
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1. State four pieces of information found in animal health records.(2 marks)
Date first symptoms were noticed.
Symptoms noticed
Disease diagnosed/suspected
Drugs used to treat disease
Cost of treatment
Remarks
Animal affected
Date of treatment
2. State four ways in which organic matter in the soil is important.(2 marks)
Increase soil aeration;
Improve water holding capacity;
Increases soil nutrient content;
Provides food and shelter for micro-organisms;
Binds soil particles together;
Buffers soil pH;
Reduces toxicity of plant poisons;
Improves soil temperatures;
Increase water infiltration;
3. Name four equipment used for large scale overhead irrigation.(2 marks)
Sprinklers
Water pumps
Pipes
Filters
4. State four functions of the Agricultural Society of Kenya (ASK).(2 marks)
Holds competitive agricultural shows/exhibitions;
Encourages breeding and importation of pure breeds of livestock;
Enourages and assists in official milk recording scheme;
Organizing national ploughing contests;
Publishing a monthly journal – the Kenya farmer magazine.
Organising the running of young farmers clubs;
Awarding bursaries for local and overseas students;
Organising tours for its members;
5. State four pieces of information found on a delivery note. (2 marks)
Date of delivery
Quantity of goods delivered.
Items delivered
Person who receives the goods/stamp of receiver.
Conditions in which goods are recived
Delivery note serial number.
Person who delivered
6. Name four implements used for primary cultivation.(2 marks)
Jembe / hoe
Ox plough
Disc plough
Mouldboard plough
7. State four factors that influence soil formation.(2 marks)
Parent rock/bedrock
Climate
Topography
Time
Living organisms / Biotic
8. State four reasons for ridging in potato production.(2 marks)
To conserve soil moisture
To prevent soil erosion
To improve soil drainage
For expansion of tubers
For easy harvesting
9. Distinguish between each of the following pair of terms as used in crop production:
(a) Thinning and Roguing.(1 mark)
Thinning is the removal of excess seedlings from the seedbed while roguing is removal and destruction of diseased or infected plants.
(b) Seedling bed and Nursery bed.(1 mark)
Nursery bed is a small piece of land where small seeds are raised into seedlings before transplanting while seedling bed is a special type of nursery which receives excess seedlings from the nursery bed after pricking out,
10. Apart from tillage, name four methods farmers use to control weeds.(2 marks)
Chemical method / use of herbicides;
uprooting;
Biological method;
Cultural method.
11. State four causes of crop diseases.(2 marks)
Fungi
Virus
Bacteria
Poor weather onditions
Lack of essential elements.
12. State four ways in which a land title deed is important to a farmer.(2 marks)
Used to secure credit facilities for land development;
Land disputes are minimised;
Encourage farmer to carry out long term investment on the land;
Enables owner to lease the farm and thus get extra income;
Provide security of ownership;
13. State four agents of soil erosion.(2 marks)
Water;
Wind;
Human activities;
Living organisms;
14. State four effects of late defoliation in pasture utilisation.(2 marks)
Forage has high dry matter content;
Has high cellulose content;
High lignin, tannin and silica which are indigestible;
Has low crude protein content;
Has low leaf : stem ratio
Has low dry matter digestibility
15. State four agricultural practices that pollute surface water sources.(2 marks)
Use of inorganic fertilizers
User of excess pesticides
Over cultivation
Over grazing
Cultivation along river banks.
SECTION B
Answer all the questions in this section.
16. The diagram below shows a bag of Calcium Ammonium Nitrate fertiliser.
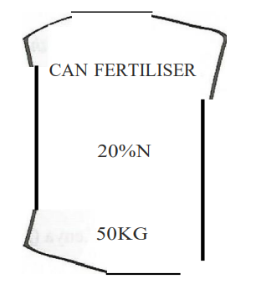
(a) Classify the fertiliser.(1 mark)
Nitrogenous / straight fertiliser
(b) Explain the effect of applying the above fertiliser on soil pH.(1 mark)
It neutralises soil acidity; Acidity produced by ammonium ions is counteracted by calcium carbonate which is a liming material. It raises / increases soil pH. It has a liming effect.
