Introduction
Definition
Mail These are letters; packages that are send or delivered by means or postal system
Courier services – is fast, door to door local or international pickup and delivery service for high value goods or urgently required documents.
Courier – it is a person or company which delivers massages package /parcels
Mail services – are official means of sending or delivering letters.
IMPORTANCE OF MAIL AND COURIER SERVICES
- They are convenient means of delivering bulky items
- It is faster means of delivering luggage (parcel)
- It saves time for users in delivering parcel or mails.
- They are safe means of delivering parcels. This is because they are official or recognized agents of transporting and delivery mails and parcels. In fact most of them are in position of compensating for an item lost.
- They are cheaper means when it comes to delivery of parcels and mails at the long run.
- It is convenient when it comes to delivery service. This is because they are widespread in their coverage they are located at the door step.
TYPES OF MAIL AND COURIER SERVICES
There are two types of mail and courier services:
- Registered
- Unregistered
Registered mail is a mail whose sending is acknowledged by the issuing of official receipt.
Advantage of registered mails
- They safe since the delivery commit itself by issue of official receipt.
- They are fast in delivery
- They are convenient because at times they are delivered at the door step/ recipient is notified about their arrival
- The recipient is about know the sender (sources of delivery)
- They save time
Disadvantage of registered mails
- Expensive to send
- They are limited to specific area.
- All times their delivery is pegged for recipient come for them.
Unregistered Mails are mail which is sent through the count once a stamp have been purchased and fixed on it.
They are normally deposited in the mail box to be delivered to their destinations thereafter.
The sender doesn’t have a proof of sending and only depends on the good will of delivering agents.
In most cases they are normally transported at the owner risk.
Advantages of unregistered/ordinary mails
- They are cheap
- Their delivery is widespread
- They can be used by anybody/ unrestricted
Disadvantages
- Delay in delivery
- Their security is not guaranteed
- There is possibility of being delivered to a wrong destination
TOPIC 2 MAIL AND COURIER OPERATION
- They must official document to indicate their status alternatively they must be unpacked / see before they are packaged for delivery.
- Material carried must be in appropriately marked and sealed containers
- They must have courier letters attached for the recipient to acknowledge the delivery by singing.
- They must bear a unique serial number/stamp before being delivered
- These agents must operate within certain hours and within define locations
- The parcels must never be opened once packed for delivery
- They must have official receipts
MAIL PROCESSING
Once received mail must be prepared to be dispatched (sent) to various destinations.
The following steps are used when it comes to processing the mails:
- Phasing/sizing: This is the grouping of mails according to their sizes e.g. large, medium, small.
- Stamp cancelations: This is the stamping of stamp fixed in each mail. This is done in order to indicate the origin of the mails and date dispatch.
- Sorting: This is grouping of mail as per their destination. This is done based on geographical region.
- Binding per destination: This is grouping of mails depending on where they are to be sent or delivered.
- Tying the mail bags: This entails placing the mails in special bags in order for them to be delivered to their destination.
- Dispatches of mail to their intended destination
Mail Storage is a type or self-storage where by customers sent items by mail or delivery service usually by the box to be stored at a central location. It may be a squabble option for people who prefer pay as you-go storage in which only items that are stored are charged storage fees rather than renting a larger storage unit that may not be fully utilize
Overview
Mail storage may not be viable or coast effective for those wanting to sore a whole house full of belongs.
It is generally an option of those who want to decanter of time. Mail storage differs from tradition self-storage. In a number of key ways:
- Mail storage allows customers to order boxes online or over the phones
- Customers pack their boxes in their offices or home and these are then collected by the storage companies
- Customers pay a monthly fee per box that may store with the mail storage company. Some companies have minimum number of boxes required to utilize the services
- Tubes, CD mailers, wine boxes
- Tape, bubble wrap liners
MAIL DELIVERY AND DISTRIBUTION
As a legal administration assistant you may be required to process the incoming mail. As the most of the mail received by legal office will relate to matters that are currently open, it is important that the mail is processed promptly and distributed to the current personnel.
Incoming mails should always be processed by following. Your firm’s policies and procedures.
In order to process and distribute and incoming mail appropriately you need to be aware of the following points:
- Receiving mail.
- Checking and registering incoming mails
- Sorting and distributing incoming mails
- Handling specific types of incoming mails
- Dealing with damaged, suspicious and missing items correctly
- Receiving mail
Mail can arrive in a variety of ways including:
- Mail delivered by Australian post.
- Mail delivered by the Australian Document Exchange (known as Aurdo or Dic)
- Mail delivered by courier
- Mail that is faxed
- Mail that is sent by e-mail
- Mail that is hand delivered
Mail Delivered By Australian Post
Some of the mail your firm receives will be delivered morning by Australian post. On occasions legal documents will be delivered using an Australia post, special delivery services, such as registered post. Register post provide an added level of security through a unique identification number of each item and the need for the recipient to sign for the mail.
Mail Delivered By the Australian Document and Exchange
The Australian document Exchange, also known as DX is an alternative to Australian post and courier companies. When a legal firm joins DX they receive a DX number and a private box at the nearest exchange. Exchanges exist throughout country and firm go to the exchange to pick up their mail and distribute mail to other organization that is members of DX. Many law firms. Courts government departments and other professional organization use DX.
Law firms, who are members of DX, include their DX number in their letterhead so that other organization can send mail to them through the DX system
Mail delivered by courier
Courier companies are often used to deliver mail that is urgent. Courier deliveries require a signature and so increase the level of security for mail items.
