line basis as follows:
Asset Cost of asset (Sh.) Rate per annum (%)
Building 14,000,000 5
Furniture and fixtures 1,000,000 10
Air conditioners 2,C00,000 10
- Peak season is assumed to be 7 months and off-peak season 5 months in a year. One month is taken to have 30 days.
- Profit including interest on investment is 25% on cost.
Required:
Advise on the amount of rent to be charged for each type of suite per day. (12 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION FIVE
1. Distinguish between “interlocking accounting systems” and “integrated accounting systems” as used in cost bookkeeping. (4 marks)
2. Highlight two advantages of marginal costing. (4 marks)
3. The standard cost card for production of a component “Wye” is as follows:
Materials I kg at Sh.4 per kg per unit
Labour 25 hours (100 units) at Sh.8 per hour
Variable overheads Sh.48,000 for budget period
Fixed overheads Sh. 120,000 for budget period
Output 24,000 units
Details for a production of 2,000 units are as follows:
Materials issued 2,000 kgs at Sh.3.50 per kg
Actual production 1,800 units
Actual wages 480 hours at Sh.8.50 per hour
Actual variable overheads Sh.4,000
Actual fixed overheads Sh. 10,600
Required:
Materials usage Variance. (3 marks)
Labour rate variance. (3 marks)
Variable overheads efficiency variance. (3 marks)
Fixed overheads volume variance. (3 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