(c) A farmer is advised to apply 50 kg of nitrogen per hectare.
How many bags of the above fertiliser will this farmer require for one hectare? Show your working.(3 marks)
If 20kg N is contained in 100kg CAN ∴ 50kg N is contained in
100kg of CAN x 50kg N = 250kg of CAN
20kg N
250kg = 5 bags
50kg
17. The diagram below shows a nursery practice carried out soon after tree seedlings have emerged.
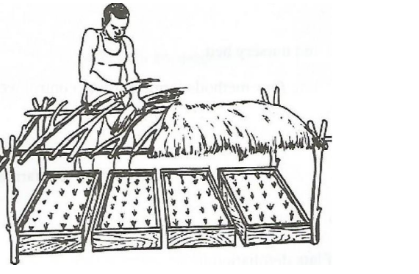
(a) Identify the practice.(1 mark)
Shading
(b) Give two reasons for carrying out the above practice.(2 marks)
– Protects seedlings from direct sunlight;
– Protects seedings from heavy rainfall which damages seedlings.
(c) State one precaution that should be observed in the practice illustrated in relation to the direction of the sun.(1 mark)
– Should be laid along North/South orientation;
– Should allow in sunlight early in the morning and late in the evening;
(d) Name the type of nursery bed illustrated.(1 mark)
Raised nursery bed; Tree nursery;
18. The diagram below shows a soil borne pest that attacks plant roots.
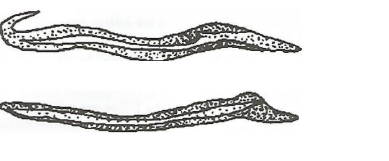
- (a) Identify the pest.(1 mark)
- Root nematode(b) State two symptoms of attack by the pest in tomato production.(2 marks)– Root swells / formation of root galls; – Wilting of crop even when moisture is adequate;
(c) State two control measures for the pest.(2 marks)
– Crop rotation;
– Use of nematicides;
– Fumigation of soil;
– Soil solarisation
– Close season
19. The table below shows a farm record for Mwamuzi Farm.
RECEIPTS ISSUES Date COMMODITY/ITEM QUANTITY DATE ISSUED TO QUANTITY BALANCE IN STOCK (a) Identify the farm record.(1 mark)
Consumable goods inventory
(b) The farm received 20 bags of DAP fertiliser from Milimani Agrovet on 07/07/2018 and another 20 bags on 21/07/2018.
On 28/07/2018, a gardener took eight bags of DAP and used it to plant potatoes on the farm. Enter this information in the farm record illustrated above.(3 marks)
RECEIPTS ISSUES Date COMMODITY/ITEM QUANTITY DATE ISSUED TO QUANTITY BALANCE IN STOCK 7/7/18 DAP fertiliser 20 bags (50kg) 20 21/7/18 DAP fertilizer 20 bags (50kg) 40 28/07/18 Gardener 8 bags DAP 32 (c) Give one reason for keeping the farm record illustrated above in farm accounting.(1 mark)
– It provides information used for drawing Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section.
20. (a) Describe the risks and uncertainties encountered by sugarcane farmers in Kenya.(7 marks)
- Fluctuation of commodity prices.
- Physical yield uncertainty where the farmer does not know how much to expect.
- Ownership uncertainty. Farmers lose produce through theft, fire, death or change in government policy.
- Outbreak of pests and diseases which affect expected outcome.
- Sickness and injury uncertainty. Farmer affected and loses ability to work due to sickness or injury.
- Uncertainty about new production techniques. The farmer may not be certain as to whether technology is as effective as the previous one.
- Farmer investing in machinery which may become obsolete within a short time.
- Natural catastrophes. Things like floods, drought, earthquakes, storms and strong winds which may destroy the crops.(b) Explain three ways in which each of the following reduces tomato production:(i) inadequate rainfall;(3 marks)
- Results to failure in seed germination;
- Results to restricted root development;
- Results to moisture stress which reduces fruit weight(ii) low temperature;(3 marks)
- Slow growth rate of crops due to slowed photosynthesis;
- High incidence of disease infection to crops e.g. late blight.