Mail That Is Faxed
Mail often arrives in the form of a fax and your firm may have a specific process that you need to follow in order to process faxes. Usually they are delivered to the person they are addressed to as quickly as possible
Mail the is send by e-mil
Increasingly mail arrives in the form of emails. Normally emails will be sent directly to the recipient. If you receive an email that is intended for someone else ensure that you forward it immediately. If you are unsure who should receive an email, ask your supervisor check your email regularly.
Mail that is hand delivered
On occasion you will receive hand delivered mail. Unless otherwise directed you should process this mail by following the same procedure that are in place for other mail.
Checking and registering incoming mails.
If you have been given responsibility of dealing with the incoming mail you need to be aware of the correct process to follow for checking and registering
Checking incoming mails
As it is very easy to accidentally damage a letter or a document when you are opening an envelope it is best to take your time and open each envelope with care.
Once you have opened an envelope ensure that you remove all the contents. Often an envelope will include a covering letter and a number of attachments. You should check that all the attachments indicate in the covering letter have in fact been included. See that handling specific types of incoming mail section below to understand what to do if items are missing.
Keep items together
Ensure that items are arrives in the same envelopes are kept together.
- You can usually attached items with a paper clip e.g. cheque that arrives with letter must be paper clipped to the letter.
- However you must be aware that will must never be attached to anything else as this can make them invalid.
- Be aware that also original documents, such as Titles Agreements or court documents should never be stapled. It is preferable to attach items to original documents with a paper clip or loull dog clip
Date stamping
- After the mail has been opened you should ensure that, where appropriate each item is date stamped.
- Date stamping the incoming mails helps identify when your legal firm received the mail.
Registering incoming mails
Mails can be registered either manually in a mail book or diary, or electronically on a computer again this will depend on the process in place at your firm keeping a register of all mail items Normally the register will indicate the date an item was sent, received and to whom it was distributed.
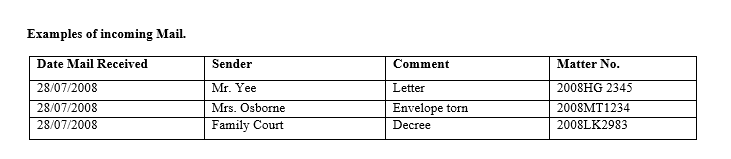
Once mails has been registered it should be sorted and distributed to the appropriate personnel
Sorting and distributing incoming mails
Once the incoming mail has been opened, date stamped and registered it needs to be sorted and then distributed to the appropriate personnel.
Distributing incoming mails
In order to efficiently distribute the mail you will need to identify and understand the structure of your firm and the titles and roles that each person has. This is important when you receive a mail item that does not specifically indicate for whom if is intended.
When this happens you will need to work out whom the letter is for. This can be done by checking the reference, asking your supervisor calling the senders or reading the letter and then directing it to appropriate person or department.
Handling specific types of incoming mail
Be aware that certain incoming mails items need to be dealt with according to specific processes. These processes may be legal requirements or they may have been developed by your firm.
Dealing with damaged , suspicious and missing items correctly
On occasions you will need to deal with mail that has been damaged, mail that appears suspicious lost mail items
- Damaged mail
Damaged mail should be stored; date stamped or registered following the same process used for other incoming mail. The damaged should be recorded in the register. Once the damaged item has been processed it should be delivered to the person to whom it has been sent with an explanation regarding the fact that it arrives in a damaged condition. The recipient can then decide what action, if any needs to be taken.
- Suspicious mail
There should be procedures define in order to deal with suspicious mails. Do not attempt to open a suspicious item.
- Missing items
Often an envelope will contain a covering letter and one or more enclosures. This covering letter should indicate what enclosures, if any are meant to be included check that all the enclosure detail in the covering letter is in fact included. It an item is missing you should register the letter and an enclosure that have been included and then inform the recipient of the letter that certain enclosure are missing, the recipient can the decided what action to be taken.
TYPES OF MAILS
- Express mail (fastest)
Is a services available to mailers for shipment of any approved mail able matter that is submitted to the post office properly prepared. Express mail services guarantee is 10 or 2 days delivery, based on destination 21 p codes.
- First class mail
Provides reliable and economical means or sending correspondence (letters and postcards), documents, and more analyze weighing up to 4 pounds.
- Priority mails
Priority mail offer faster delivery at the least expensive rate in the industry, you also have the option of sending mail weighing less 11 ounces as priority mail.
The maximum weights for priority mail is 70 pounds and the maximum size is 108 inches in length and girth combined.
MAIL SCHEDULING
This is a programme which is adopted in sending delivery mails, various schedules can be adopted when delivering mail i.e. install Boomerang is used to schedule an email now then schedule it to be sent automatically at the perfect time.
E.g. a. Daily basis. It is a situation where mails are collected and send on daily basis.
- Weekly basis. It is a situation where mails are collected and delivered after a week.
CRITERIA/ MEASURES FOR DETERMINING AN EFFECTIVE MEAL SERVICE
An ideal mail service should be able to meet the following standards as far as mail delivery is concerned.
- Security
- Speed
- Cheap
- Widespread
- Reliable
- User friendly
- Security: An ideal mail service provides adequate security for mails that is; they should not be tampered with.
- Speed: A good mail service should be one which will have the mails delivered within the shortest time possible.
- Cheap: It should be affordable to most users but not compromising on security of mails.
- Widespread: A good mail service should be one which is able to overcome geographical barriers. The is it should not be limited to its coverage.
