
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1. State four effects of fleas in poultry.(2 marks)
- Irritation
- Anaemia
- Wounds/damage on the skin/swellings/injuries
- Damaged/raffled feathers
- Retarded growth2. Name two breeds of dairy cattle with the highest(a) butter fat content (2 marks)
- Jersey
- Guernsey(b) milk yield (2 marks)
- Friesian/holstein
- Ayrshire3. State four ways in which vaccines are administered to livestock.(2 marks)
- Through injections
- Orally through the mouth
- Through the nose/inhalation
- Through the cloaca
- Through the eye/occular4. State four characteristics of animals which require a high maintenance ration.(2 marks)
- Large animals
- Young animals
- More active animals
- Highly productive (yielding) animals5. State four microbial activities that occur in the rumen.(2 marks)
- Food fermentation
- Synthesis of vitamins(K and B Complex)
- Synthesis of amino acids
- Breakdown of proteins to peptides, amino acids and ammonia
- Breakdown of cellulose and carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and volatile fatty acids6. Name four pests that attack bees. (2 marks)
- Honey badger
- Bee louse
- Wax moth
- Ants
- 7. Name four mineral deficiency livestock disorders.
- Milk fever Parturient paresis
- Parakeratosis
- Goitre
- Enzootic neonatal ataxia (sway back in lambs)
- Anaemia
- Hypomagnesemia (Grass staggers/grass tetany8. State four control measures for fowl typhoid.(2 marks)
- Kill and properly dispose infected birds
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Regular vaccination
- Obtain chicks from reliable sources
- Treatment using sulphur drugs9. State the function of each of the following:(a) Mallet (½ marks)
- Driving wood chisel(b) Trocar and canula (½ marks)
- Removal of accumulated gases which cause bloat in ruminants.(c) Garden line (½ marks)
- Setting straight lines; measuring distances;Stock and die (½ marks)
- Cutting threads on pipes10. State four maintenance practices carried out on a wheelbarrow.(2 marks)
- Greasing/lubricating the moving parts
- Repairing broken parts
- Replacing worn out parts
- Cleaning after use
- Proper storage
- Tightening loose nuts and bolts
- Painting to prevent rusting
- Apply old engine oil11. State four limitations of biogas as a source of power on the farm.(2 marks)
- High initial capital is required to construct the digester.
- Require high skilled labour
- It requires rearing of livestock to sustain gas production.
- It is laborious in refilling with dung.12. State four function al difference es between disc and mouldboard ploughs. (2 marks)Disc plough Mouldboard plough
- Rolls over obstacles – Rigid and slides along:
- Does not completely – Completely inverts furrow slices invert furrow slices
- Requires more secondary Requires fewer secondary cultivations – cultivations
- Ploughs at varying depths Ploughs at a uniform depth
- Not easily broken by – Easily broken by obstacles. obstacles.
- 13. State four advantages of the Kenya Top Bar Hive (K.T.B.H.) over the log hive. (2 marks)
- Top bars can be removed and replaced to inspect the combs.
- Honey combs are harvested without disturbing the brood.
- Good quality honey is harvested without brood combs.
- More wax is harvested because combs are not returned to the hive.
- It is easy to construct and repair.
- Utilizes queen excluder to separate honey combs from the brood combs.
- Is cheap to extract honey14. Distinguish between the following practices as used in livestock production:(a) tapping and serving (1 marks)
- Tapping: Act of mating in sheep and goats
- Sevigne: Act of mating in catt1es and pigs(b) ringing and raddling (1 marks)
- Ringing: Trimming of wool around the sheath of the penis to facilitate mating in sheep
- Raddling: Is the fitting of rams with breeding chutes painted in different colours or painting of rams in different colours on the underside to identify sires of lambs, infertile ewes and ewes with repeated heat;15. (a) Name the causal organism for East Coast Fever. (½ marks)Protozoa: Theileria parva
(b) State three ways in which infectious diseases spread from one animal to another. (1½ marks)
- Through contact:
- Through inhalation;
