
Section A (30 marks)
1. Disadvantages of intensive system of farming.
i) Requires high initial capital/Expensive
ii) Is labour expensive
iii) Requires high level of management/skilled labour (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
2. 4 methods of farming.
i) Shifting cultivation
ii) Nomadic pastoralism
iii) Organic farming
iv) Mixed farming
v) Agroforestry (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks) 3. a) Nitrogen fixation
– Process in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted to nitrates for plant uptake. (1 x 1 = 1 mark) b) Phosphorous fixation
– Process in which phosphorous combines with other elements to form compounds that cannot be absorbed by plants. (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
4. 4 reasons for keeping livestock health records.
i) Help in calculation of treatment and health costs
ii) Help in culling/selecting livestock
iii) Help in future diagnosis treatment and control measures
iv) Help determine the common diseases and parasites/prevent diseases and parasites
v) Help to support livestock insurance claims (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
5. Relationship between scarcity and choice.
– Scarcity is where production resources are limited in supply relative to demand; therefore a choice has to be made on which enterprise(s) to allocate the limited resources. (2 marks – mark as a whole)
6. 2 reasons for land fragmentation.
i) Buying/selling/paying debts/compensation
ii) Inheritance
iii) Settlement and resettlement
iv) Gift/donations
v) Shifting cultivation (2 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
7. Advantages of individual tenure system.
i) Easy to acquire credit.
ii) Land disputes are minimized
iii) Long term investment is encouraged
iv) Incentive to conserve and improve land
v) Easy to plan and make decisions
vi) Easy to sell/lease whole or part of the land. (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
8. 4 features for choosing powers
i) Durability
ii) Strength/ability to withstand pressure/thickness of the wall of the pipe
iii) Diameter/size of the pipe
iv) Workability/manoeverability of the pipe
v) Colour (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
9. 4 reasons for treating water.
i) Remove chemical impurities/softening of water
ii) Kill disease causing organisms/kill germs/pathogens
iii) Remove bad smells and taste
iv) Remove impurities of solid particles (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
10. 4 Statutory Boards
i) Kenya Sugar Board/Authority (KSB/KSA)
ii) Kenya Tea Development Authority/Agency/Tea board of Kenya (KTDA, TBK)
iii) National Cereals and Produce Board (NCPB)
iv) Coffee Board of Kenya (CBK)
v) Pyrethrum Board of Kenya (PBK)
vi) Cotton Lint and Seed Marketing Board/Cotton Board of Kenya (CLSMB, CBK)
vii) Horticultural Crop Development Authority (HCDA)
viii) Kenya Sisal Board (KSB) (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
11. 4 marketing functions of KCC
i) Buying and assembling milk/collection
ii) Processing milk
iii) Market research
iv) Advertisement/promotion of milk/milk products
v) Strategic storage of milk products
vi) Distribution of milk/transportation
vii) Selling milk
viii) Marketing and packaging
ix) Risk bearing
x) Financing – related to marketing function
xi) Grading/standardization
Rej: Marketing alone (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
12. i) Increases seed soil contact
ii) Compacts soil/seed to protect it against agents of erosion
iii) Crushing large soil clods
iv) Soil levelling (2 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
b) Levelling
i) Ensures uniform depth of planting/uniform germination/uniform fertilizer application
ii) Ensures uniform water level in paddy
iii) Rice fields
iv) To remove depression which collect water leading to rotting of seeds.(2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
13. 3 activities in clearing land
i) Tree felling
ii) Stumping/removal of stumps/destumping
iii) Slashing/mowing (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 marks)
14. 5 Advantages of zero grazing
i) Requires little land
ii) Quick accumulation of manure
iii) Easy to control diseases and parasites
iv) Less wastage of feeds
v) Has high stocking rate
vi) High milk yield
vii) Efficient use of fodder (5 x 1/2 = 21/2 marks)
15. 4 factors determining stage of crop harvesting.
i) Intended use of the crop
ii) Chemical concentration of the produce/stage of maturity/change in colour
iii) Prevailing weather conditions
iv) Market demand for the produce/market price (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
16. a) Growth Cycle
i) Annual weeds
ii) Biennual weeds
iii) Perennial weeds (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
b) i) Broad leaved weeds
ii) Narrow leaved weeds (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
Section B (20 marks)
17. a) Weed
– Couch grass/Digitaria scalarum (1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
b) Why its difficult to control.