- Reliable: This entails have a programme when it comes to mail receiving and delivery. At the same time it should have a feedback plan in case of a crisis.
- User friendly: an ideal service should be one which focuses on the user’s needs before thinking or focusing on money.
PROCEDURES FOR ESTABLISHING MAIL SERVICES
- License application: This entails apply for the licenses in order to be allowed to engage in mail services business. This licenses if applied form C.C.K ( communication commission of Kenya)
- Starting route of operation : This entails giving the location of the business together with its physical address
- Starting capability: The Company must indicate its ability to engage in mail services. It must state its storage capability and ability together with its man power that is qualification of its personnel.
- Stating mode of operation: It entails one indication how the business will operate either single venture or partner. In case of a partnership one must avail an agreement between the parties indicating their willingness to the operate as a joint its personnel
- Receipt and delivery: One has to give the kind as receipt to be issued and give the kind procedure of receiving and delivering mails.
- Packaging: This is stating how received mails will be packaged that is the kind of containers to hold the mails while being transported.
- Statement of loss of coverage: It entails starting how compensation will be affected incase the mail get loss or damaged. It must be clear statement which is measurable in case of an eventually.
Note: Having done all the above applicant send his or her application to the licensing body (CCK) and await for the feedback if the licensed body is common that everything is okay and trading license is issued after one can apply for the local authority trading license and get started his or her own business.
SAFETY MAIL SECURITY
Is the act of ensuring that mails are probably taken care of on receiving them until they delivered to receiving recipient.
SAFETY AND SECURITY MEASURES OF MAIL
In order to ensure safety/security of mail the following measures must be put in place.
- Keeping them in special mail bags
Specially produced bags in which are used to store mails which is are under transit or circulating transit. The bags should be lockable if possible.
- Responsibility staff.
This entails employing staff who are committed in their work.
- In so doing them always be ready to ensure the safety of the mails.
- Right hour transport
This entails as much as possible to transport the mails during the day or towards the day.
- Security escorts
This is a situation where mails are transport under armed escort, in case of any problem the situation can be easily be handled since security is assured.
- Oath of secretes
This entails making all the employees to swear to keep secretes as far as the mails received is concerned.
- In so doing it makes them label to any disclosure or even summary dismissal
- Keeping mails in fortified area
This is the act of keeping the mails in safe environment.
IMPORTANCE OF MAIL SAFETY AND SECURITY
- Timely delivered when mails are protected it ensures that they are delivered within the specified time to the recipient.
- To curb the theft
When mail is in safe custody it reduces the chances of them falling on the wrong hands. In so doing, they cannot be prone to any kind of theft either deliberate or by chances.
- To enhance privacy
Mails are in most cases private (individualized by provided security) to them it ensures that their privaciy is safe –guarded i.e. it is only the individual owners who will get access to it.
- To prevent disclosure
This means receiving mails and ensuring that the counter of mails is not disclosure or known to someone who is not supposed to know.
- To keep them in good shape
Once mails are in safe hands, it makes it possible for them to retain their physical status
- Reduces the chance of the mails getting lost or possibility of falling in to wrong hands.
Threats for mail security and safety
- Theft: Is a situation where mails are stolen either during storage or transit. This is done with the perception that they contain something valuable.
- Privacy: Is a situation where mails are illegally co-copied for selling purposes. This is done to mails which are persisting to crucial condition information.
- Disclosures: this is making of mail convenient known to someone who is not supposed to know it is
- in so doing it erodes the confidentiality of the mails
- Wrong hand: Here mails are delivered to the worn person by accident. Normally happens during the process of dispatching them to their owners.
- Saboteurs : It`s the act of deliberately destroying something so that it is not/ helpful to the intended person.
- Natural disasters: Here is whereby natural calamities comes and destroy the mails e.g.
- Floods
- Fire
- Earthquake
- Authority degrees: These are directives form of authority which automatically becomes code in so doing it might require any mail to be disclosed before being send to the owner as a result the content shall become public
PROCEDURE FOR ESTABLISHING COURIER SERVICES
- Decide what types of items to transport and the geographical area to serve. Consideration and packages size and content. e. hazardous, chemical or perishable item.
- Research watch competitors offers to address and owner need.
- Buy or rent a dependable vehicle based upon the services offered outfit the transportation with necessary equipment, refrigeration for perishable items.
- Obtain permit and licenses: check with the local and state authorities for requirements since they vary by jurisdiction. An occupation licenses is usually required before a business begins operation.
- Obtain insurance: in addition to personality vehicle insurance, occupation insurance is required since the vehicle is used commercial. Coverage for items transport is also important. Check with an insurance agent on the proper time and mount of coverage
- Consider hiring independent contractors to meet scheduling needs that from day-day. The messenger courier of America provides an outline of the best practice to ensure that in depends contractor’s traders is maintained. Taxi responsibilities are different for employees and independent contract
- Establish a reliable method to schedule the referees and communicate with drivers. Dedicate a phone line for customers use. Dispatch delivery requirements to drivers through a two way communication device. Use software to accurately estimate delivery time.
- Advertise services, place a magnetic sign on the delivery vehicles. Sent out a news release when the courier services open. Conduct doctors, lawyers, architect manufactures and other business that need your services provide brochures and business cartels to prospective clients:
Facilities to courier services
- Refrigerator – for transporting perishable goods
- Mobile phone – for easy communication
- Computers – for tracking system, security system accuracy and efficiency
- Vehicles – for transporting goods and parcels
- Boats – for transporting goods from one country to another using water transport
- Aero plane
TOPIC 3 MAIL AND COURIER TRANSPORT
It is an act of moving mails from the receiving point to the destination or recipient.