- Through ingestionSection B (20 MARKS)Answer all the questions in this section
16. The diagram below illustrates a practice in poultry rearing.
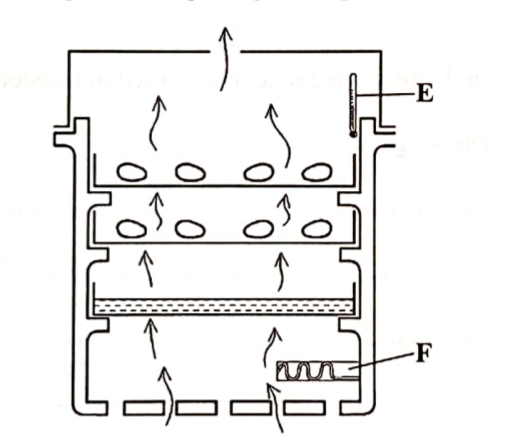
- (a) Identify the practice.(1 mark)Artificial Incubation(b) Name the part labelled
- E – Thermometer
- F – Source of heat(c) Explain two activities not shown in the illustration but very important for the practice to succeed. (2 marks)
- Egg turning to prevent chicks from sticking on shells;
- Cleaning and disinfection to ensure proper hygiene/destroy disease agents;
- Egg candling to remove infertile, broken and abnormal eggs;
- Disinfection to destroy disease agents17. The diagram below shows the reproductive system of a hen.
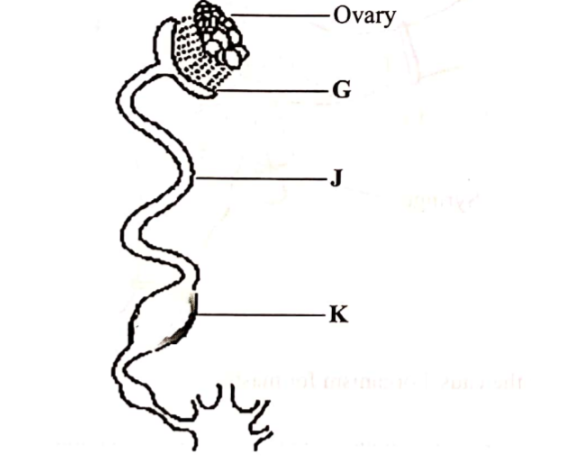
- (a) Name the part labelled K (1 marks)
- Uterus/shell gland(b) State one function of each of the parts labelledG — Site of fertilization;
– Addition of chalazae;
-Stores sperms
-receives the ovum from the ovary
J — Addition of thick albumen;
-Addition of water and mineral salts;
(C) (i) What is the maximum number of eggs a hen can lay in a day?(1 marks)
One;
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (C) (i) above. (1 mark)
It takes 24 (18-36) hours for an egg to form;
18. The diagram below illustrates a treatment practice for a cow’s udder infected with mastitis.
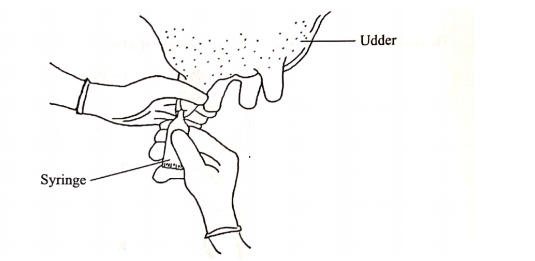
- (a) Name the causal organism for mastitis.(1 mark)
- Bacteria — streptococcus agalatiae /5taphy1ococcus spp./ pasturella spp.(b) Explain the treatment practice illustrated.(1 mark)After milking, the infected teat/quarter is infused with antibiotics to destroy/kill the bacteria
(c) How is mastitis infection detected in a lactating cow? (1 mark)
By stripping milk into a strip cups, before actual milking stars. Watery milk/bloody milk/ clots/pus/ on the strip cup indicate mastitis infection;
(d) How is an infected cow handled during milking to prevent spread of the disease to other animals? (2 mark)
- Milk the infected animal last; milk the infected quarter last and discard the milk;
- Use Separate udder cloths for each animal;19.The diagram below shows a farm structure for storing gains(a) Identify the farm structure.(1 mark)
- Traditional granary(b) State the function of the part labelled L. (1 mark)
- Prevent entry of rats/rodents/vermin into the store;
- Prone to damage by insects; fire risk; less durable;
- Cleaning;
- Dusting;
- Clearing the vegetation around the granary;
- Repairing/replacing worn out/broken parts;
- replacing broken parts/worn out parts;(c) State one disadvantage of the roofing material used on the farm structure. (1 mark)Prevent entry of rats/rodents/vermin into the store
(d) State two ways in which the structure is made ready for grain storage. (2 marks)
- Prone to damage by insects;
- fire risk;
- less durableSECTION C (40 marks) Answer any two questions from this section20.(a) State five disadvantages of artificial insermination. (5 marks)
- Harmful traits can be spread quickly by one bull to tfie offsprings sired;
- Requires skilled labour;
- Low chances of conception;
- More laborious than natural mating;
- Difficult to detect heat signs;
- Storage and transportation equipment are expensive.(b) State five differences between ruminant and non-ruminant digestive systems. (5 marks)Ruminants nonruminants
- Chew the cud – Do not chew the cud.