- Lowers the quality of tomato fruits.(iii) strong wind.(3 marks)
- Agent of soil erosion carrying top fertile soil reducing nutrients.
- Causes lodging and damage to crops.
- Increases rate of evaporation from soil leading to water loss.
- Increases spread of pests and disease attack.(c) Give four reasons why farmers prefer using tillage to control weeds.(4 marks)
- Cheap therefore a good option for small scale farmers.
- Tillage opens up soil allowing infiltration of water to occur and thus minimize soil erosion.
- During tillage, earthing up is done which encourages root growth.
- During tillage, crop residue is incorporated into the soil to form organic manure.
- Improves soil aeration.
- Exposes soil borne pests and disease agents.21.(a) Describe how maize is planted in the field.(7 marks)
- Plant suitable varieties.
- Plat early at onset of rain/dry plant.
- Plant at 2.5cm to 10cm depth;
- Spacing at 20cm to 30cm by 75cm to 90cm;
- Apply DAP at planting
- Plant 25kg seed per hectare
- Place one or two seeds per hole.
- Plant by hand or machine planter
- Use organic manure / handful per plant(b) Explain seven factors that determine spacing in bean production.(7 marks)
- Type of machinery used; use of machines requires wider space;
- Soil fertility, fertile soil, closer spacing
- Type of beans / varieties of beans. Spreading beans require wide spacing.
- Moisture avalability; High rainfall – closer spacing.
- Use of the crop – close spacing
- Pest and disease control; wider spacing control pest spread.
- Number of seeds per hole. More seeds per hole – wider spacing.(c) Give six reasons why tree seedlings should be established using a nursery.(6 marks)
- Facilitates production of many seedlings in a small area.
- Routine management practices are easily and timely carried out in a nursery than sun the main seed bed;
- Makes it possible to provide the best conditions for growth such as fine tilth, levelled field and shade;
- Facilitates the planting of small seeds which develop into strong seedlings that are easily transplanted.
- It ensures transplanting of only those seedlings that are healthy and vigorously growing.
- Excess seedlings from the nursery may be sold, thus become a source of income to the farmer.22. (a) Describe how a plucking table is maintained in a tea plantation.(5 marks)
- Cute back the tea bush to 5cm above the last pruning height after 2 – 5 years;
- Carry out tipping after 3 months.
- After many such running, tea bush is cut down to 45cm above the ground;
- Rehabilitation done after every 40 – 50 years.(b) Describe how onion seedlings are transplanted.(7 marks)
- Water the nursery bed before transplanting.
- Selecting healthy and vigorous growing seedlings;
- Lift the seedlings using a garden trowel and put then into a container for transporting to the seedbed.
- Plant one seedling per hole at the same depth as it was the nursery.
- Firm the soil around the base.
- This should be done preferably late evening or during a cloudy dat.
- Mulch the seedlings and water them regularly.
- Put appropriate amount of fertiliser/manure into planting holes and mix with soil.
- Transplant when seedlings are about one month old.
- Plant at spacing of 30cm between rows by 8 – 10 cm between plants.(c) Describe eight types of micro-catchments used in water conservation.(8 marks)(i) Negarim micro catchment;
Are closed grid of diamond shape or open-ended “V”s formed by contracting small earth ridges with infiltration pits for purpose of collecting water.
(ii) Contour bunds;
These are earthen binds constructed along the contours’ and are spaced 5cm to 10cm apart.
(iii) Contour Ridges;
Are small earth ridges constructed along contours and are spaced 1.5m to 5m apart and are used to conserve water.
(iv) Semi-circular bunds;
These are semi-circular shaped earth bunds with tips, constructed along contour. Used in rangeland dance appropriate for pasture and tree planting.
(v) Trapezoidal bunds;
Are earth bunds which are trapezoidal in shape. They capture surface flow and allows the excess water to overflow around wing tips.
(vi) Contour stone bunds
Formed by heaping small stone bunds along the contours to slow surface flow and filter eroded soil.
(vii) Rock dams;
Constructed across valleys to slow surface flow.
(viii) Water spreading bunds;
They are used to divert water from watercourse onto crops or pasture.