Importance of mails and courier transport
- Enhance communications: by the virtue of moving the mails from one point to another, from receiving point to the delivery point/ destination
- It is a cheap way of communication: because the charges of moving mail from the receiving point to another destination is relatively available to many people.
- Save time of users during transportation because everything is alone (transportation of goods on behalf of customers and wait for the feedback .
- Convenient means of communication : especially when transporting agents are widely spread (facilitates con)
- It creates job: various organization, companies are enjoying in this as a means of earning a living.
MODES OF MAIL AND COURIER TRANSPORT
A mode of Transport (means of transport or mode of Transport modernity or form of transport) Is a term used to distinguish substantially different ways to perform transport.
Mails and courier can be transported using the following:
- Road
- Air
- Railway
- Water
Description
- The most dominant modes of urban transport are launch transport, including road, mail, water and air transport. Other modes also exist, including pipelines, cable transport and space transport.
- Transport using more than one mode is described as multimodal transport. Transportation that carries around many people and can be used by the public is known as Mass transport.
- Each mode has its own infrastructure, vehicle and operations and often has unique Each mode of transport therefore also has different security issues which should be accounted for in the design and operation process.
Road transport
- People travelling on the road are either pedestrians, cyclic or they are using a certain type of vehicle, such as automobiles, bicycles, buses, vans or trucks. Passengers transport my furthermore be public. Where operators provide scheduled services or private.
- Potential risks for road transport are blocked road and traffic accidents
- Blocked roads can be prevented or the consequences can be minimized by using Traffic Management such as incident management and designing a robust road Traffic accidents can also be minimized by these measures, and road safety.
Automobile
A motor vehicle or road vehicle that is a self-propelled wheeled vehicle that does not operate on rail, such as trains or trolleys. The vehicle propulsion is provided by an engine or motor
Non – Motorized Transport
Non – motorized transportation (also known as active transportation or human powered transportation) include s walking and bicycling, and variants such as small wheeled transport skates, skate boards, push scooters and hand cart) and wheel chair travel. These modes provide both recreation and utilitarian transportation, although users may consider a particular trip to serve both objectives.
Regarding personal security this refers to freedom form risk of assault, theft and vandalism. Such risks can discourage walking, cycling and transits travel. These problem can be addressed though various programs and design strategies that increase security.
- Walking
Walking us a means of transport that is commonly users for short trips. At present, the importance of walking is underestimated because national travels surveys often do not register the shorter trips and the walking parts of trips made by public transport are usually not taken into account
- Walking ability is a measure to assess the overall attractiveness for waking mobility in an areas.
- cycling
Cycling or also known as bicycling or biking is a means of transport that is commonly used for short to moderate distance:
- It is very cost – efficient for its users.
- The infrastructure investment costs are much lower than for. (private) motorized traffic infrastructure
- The bicycle is as time – effective or even better as motorized traffic in dense and congested urban areas.
- It has zero – emissions
Regarding safety and security cyclist are more vulnerable when in conflicting situations with motorized transport.
Safety can be increased with proper bicycle path facilities such as segregated bicycle pathways
In general cycling improves the urban liability because it involves more human activity on the streets and reduces motorized high speed transportation.
Other non – motorized
Other non – motorized mode include small – wheeled transport such as skates, skateboards, push scooters and hand carts but also wheelchairs. These modes are primarily used for recreation purposes.
Light commercial vehicles
Light commercial vehicles LVC, also sometimes light goods vehicles or LGV is a commercial carrier vehicle with a gross vehicles weight (GVW) of up to 3.5 tones.
Heavy duty vehicles
A truck (North American, Irish and Australian English) is a motor vehicles designed to transport cargo. Trucks vary greatly in size, power and configuration/ commercial trucks can be very large and powerful, and may be configured to mount specialized equipment, such as in the case of fire trucks and concreter mixers and suction excavators.
Bus
A bus (also omnibus, multibus or autobus) is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses normally have a capacity of 10 to 60 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single- decker rigid bus with larger loads carried by double – decker buses ban articulated buses and smaller loads used for longer distance services.
Buses may be used for scheduled bus transport, scheduled coach transport, school transport, private hire, tourism; promotional buses may be used for political campaigns and others are privately operated for a wide range proposes.
Rail transport
Rail transport includes all transport over rails. This can be either for passengers or goods transport, or with different modes of transport, such as trains, metro and trams.
With rail transport, more people or goods can be transported within the same transport vehicle (LC) than with road transport. However there is less flexibility for choosing a different route or time. A schedule is needed to manage all vehicles. Trains on the rail road network. Also, disruptions can have large consequences on the schedule, since passing a standstill trim is not always possible. This makes a railway system especially vulnerable for incidents or possible terrorist attacks
Train
A railway or railroad train is connected series of vehicles for rail transport that move along a track( permanent way) to transport cargo or passengers from one place to another, the track usually consist of two rails, but might also be a monorail or magler guide ways.
Tram
A tram also known an tramcar, streetcar, trolley car is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets, and also sometimes on separate right way.
It may also run between cities and /or towns ( interurban tram – train ) and/ or practically grade separated ever in the cities (light rail) trams very occasionally also carry freight.
Water transport
Water transport or ship transport is water craft carrying people (passengers or goods /cargo)
- Sea transport has been the largest carrier of freight throughout recorded history – although the importance of see travel for passengers has decreased due to aritic it is effective for short trips and pleasures cruises.
