
- Section A
1. Name two types of hypabyssal rocks.
Dolerite
Porphyry
Diabase
Lamprophyre
Porphyrite.
Granophyre
Any 2 x 1 = (2 marks)
2. (a) The diagram below shows intrusive volcanic features.
Name the features marked E, F and G.
E – A sill
F – A batholith
G – A laccolith/baccolith (3 marks)
Name two active volcanoes in Kenya.
– Longonot
– Teleki
– Likaiyu/ Likaiu
– Ol Donyo Lengai
– Menengai – Suswa
– Homa hills
3. (a) Give three processes in the hydrological cycle.
– Evaporation/ evapotranspiration / moist air rising/moist air rising.
– Condensationl moist air cooling
– Infiltration/ percolation
– Surface runoff/ overland flow
– Precipitationl rainfall / snow fall
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) State four factors that facilitate deposition in rivers.
– Reduction in river gradient which decreases the velocity of Water.
– Freezing of river Water leads to embedments of the load in the ice.
– River entering a large water body reduces the speed of the river flow.
– Presence of obstacles on the river course which blocks some of the load.
– Reduction in river volume Which reduces the strength of the river.
– Increase in Width of the channel makes Water to spread over wide area.
– Increase in the amount of load / size of the load.
Any 4 x l = (4 marks)
4. (a) Explain two reasons why wind is the dominant agent of erosion in arid areas.
– The areas have scanty/ no vegetation which exposes the land to erosion.
– The areas experience strong tropical winds which erode the materials.
– The areas have dry unconsolidated soils/ materials which are easily eroded.
Any 2 x 2 = (4 marks)
(b) Identify two features formed as a result of wind deposition in arid areas.
– Loess
– drass/ draas
– dunes / self / longitudinal dune, barchan, wake /transverse dunes.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
5. (a) Describe podzolization as a process of leaching.
– It occurs in areas with high rainfall and low temperature / cool & Wet conditions (cool temperature regions) / humid temperature regions/ conferous forest.
– Slow decomposition of vegetative matter results in formation of humic acid.
– Calcium / iron/ magnesium / alminium / pottassium / bases / salts/ carbonates minerals in the soil are dissolved and moved/ translocated from horizon A to horizon B.
– The soil is left extremely acidic/ humic / ash grey / broWn-grey/ red-yellow / White/ light in colour.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(b) State three ways in which mulching helps in soil conservation.
- Plant materials used decompose increasing soil humus.
- It protects the soil against erosion.
- It helps to increase infiltration rate of water into the soil.
- It helps reduce water loss from the soil / retain soil moisture.
- It helps to increase soil aeration.Any 3 x 1 = (3 marks)
Section B
6. Study the map of Migwani (1 :50 000) sheet 151/ 1 provided and answer the following
(a) (i) Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
38.01 E – 38.13 E/12’E(l1‘.3O” -12.30”)
38°00 30” — 38 13‘ 30 (2 marks)
ii) What is the magnetic variation of the map?
2“ 23 ‘ (1 mark)
(iii) Give the six figure grid reference for the junction of the roads D503 and D507.
119707 / 119708 (2 marks)
(b) (i) Using a vertical scale of 1 cm to represent 100 metres, draw a cross section along the line marked J – K.
On it mark and label the following:
– footpath (1 mark)
– road (1 mark)
– water pipeline (1 mark)
– steep slope (1 mark)
Features
Footpath (1 mark)
Road (1 mark)
Water pipeline (1 mark)
Steep slope(1 mark)
Total = (4 marks)
(iii) Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section
VE= V.S/H.S : 10,000 ” 50,000
_ 1 50,000
– 10,000 X 1
=5
(c) Citing evidence from the map, give three economic activities carried out in the area covered by the map.
– Transport as evidenced by presence of many roads / water pipeline.
– Trade evidenced by presence of many shops / market / petrol station / Water pipeline.
– Communication evidenced by post office.
Activity = 3 marks
Evidence = 3 marks
(6 marks)
(d) Explain how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map.
– There are many settlements in the north Western part because the land is gently sloping.