– Presence of underground stems/rhizomes which are difficult to control/underground storage structure (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
c) 4 control
i) Uprooting
ii) Cultivation
iii) Slashing
iv) Use of herbicides
v) Mulching
Rej: Rogueing (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
18. a) Soil Sample with highest acidity
– Sample S1 (1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
b) Lowering pH
i) Application of acidic fertilizers: Accept S/A; ASN; DAP; MAP
Rej: Nitrogenous fertilizers
ii) Application of sulphur (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
c) Soil sample suitable for tea growing
i) S2
ii) S3
iii) S4
19. i) Extraction to remove seeds from pods/fruits
ii) Drying to reduce seed moisture content
iii) Testing to verify seed quality
iv) Treatment to break dormancy/helps improve germination/soaking in water
v) Seed dressing to control pests and diseases
vi) Seed innoculation to improve nitrogen fixation
vii) Washing/cleaning to remove mucilage (4 x 1 = 4 marks)
20. a) i) Correct pruning
– B
NB: Wrong identity
Wrong reason
(1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
ii) Reason
– Slant cut is a few centimetres above the bud/leaf (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
b) 2 how pruning controls diseases
i) Removes diseased parts
ii) Creates unfavourable conditions/environment for disease agents
iii) Facilitates penetration of chemical sprays. (2 x 1/2 = 1 marks)
21.
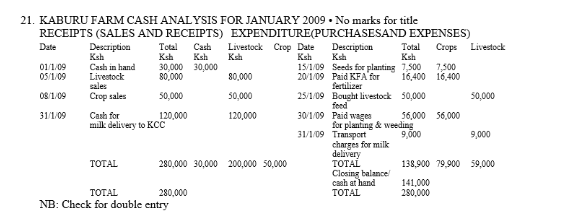
21. • Correct labelling of expenditure and receipt columns 1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark
• Correct entries by dates 9 x 1/2 = 41/2 marks
• Balancing 1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark
Closing balance
Cash at hand i.e 141,000
22. a) Figures 18:46 on a fertilizer bag mean
i) 18% Nitrogen (NO
ii) 46% phosphorous pentoxide (P2O5)
iii) 10% Potassium oxide (K2O) (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 marks)
b) Filler material
= 100 – (18 + 46 + 10)
= 100 – 74
= 26kg or 26%
Ignore working
Mark answer only i.e 26
Unit must be therefore a score. 1 x 1 = 1 mark
Section C (40 marks)
23. a) 8 Factors that encourage soil erosion.
i) Lack of ground cover exposes soil to agents of soil erosion/removal of cover crops
ii) Steep slopes increase the speed of surface run-offs hence erosive power of water
iii) Light/sandy soils are easily carried away by agents of soil erosion.
iv) Shallow soils are easily saturated with water and carried away
v) High rainfall intensity on bare ground/leads at detachment of soil hence run off
vi) Frequent cultivation/over cultivation pulverizes the soil making it easy to detach and carry away.
vii) Overstocking leads to overgrazing which destroys ground cover exposing it to agents of erosion.
viii) Burning/deforestation destroys vegetation cover and exposes soil to agents of erosion.
ix) Ploughing up and down the slope creates channels which speed up and increases the erosive it to agents of water.
x) Cultivation of river banks destroys riverine (Viparia) vegetation & destroys soil structure exposing it to agents of erosion.
xi) Cultivating the soil when too dry destroys soil structure making it easy to be eroded.
xii) Long slopes increases volume speed of run off hence increasing erosive power of water.
Question if filter not qualified = No mark
Factor & effect
xiii) High rainfall amount increase saturation of soil hence increase in soil erosion.
b) i) Mulching to conserve moisture
ii) Erection of shade to minimize evapotranspiration
iii) Weed control to reduce competition with seedlings for nutrients, light, space etc
iv) Pest and disease control to ensure healthy and vigorously growing seedlings
v) Pricking out/thinning to minimise competition for growth elements
vi) Fertilizer application to supplement nutrients in the soil
vii) Watering to ensure adequate moisture supply
viii) Hardening off/removing shade/reducing watering to acclimatize the seedling to conditions in the field.
ix) Removal of mulch immediately after germination
NB: Correctly stated (7 x 1 = 7 marks)
c) 5 soils factors that determine a crop growth in an area.
i) Soil drainage/rate of water infiltration and percolation through the soil
ii) Soil structure/arrangement of soil particles or aggregates/water holding capacity
iii) Soil nutrient content/variety and quantity of mineral nutrients in the soil/Soil fertility
iv) Soil profile/soil depth/depth and arrangement of soil horizons in relation to the rooting systems of the crop
v) Soil pH/chemical properties of the soil/degree of acidity or alkalinity of the soil solution
vi) Soil borne pests and diseases/the prevalent pests/diseases in the soil
vii) Water holding capacity
5 correctly stated (5 x 1 = 5 marks)
24. a) 5 effects of high temperature
i) Increases incidences of some pests/parasite and diseases
ii) Improves quality of certain crops e.g fruits, pineapples, papaws’
iii)Lowers quality of certain crops e.g pyrethrum
iv) Increases rate of evapotranspiration/wilting in plants
v) Increases rate of growth for early maturity in crops
vi) Limits distribution of exotic livestock breeds
vii) Lowers production in livestock
viii) Influences design of farm buildings and structures
ix) Lowers labour productivity (5 x 1 = 5 marks)
b) 4 precautions observed in cotton harvesting
i) Sisal bags/gunny bags should not be used to prevent mixing of lint and sisal fibres which causes ginning problems
ii) Hands should be cleaned to avoid staining of the lint
iii) Picking should be done when the lint is dry to prevent fibres from sticking together
iv) Use clean containers for picking
v) Use different containers for AR (Safi) and BR (fifi) gardens of cotton to ensure quality/separation
vi) Picking should be done immediately the bolls open/split to prevent staining by dust/dirt
vii) Avoid picking leaves & twigs to avoid (containers) 1 x 4 = 4 marks
b) Sugar cane harvesting
i) Harvest at the correct age / 13 -22 months for plant crop/ 12 – 18 months for rotation
ii) Take sugar can samples of testing to determine maturity.