- Transport by water is cheaper than transport by air.
- Ship transport can be over any distance by boat, ship sailboat or barge, over oceans and lakes, through canals or along rivers.
Air transport
Air transport includes all transport through air. In urban region context this air transport include local air traffic such as small airplanes or helicopters. In urban security air transport is explicitly high impla
Public transport
Public transport is passenger transport which is publicly available. This can furthermore be distinguished in collection and individual transport.
Examples of collective public transport are transport by
- Busses
- Tram metro
- Train
- Plain
Examples of individual public transport
Taxis. and in some countries called riksjas or tuk tuks a bicycle or moped with a backseat for a few people.
Public transport management is used to manage the public transport in order to be able to get people from A to B with public transport as efficiently possible.
If the public transport is disrupted due to a security issue public transport management measures can be used to minimize the hindrance, such as sending temporary busses or letting trains drive over alternative routes
Public transport is very vulnerable to terrorist attacks, since many people use the same means of transport on the same time and the schedule and routes are publicly available. An attack is therefore easy and the consequences are big.
Freight transport and logistics
A special discipline within transportation is freight transport and logistics. It concerns the distribution of goods from the source to their destination, such as a warehouse terminal for further distribution to e.g. Shops. This can involve different modes of transport.. The total system of organization, people technology, activities informat and sources involved in moving a product or services from supplier to customer is called a supply chain.
Multimodal transport
Multimodal transport recates to trips for which travelers use two or more transport modes, for example bicycle and train, and bus, or private car and metro. The requirements for multimodal transport are numerous transfer modes, travel information, synchronized transport services, and so on. Multimodal transport requires new organizational and financial arrangements between all actors involved.
Multimodal transport nodes such as ports or public train terminal from a critical aspect of multimodal transport planning. Due to the large flows of passengers and goods these location are vulnerable to security threats and needs to be designed and operated accordingly.
Mass transport
Mass transport or mass transportation is a typical form of public transport. Transport where in large flows of people are transported, most common examples are subways, rails, trams, bus rapid transit and airplanes.
Mass transport has specific vulnerabilities for security threats, sometimes specifically linked with the use of transportation hubs.
Advantages and disadvantages of road transport
Advantages
- Less capital outlay
Road transport requires much less capital investment compared to other mode of transport such as rail way and air transport. The cost of constructing ,operating and maintain roads is cheaper than that of the railway.
- Door to door services
The outstanding advantages of road transport is that it provides door to door or warehouse to warehouse services
- Services in rural areas
Road is most suited for carrying goods and to and from rural areas which are not served by rail, water or air transport. Exchange of goods, between large towns and small to and from rural areas which not served by rail eater or air transport. Exchange of goods, between large towns and small villages if made possible only though road transport.
- Flexibility
Has great advantage for its flexible services – its routes and timings can be adjusted and change to individual requirements without much inconveniences
- Suitable for short distance
More economic and quicker of carring goods and people over short distances. Delays in transit of goods on account of intermediate loading and handling are avoided. Goods can be loaded direct into a road vehicle and transported straight to their places.
- Less risk of damage in transit
As the intermediate loading and handling is avoided there is less risk of damage, breakage e.t.c goods in transit. Thus, road transport is most suited for transporting delicate goods like Chinaware and glassware which are likely to be damaged in the process of loading and unloading.
- Saving in packing cost
As compared to other modes of transport, the process of packing in motor transport is less complicated. Goods transported by motor transport require less packing or no packing in several.
- Rapid speed
If the goods are to be sent immediately or quickly, motor transport is more suited that the railways or water transport. Water transport is very slow. Also much time is wasted in booking the goods an taking delivery of the goods in case of rail and transport.
- Less cost
Road transport not only requires less initial capital investment the cost of operation and maintenance is also comparatively even if the rate charged by motor transport is a little high than that by the railways, the actual effective cost of transporting goods by motor transport is less.
- Private owned vehicles
Another advantage of road transport is that big business men can afford to have their own motor vehicles and initiate tier own road services to market their product without causing any delay.
- Feeder to other modes of transport
The movement of goods begins and ultimately e.g. making use of roads. Roads and motor transport act as a feeder to other modes of transport such as railways, ships and railways.
Disadvantages
In spite of various merits, road/ motor has some serious limitations
- Second nature
Motor transport is not as reliable as rail transport. During rainy or flood season, roads become unfit or unsafe for use.
- Accidents and breakdowns
There are more chances of accidents and breakdown in case of motor transport. Thus, motor transport not as safe as rail transport
- Unsuitable for long distance and bulky traffic
This made of transport is unsuitable and costly for transporting cheap and bulky goods long distance.
- Slow speed
The speed of motor transport is comparatively slow limited
- Lack of organization
The road transport is comparatively less organized. More often it is irregular and undependable
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Transport
Advantages
- High speed
Air transport is the fastest mode of transport and therefore suitable carriage of goods over a long distance requiring less time. There is no substitute for air transport when the transport of goods is required urgently
- Quick services
Air transport provides comfortable, efficient and quick transport services. It is regarded as best mode of transport for transporting perishable goods.
- No infrastructure investment
Air transport does not give emphasis on construction of tracks like railways. As no capital investment in surface track is needed, it is a less coastally mode of transport.
- Easy access
Air transport is regarded as the only means of transport in the area which are not easily accessible to other modes of transport. It is therefore accessible to all areas regardless the obstruction of land.