– There are no/few settlements in Mutito forest because the slope is very steep.
– There are few settlements on Kitui hills as the land is rugged/steep.
– There are no settlement on the ridges in the central and southern West areas because they are steep.
– There are few/no settlements in Usian because the land is rugged.
Any 2 x 2 = (4 marks)
7. (a) (i) Describe the solar system.
– It is the sun, planets and other celestrial bodies. They are held together by the force of gravity.
– The celestrial bodies revolve / orbit the sun.
– Most celestrial bodies are spherical in shape. (2 marks)
(ii) The local time at Manau, 60″W is 11.30 am. What is the time in Nairobi 37° E?
‘ The difference in longitude is 60 + 37 = 97° \/
‘ 1° = 4 minutes
(b) (i) 11) 97° => (1975 4 )hrs
= 6hrs 28 mins
Time in Nairobi = 1130
+628
1758 hrs or
5.58 pm v
Total = (3 marks)
(b) (i) State five characteristics of the mantle in the interior structure of the earth.
– The mantle is divided into two parts / the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
– It is about 2900 km thick.
– The average density is between 3.0 – 3.3 gm/cm3
– The upper mantle has a lower temperature than the lower mantle / 1000“ to 3000″ C.
– The upper mantle is in semi-solid state.
– The lower mantle is composed of rocks in viscous fluid state.
– The dominant minerals are silica, iron and magnesium / ferro – magnesium silicate / olivine.
Any 5 X l = (5 marks)
(ii) Outline the evidence which support the theory of continental drift.
– Palaeontological / palaeozological evidence the fossils of plants/ animals found in Africa are also in other continents .
– Adjacent continents have jig saw fitting coastlines or continental margins.
– There exists similarity in animal species/ plant species in the continents.
– Paleoclimatic evidence / Southern continents seem to have experienced large scale glaciation at the same period/presence of ancient glacial deposition in southern continents.
– Sea floor spreading recent volcanic eruption in mid-Atlantic ridges fill the gaps left by drifting continents.
– The location of major world fold mountains of the world/ trend of the folds / age of the fold mountains are similar.
– Paleamagnetism / the alignment of iron minerals in igneous rocks along the earths magnetic field indicate that the continents must have once been together.
– Geological evidence / existence of rocks which are similar in their formation/ structure/types/age along margins of different continents (sharing of oceans).
Any 4 X 1 = (4 marks)
(c) The diagram below represents the revolution of the earth.
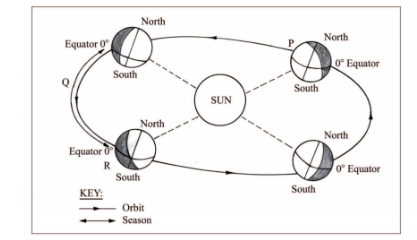
(i) Name the solstice marked P.
Winter solstice (1 mark)
(ii) Identify the season represented in the region marked Q.
Spring. (1 mark)
(iii) Describe the climatic conditions in Europe when the earth is in position R.
– High temperatures / hot conditions are experienced.
– There are long hours of sunshine.
– There is precipitation in form of rainfall / wet conditions.
– There is high humidity.
– There is low pressure.
– There is convergence of winds.
– It is cloudy.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
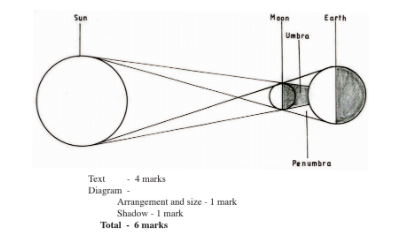
(d) With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the occurrence of the solar eclipse.
– It occurs when the moon lies between the earth and the sun / when the sun rays are blocked by the moon from reaching the earth.
– The shadow of the moon is cast on the earth’s surface.
– The shadow is the solar eclipse
– The shadow has two parts namely the umbra and penumbra.
– The umbra shadow causes total solar eclipse.
– The penumbra causes partial solar eclipse.