- Four chambered stomach/polygastric – One stomach.
- Regurgitates food – Does not regurgigate Can digest cellulose Cannot digest cellulose except animals with functional caecum;
- Lack ptyalin in saliva – Have ptyalin in saliva.
- Digestion and absorption mainly – Occurs in the small occurs in the rumen. intestines.
- Have alkaline saliva – Saliva is neutral(c) Describe anaplasmosis (gall sickness) disease under the following sub-headings:(i) causal organism (1 mark)
frotozoa/ Anaplasma marginale naplasma centrane
(ii) modes of transmission (2 mark)
BLue ticks; red legged tick; contaminated surgical instruments; hypodermic needles; contaminated blood; biting insects;
(iii) symptoms (4 mark)
- Fever
- Constipation
- Pale eyes, gums and lips Reduced milk production
- Anaemia(iv) control measures. (3 mark)
- Control ticks; and biting insects;
- Treatment using intramuscular injections of antibiotics;
- and iron giving injections21. (a) State the functions of any six parts of a piggery unit.(6 mark)Food store: Storage of pig feeds.
- Records room: Keeping feed and weight records. Furrowing pen: For furrowing and rearing
- piglets. Gilts pen: Rearing weaned females upto service age.
- Boar’s pen: Houses the breeding boar; for mating.
- Inpig pen: Houses pregnant pigs awaiting furrowing.
- Weaners/fatteners pen: Houses piglets after weaning up to the age of six months.
- Running yard: Used for dunging and basking.
- Water troughs/drinking nipples: Used as watering points for pigs.(b) Explain six disadvantages of animal drawn implements. (6 mark)
- More laborious in guiding the implement and the animals.
- Animals are slower than tractors and the output is less.
- Animals get tired faster hence slow down the work.
- Some areas are prone to diseases hence difficult to use some animals.
- Extra costs required for rearing the animals.
- It is more tedious, i.e. operators tire more than those using tractor drawn implements.(c) State eight symptoms of tapeworm infestation in cattle. (8 mark)
- Pot bellies
- Starring coat
- Anaemia
- Emaciation
- Constipation due to indigestion
- Oedematous swillings under the jaw;
- Proglottids observed in the dung
- Excessive appetite
- Obstruction of intestines on heavy infestation22. (a) Explain five precautions taken by dairy farmers to ensure clean milk production. (10 marks)
- Maintain healthy milking herd to prevent transmission o1 the disease agents to milk and milkman;
- Clean milking cows to prevent contamination of milk with dirt;
- Maintain healthy and clean milkman to prevent transmission of zoonotic diseases and contamination of milk with dirt ;
- Maintain clean milking shed to prevent accumulation of dirt and disease agents;
- Maintain clean milking equipment to prevent contamination of milk; Ensure milk is filtered to remove solid impurities;
- Ensure milk is cooled and properly stored to give it a long shelf life;
- Avoid flavours in milk: strong flavoured feeds should be fed to the animals after milking;(b) Describe how chicken is dressed for sale.(10 mark)
- lay the bird on its breast on the table
- Pull and cut off the skin of the neck at the point where the neck enters the body;
- Cut the neck from the head at the point of dislocation/the cut;
- Turn the carcass on its back;
- Grasp and gently pull out this crop;
- Insert the index finger as far as possible into the body cavity through the opening left after removing the neck and crop;
- Work around the finger close to this body to loosen the organs from the ribs and the back;
- Turn the bird and hold the abdomen with the left hand;
- Make a horizontal cut between the vent and the keel bone to expose the intestines;
- Insert a finger into the abdomen through the cut and loop around the vent to close the intestines;
- Hold the intestines away from the vent and then cut around with the bowels still attached;
- Insert the right hand into the abdominal opening gently grab the gizzard and pull it out accompanied with other internal organs;
- Cut the skin around the shank to remove the sinus just below the hocks and pull them out strongly from the body;
- Pack this carcass in a polythene bag for sale;