- No physical barrier
Air transport is free from physical barrier because it follows the shortest and direct routes where seas, mountains and forest do not obstruct.
- Natural routes
Aircrafts travels to any places without any natural obstacles or barriers. Because the custom formalities are complied very quickly. It avoids delays in obtain clearances.
- National defiance
It plays a significant role in National Defense of the country because modern wars are conducted with the help of aero planes. Airways has a upper hand a destroying the enemy in short period.
Disadvantages
- Risky
Air transport is the most risky form of transport because a minor accident may put a substantial loss to the goods passengers and the crew. The chances of accident are greater in comparison to the other modes of transport.
- Very costly
Air transport is regarded as the costliest mode of transport. The operating cost of aero plane is higher on it involves a great deal of expenditure on the construction of aerodromes and air craft. Because of this reason the fare of air transport are so high that is becomes beyond the reach to the common people.
- Small carrying capacity
The aircrafts have small carrying capacity and therefore these are not suitable for carrying bulky and cheaper goods, the load capacity cannot be increased as it is found in case of rails.
- Unreliable
Most of air transports are uncertain and the unreliable because these are controlled by weather conditions. It is seriously affected by adverse weather conditions. Fog, sow and heavy rain weather may cause cancellation of the same flights.
- Huge investment
Air transport requires huge investment for construction and maintenances of aerodromes. It requires trained experienced and skilled personnel which involves a substance investments
Advantages of disadvantages of railway transport
Advantages
- It facilities long distance travel and transport of bulky goods which are not easily transported through motor vehicles.
- It is a quick and more regular form of transport because it helps in transportation of goods of goods and certainty.
- It helps in the industrialization process of a country by easy transportation of coal and raw materials at a cheaper rate.
- It helps in the quick movement of goods from one place to another at the time of emergencies like famines and scarcity
- It encourages mobility of labour and thereby provides a great scope for employment
- Railway is the safest form of transport. The chances of accidents and breakdown of railway are minimum as compared to other modes of transport.
- The carrying capacity of the railways is extremely large moreover, it is capacity is elastic which can easily be increased by adding more wagons
- It is the largest public undertaking in the country, railway perform many public utility services. Their charges are based on charge what the traffic can bear principles which helps the poor. In fact, it is a national necessity.
Disadvantages
- The railway requires a large investment of capital. The cost of construction maintenance and other over head expenses are very high as compared to other modes of transport. Moreover, the investment is specific and immobile. In case the traffic is sufficient the investment may mean wastage of huge resources.
- Another disadvantage of railway transport is it is inflexible. It routes and time cannot be adjusted to individual’s requirements.
- Rail transport cannot provide door to door services at it is tied to a particular track. Intermediate loading or unloading involves greater costs, more wear and tear and wastage of time. The time cost of terminal operations are great disadvantages of rail transport.
- As railways require huge capital outlay, they give rise to monopolies and work against public interest at large. Even if controlled and managed by the government, lack of competition may breed in inefficiency and high cost.
- Railway transport is unsuitable and uneconomical short distances and small traffic of goods.
- It involves much time and labour in booking and taking delivery of goods through railways as compared to motor transport.
- Because of huge capital requirements and traffic, railways cannot be operated economically in rural areas. Thus large rural areas have no railway even today. This causes much inconvenience to the people living in rural areas
Advantages and Disadvantages of Water Transport
- Less maintenance cost
Maintenance cost in rail and road transport is quiet high but maintenance cost of water transport is quite less.
- Cheap
The transport channel is quite cheap as compared to rail and road transport
- Useful for bulky goods
Heavy and bulky goods can be transported easily at little cost though water transport.
- Useful during natural calamities
During natural calamities like flood and rains, when rail and road transport is disrupted, relief operations can be operated though water transport
- Helpful defense
Developments of shipping are essential for the defense of the country also. It is also called second line of defense.
- Importance of foreign trade
Disadvantages
- Slow speed
It is a slow mode of transport. Failure of monsoon results into fall in the water level of rivers making navigation difficult.
- More risky
Factors to consider while choosing the most suitable mode of transport
- Cost of serve
The cost of transportation adds to the cost of the goods so it should always be kept in mind.
Rail transport is comparatively a cheaper mode of transport for carrying heavy and bulky traffic over short distances. Motor transport saves packing and handling costs. Water transport is the cheapest mode of transport. Suitable to carry only heavy and bulky goods over long distances where time is not an important factor. Air transport is the most costly means of transport but particularly suited for carrying perishable, light and valuable goods which requires quick delivery.
- Speed of transport
Air transport is the quicker mode of transport but i.e. is costliest of all. Motor transport is the quicker than railways over short distances. However, the speed of railways over long distances is more than that of other modes of transport except air transport and is most suitable for long distances. Water transport is very slow and thus unsuitable where time is an important factor
- Flexibility
Railways, water and air transport are inflexible modes of transport. They operate services on fixed routes and at preplanned time schedules. The goods have to be carried to the station ports and airports and then take form there.
Motor transport provides the most flexible services because it is not tied routes or time schedules. It can operate ant anytime and can reach the business premises for loading and unloading.
- Regularity of services
Railway services is more certain, uniform and regular as compared to any other mode of transport.
Not much affected by weather conditions motor transport, ocean transport and air transport are affected by bad weather such as heavy, snow, fog, and storms.
- Safety
Safety and security of goods in transit also influence the choice of a suitable means of transport.