8. The map below shows some climatic regions of Kenya. Use it to answer question (a).
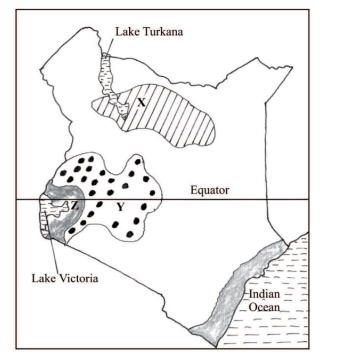
(a) (i) Name the climatic regions marked X and Y.
X – Desert climate ( l mark)
Y – Modified tropical climate ( l mark)
(ii) State three characteristics of the climatic region marked Z.
– lt has a small annual temperature range / 3“ – 5° C.
– It has a small diurnal range of temperature.
– It has a mean annual temperature of between 20° C and 32° C/ high temperature / moderate temperature.
– Receives moderate to high rainfall / rainfall ranges between 750 mm and 1500 mm per year, with no distinct dry month/ it rains throughout the year.
– The relative humidity is high / 80%
– The area receives convectional type of rainfall / rain falls mainly in the afternoon / accompanied by thunder and lightening.
– It has a double rainfall maxima.
– It experiences low pressure.
– There is a thick cloud cover.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) Explain how each of the following factors influence climate.
(i) Altitude.
– Temperature decreases with increasing height above sea level/ decreases at 0.6“ C for every 100 metres rise because the air is at the dense at lower altitude and rarefied at the higher attitude.
– Atmospheric pressure is higher at low altitude and lower at high altitude. This is because the weight of atmospheric air at low altitude is more than at high altitude.
– The temperature is higher at low altitude / lower at high attitude because the air is heated from below and not directly from the sun.
Statement = 3 marks
Explanation = 3 marks
(ii) Ocean currents
– Onshore winds blowing over warm ocean current, are warmed and absorb more warm vapour causes a warming effect on adjacent land resulting into increased rainfall and high humidity.
– Onshore winds blowing over ocean currents are cooled and moisture condenses resulting to rainfall in the water and a cooling effect on adjacent land leading to desertification / little rainfall / fog / mist.
– Onshore winds blow over warm ocean current causing a warming effect on the adjacent lands.
(c) What are the negative effects of climate change on physical environment?
– Disruption of natural ecosystem / loss of biodiversity /abnormal growth of plants caused by the increase in ultraviolet radiation /global warming/ seasons/ rainfall patterns.
– Flooding of land / coastal lands caused by increased temperature which leads to melting of glaciers thereby causing a rise in sea level/ change in rainfall patternl change in seasonal pattern/change in winds / air mass pattern.
– Increased temperatures may lead to drying up of water reservoirs thereby reducing their lifespan.
– Draught caused by increased temperature may lead to high evaporation / change in rainfall pattern/season’s pattern.
– Increase in rainfall leads to flooding / rise in sea level / soil erosion. – Soil erosion by wind caused by change in wind/air mass pattern.
– High ocean/sea waves/storms due to change in wind/air mass pattern when they blow more frequency and are more destructive (such as cyclones)
Any 3 x 2 = (6 marks)
(d) Students visited a weather station to study recording of weather elements.
(i) State three qualities in the construction of a stevenson screen they would have observed during the study.
– It is a wooden box.
– It is raised on stilts/ placed on a stand, about 121 cm above the ground level.
– It is painted white.
– It has a double roof.
– The sides are louvred to allow free circulation of air.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(11) Identify three types of data they are likely to have collected during the study.
– Types of weather measuring/ recording instruments
– Statistical data / tables / diagrams / maps on previous weather records.
– Diagrams/ photographs on instniments.
– Information on weather forecasting.
– Information on operations of weather measuring / recording instruments.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
9. (a) (i) Name two types of submerged highland coasts.
– Longitudinal / Dalmation
– Ria
– Fiord / / Fjord
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Identify two resultant features of the emerged highland coasts.
– Raised geos / blow holes
– Raised cliffs
– Raised wave cut-platforms
– Raised beaches
– Raised caves
– Raised notches
– Raised archs / stumps / stacks.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(b) State three factors influencing deposition by ocean waves.
– The existence of gentle sloping shore.