iii) Cut the mature cane at the base/near the ground
iv) Cut off the green tops
v) Strip off green leaves/burn the cane
vi) Deliver the cane to the factory within 48 hours/immediately after cutting
vii) Use a cane harvesting machete. (6 x 1/2 = 3 marks)
c) 8 factors considered in farm planning
i) Risk and uncertainties: enterprises should be analysed to determine the risks and uncertainties involved.
ii) Security: enterprises which require more security should be sited near the farm house/provision of adequate security
iii) Land size: a large number of enterprises can be established on a large scale compared to a small scale farm.
iv) Current trends in labour market: to determine availability and cost of labour especially during peak period.
v) Farmers objectives and preferences: to ensure the farmer who is the operator has a sense of ownership of the plan and brings about motivation
vi) Current market trends and prices of outputs: to ensure consideration of enterprises with high profits returns.
vii) Availability and cost of farm inputs: to identify enterprises that are affordable and whose inputs are readily available.
viii) Government policy/regulation: to seek permission for enterprises undertaken on quota system e.g coffee growing and avoid enterprises and farming systems prohibited by the government
ix) Environmental factors: soil, climate and topography should be analysed to determine livestock crop enterprises that are suitable to the local ecological conditions.
x) Communication and transport facilities and facilitate movement of outputs to the market and supply of inputs. Also helps in conveying improved methods of farming and market trends.
xi) Availability of capital: to acquire farm inputs
xii) Possible production enterprises: should be identified and analysed so that suitable and profitable enterprises are selected
– Wrong factor
Award for explanation 1/2 mk – stating the factor = 1/2 x 8 = 4
25. a) 6 physical methods of controlling crops pests
i) Trapping/picking and killing the pests
ii) Use of lethal temperature to kill the pests
iii) Flood the suffocate and kill the pests
iv) Use of physical barriers e.g fences, rat guards, etc to keep the pests away from the crop/produce
v) Proper drying to make penetration difficult
vi) Use of explosive to destroy breeding grounds and the kill the pests
vii) Suffocation: carbon dioxide build up to suffocate pests in stores especially cyprus bins. (6 x 1 = 6 marks)
b) Field management of bulb onions
i) Weed control through shallow cultivation to avoid damage to the shallow inion roots
ii) Remove excess soil around the roots gradually to facilitate bulb expansion
iii) Water regularly at the early stages to ensure adequate moisture supply
iv) Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizer at appropriate rates
v) Control pests e.g thrips using appropriate pesticides
vi) Control diseases e.g rusts, mildews using appropriate method. (4 x 1 = 4 marks)
c) Harvesting of bulb onions
i) Is done 4 -5 months after planting/when leaves wither/turn brown
ii) Cut break and bend this tops at the neck
iii) Harvesting is done by lifting/pulling/digging out the crop
iv) Leave the bulbs on the ground/undershade to dry for 3 days and turn frequently to ensure uniform drying. 3 x 1 = 3 marks
c) 7 factors influencing seed rate
i) Intended use of the crop e.g fodder maize requires high seed rate than grain maize.
ii) Germination percentage – high speed rate is required for seeds with low germination percentage
iii) Method of planting: Broadcasting requires high seed rate than row planting.
iv) Number of seeds per hole: two or more seeds per hole requires more seed rate than one seed per hole.
v) Soil fertility: poor/infertile soils require low seed are because crops are widely spread compared to fertile soils.
vi) Growth characteristics of the crop: tall/tillering/indeterminate varieties require low seed rate compared to short/less tillering/determinate varieties
vii) Spacing: High sped rate is required in closer spacing than wider spacing
viii) Seed purity: Impure seed/containing chaff and foreign materials will lead to high seed rate compared to pure seed
ix) Pure/mixed stand
High seed rate for pure stand and low seed rate for mixed stand.
1/2 mk for stated factor = 1/2 x 7 = 31/2 mk
1/2 mk for explanation given = 1/2 x 7 = 31/2 mk