Motor transport may be preferred to railway transport because losses are generally less in motor transport. Water transport exposes the goods to the perils of sea and hence from safety point of view, sea transport is thought of as a cost resort.
- Nature of commodity
Rail transport is most suitable for caring cheap, bulk and heavy goods. Perishable goods which require quick delivery many be carried through motor transport or air transport keep in mind the cost and distance.
- Other considerations
A number of special services such as warehousing, packing loading and unloading are also taken into consideration while deciding about a made of transport.
The rail transport is particularly suited for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances
Motor transport is suitable for carrying small consignments over short distances
Air transport is suited to light and precious articles which are to be delivered quickly
Ocean transport is appropriate for carrying heavy bulky goods over long distances at the cheapest possible cost.
TOPIC 4
APPLICATION OF ICT IN MAIL AND COULIER SERVICE
MEANING OF ICT IN MAIL AND COULIER
DEFINITION-Influstructure and component of modern computing that increases the efficiency of communication process
Role of ict in mail and coulier
- it helps to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of services delivery
- it save on time when delivarlying masis
- through ict company don’t require more skills and labor
- help in minimized physical damaged
- tracking mails are easier when using ict
- ict companies winded their coverage
- ict reduces risk of sending dangerous mails
- helps to make good relationship between company and their clients
Importance of ict using mailing service
- faster compared to postal and courier service
- it can be used by many people
- minimal barriers which decreases security threat
- very convenient to both sender and receiver
- easy to update-collect an error to mail hence avoid inconvenient
- easy to allocate a lost mail since the detail of receiver are available
- the mail remain confidential until it received by respected receiver
- there is instant feedback that mail has delivered or sent
Disadvantages of using ict in mail and courier services
- can not be used by people who don’t have internet conducting
- can not be used illiterate people
- requires technology skills which most people don’t have
- those whom don’t know some skills can be cheated by link their confidential messages
- ict are easily stolen
- ict are power dependant
- machine are expensive to buy and maintain
Areas where ict is applicable or used in mail and coulier services
- Storage – ict is used to record in mail and couliers services companys
- Processing – used in processing of information in mails and courier company
- Sending – ict is used to send information g e-mail ,scan
- Delivary – most messages are sen t online
- Marketing – through ict company can market their services to their customer online
TOPIC 5
COMMUNITY INTEGRATION
Definition
Community integration- is the opportunity to live in the community and be valued for one’s uniqueness and abilities like everyone else
Importance of community intergration
- helps in building practicle life skills
- provides a path to recovery for those who fell isolated and unwanted
- offers chance to engage with others
- give access to inclusive workplaces
- offers chances to engage with others and satisfaction of being part of a diverse community
Approaches to community integration
- self-help approach
- special purpose problem –solving approach
- demonstration approach
- experimental approach
- power-conflict approach
Impact on developing community intergration(assignment)
Factors That Affect Community Integration
Several key factors affect the ability of people with disabilities to participate in community integration. These include (but are not limited to) the:
- Severity of their disability or impairment
- Accessibility (or lack thereof) of their surroundings
- Availability of assistive technologies and devices
- Underlying cultural and political influences/expectations in their area
Benefits of community integration
Community living has many benefits for people with disabilities. People with disabilities generally have the same wants and needs as nondisabled people. Unfortunately, institutional living does not give people with disabilities the freedom to satisfy these needs. Moving into the community can open up a whole new world for people with disabilities by providing them:
- A choice of where and with whom they live
- The ability to see friends and family more often
- The opportunity to work in the community
- The opportunity to develop new hobbies
- The opportunity to participate in the life of the community by going to the library, restaurants, concerts and other public venues.
- Integration also makes the community more diverse.
DISASTER CONTROL PLANNING
A disaster – is an event or occurrence mostly of unexpected nature but with remaining negative results on the physical aspects of the records or documents.
A disaster also refers to a greater misfortune or calamity which comes suddenly.
Planning – is management functions that determines what the organization wishes to achieve and deciding on the means of attaining the desired goal.
Control – refers to management functions compare achieve results with planned goals.
Therefore – disaster control planning refers to an institution management whose aim is protects collection form damage.
Disaster plan- this is an information centre prepared themselves to face any event whit negative results
A source of useful information which the institution is offering necessary training to the personnel to ensure effective response in case of an event.
Disaster preparedness occurring
The purpose of disaster preparedness is to ensure information centers are able to identify the key person and other resource likely to be involved in dealing with and emergencies of any nature i.e. in term of disasters.
Recommend measures of disaster preparation
Personnel
It is important to provide a list of the key people who are involved in responding to a disaster
Disasters response coordinator
To ensure that the team is relevant and quality formal training is offered
Also identify and acquire relevant equipment materials which are useful for use in case of any emergencies
Pre – disaster planning team
Pre – disaster committee is responsible for the preventive and preparation stages of the programmer
The committee responsibility is
- To coordinate planning and general preparation
- To ensure that effort are made to prevent potential disasters
- Provide documentation of the organization readiness to respond to a disaster.
Post –disaster planning team
- This deals with actual salvaging of the documents. The tam possess knowledge of salvage procedure cost or results to the extent necessary to ensure competent timely response.
- Their other duties of the team include preparing budget for equipment and supplies g. purchase of helmets, overall, boots etc.
- Accessing the conditions of the buildings and levels of maintenance e.g., wiring, water pipes and conditions of roofs.
- Assess virtues hazards training the staff to use the equipment.
- Testing the equipment to ensure that they are not absolute.
- Prepare and avail literature on the various salvage procedure that ought to be followed in case of a problem.