– Presence of shallow water along the coastline.
– The occurrence of a strong swash and weak backwash / constructive waves.
– The existence of indented coastline.
– Ample longshore drift materials to be deposited.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(c) With the aid of labelled diagrams describe the formation of the following coastal features.
(i) Fringing reef.
– It is formed when coral polyps start building a reef near the shore extending seawards.
– The rate of accumulation is faster seawards than towards the shore.
– The reef therefore becomes steeper seaward than towards the shore, enclosing.
a narrow and shallow lagoon.
– The accumulated coral materials form a fringing reef.
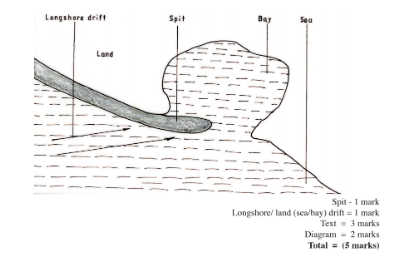
(ii) Spit
– It forms on a shallow shore at a point where the coastline bends landward
– Deposition occurs as the longshore drift is halted.
– More materials / deposits are piled up forming an elongated low lying ridge growing towards the sea.
– The elongated low lying ridge with one end attached to the coast and the other projecting into the sea is the spit.
(d) Explain the significance of oceans to human activities.
– Oceans provides building materials.
Text : 3 marks
Diagram : 2 marks
Total = (5 marks)
– Oceans modify the climate of the adjacent lands thus enhancing agricultural activities.
– Oceans are used by water vessels thereby enhancing transportl communication.
– Oceans provide sites for recreational activities thus promoting tourism.
– Oceans are habitats for aquatic life hence providing food/ income to humans.
Oceans habour minerals which are extracted for economic developr””‘
– Ocean waves/ tides are harnessed which generate electric power for industrial/ domestic use.
– Oceans provide water for cooling industrial plants.
– Oceans encourage education and research.
– Ocean provide ideal grounds for testing millitary weapons.
Any 4 x 2 = (8 marks)
10. (a) (i) Name two mountains in East Africa which are ice capped.
– Mt Kenya
– Mt Kilimanjaro
– Ruwenzori mountains
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Identify three Ways in which ice moves.
– Plastic flowage
– Basal slip
– Extrusion flow
– Internal shearing
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) Describe the formation of the following glacial features:
(i) Hanging valley
– It is formed in glaciated highlands where there is a main valley and a tributary valley.
– The two valleys get filled with ice. The main valley has more ice than the tributary valley.
– As the ice gets heavy/ thick, it begins to flow down the slope eroding by plucking and ubrasion.
– The main river valley is deepened and widened more than the tributary valley.
– When ice melts the tributary valley is left hanging at a higher level.
– The tributary valley left hanging above the main river valley is known as hanging valley.
6 x l = (6 marks)
(ii) Pyramidal peak.
– Ice accumulates in several shallow pre-existing depressions on the mountain sides.
– As the ice moves, it plucks the rocks on the sides of the hollows/ depression.
– Continued erosion by abrasion deepens and widens the hollows forming cirques.
– Adjacent hollows (cirques) continue to be eroded causing back walls to receed until they are separated by narrow steep ridges called aretes.
– Where aretes converge at the top of the mountain, they form a sharp – steep sided peak known as a pyramidal peak.
6 x l = (6 marks)
(c) You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland area.
(i) Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule.
– It enables the planned activities to be carried out systematically.
– It allows for proper use of available time.
– It enables the assessment of the progress of the fieldwork.
– It enables the estimation of total time required for the study.
– It confines the researcher to the scope of the topic.
– It ensures all areas are adequately covered.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Name three erosional features you are likely to observe during the field study.
– Depressions
– Crag and tail
– Ice eroded plain
– Roche montonnee
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(iii) Give three follow-up activities you would undertake after the field study.
– Sketching the features.
– Note making/ writing field reports.
– Asking / answering questions/ quizes.
– Discussing the findings.
– Display photographs.
– Analysing data collected.
– Reading more about the topic.
– Drawing conclusions.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