- Needed materials for salvage can be availed at very short time notices:
Materials required
- Torches and flood lights
- Clean polythene sheets for covering affected materials
- Pumps
- Vacuum cleaners
- Buckets
- bloating papers
Insurance
Also important aspect of disaster planning to make sure that modern equipment and the
Revision questions
- Types of mails
- express mails (fastest) a service available
- first class mails- reliable
- Priority mails
- Criteria/ measures for determining an effective mail service
- Security – determine for them to be protected i.e. no mail is tampered.
- Speed – fast
- Cheap – cost, convenient , many customers
- Widespread – many people can access
- Reliable – security
- User friendly
- Procedure for establishing mail services
- Find licenses application
- Stating route of operation
- Starting capability
- Starting mode of operation
- Receipt and delivery
- Packaging
- State of laws coverage
- Threats of mail and services
- Theft
- Wrong hand natural disaster
- Authority degree disclosure
- Sapotonures
- Privacy
- Highlight 6 factors to consider in the provision of online mail services
- The type of mails and parcels that can be used should be available in that the mail that can be used should be available.
- Also the type of user – the users who can be able to use the online mail must be available
- The type of mail services adopted by other services
- Should be considered if it is in a good condition
- The durability of mail, whether the mail can stay for a longer period of time
- Accessing policy in that whether the mail is in a position to access the information easily.
Reason that may prompt the user of airfreight courier services
- There is enough security
- Airfreight cannot prone to accident
- When the parcels are urgently needed
- Airfreight can save time since it is faster
- Because of perishable good that cannot stay for a longer period of time
Highlight six value added services that a courier services operator may offer
- Certification of excellence
- IPE performance operation
Explain factors that may contribute to the loss and damage of mails on transit
- Unqualified personnel – a person who is not qualified do not know how to operate mails when they are being transported.
- Poor storage
- Inadequate funds to promote the services
- Lack of co-operation
Highlight the information needed to identify the recipient of a mail
- Address
- Telephone number
- Location
- Name of the recipient
- Photograph
Explain factors to consider in determining mail services operator to user
Security : An ideal mail service provide adequate security for mails that is ; they should not be tampered with.
Speed : A good mail service should be one which will have the mails delivered within the shortest time possible.
Cheep: It should be affordable to most users but not compromising on security of mails.
Widespread : A good mail service should be one which is able to overcome geographical barriers. The is it should not be limited to its coverage.
Highlight advantages of using ICT in mail and courier services
- It is easy to access
- It saves time to staff and to the users since the machine work
- ICT serves many user at the same time
- It can only stay the mail for a longer period of time
- Accuracy and efficiency of work is achieved.
Explain 4 challenges that may be encountered by users of unregistered mail and courier operator
- Delay in delivery
- Their security is not guaranteed
- There is possibility of being delivered to a wrong destination
- There is possibility of mail getting loss
- There is language barrier among the users
- Lack of cooperation among users
highlight 6 ways of coping with the increased completion in mail and courier services
- By employing qualified and polite personnel
- By also providing quality services
- By using special bags in improving the service
- By ensuring they are user friendly
- They ensure that there is security to the users
explain 4 benefits delivered by a mail and courier operator form offering efficient services
- in case of changed of physical location or state, users should be informed using telephone to collect the mail
- they create good public relations between the company and the user
- they are in a positon to get more customers
- they are also good in marketing their services
highlight challenges encountered by courier operators in urban centers in Kenya
- insecurity of mails
- congestion
- lack of co-operation from the custodians
- tiresome and cumbersome
- language barrier or problem
highlight 6 measures that can be put in place to improve security of mails by courier companies
- formulate rules and regulation regarding to the mails
- employment of qualified and faithful personnel to manage or in charge of mails
- availing of goods and services storage mails facilities
- installation of security systems i.e. CCTV
- employment of vigilant at the entrance of courier company
advantage of using folio number in mail and courier services
- creates order in filing process
- reveals order in which mails were received
- acts as a reference number when replying to a memory
- prevents creation of bulky mails
- ensures that every mail is dealt with
- assist in refilling in event of a disaster
list 3 promotional tools that may be used in mails
- computers
- mails
- phones
identify 4 international courier companies
- Fedex courier company
- Western union courier company
- EMS
- UPS- united parcel services
- TNT
- DHL – dais H Lnn
Professional bodies
- LSK – law society of Kenya
- KLA – Kenya library Association
- CPA- certify public accountant
- RMAO – record management association organization
TYPES OF COURIER SERVICES
- On – board courier
A side from chartering a plane, an on – board courier is the most expensive and in depth courier services. While being extremely expensive, these types of courier are often necessary when items of extreme importance need to travel (often n internationally) this could be the case for things such as medical cargo ( such as organs needed for a transplant critical parts or tools or sensitive business or legal information
- Personal courier services
This type of courier is often used in big cities or over relatively short distances
- They can carry a range of cargo form super – sensitive or delicate materials to standard office documents and files. Often these types of couriers will be used in large companies with complex mail systems to ensure that a package reaches the right person in a timely manner.
- In some cases these couriers are also bike courier in that they use motorbike or pushbike to navigate between locations quickly, however, they may also use typical transport such as cars, vans and trucks.
- Someday courier services
Some day courier services are often available for location within a reasonable distance of the sender. It is normally item of an urgent or delicate nature that arte send through a someday courier services, and this category may – carry over to the personal courier services but not necessary if a longer distance is covered obviously, this type of courier services comes at an additional price.
