CHAPTER 4
INFORMATION SYSTEMS PLANNING
Planning is primary management function which is a process of setting objectives for the future and lay out the action necessary to reach those objectives. A plan is a specific statement of objectives and gives the links by which a firm aims to achieve this.
Many plans that are drawn up by managers are either financial, personnel or production in nature. Planning can be strategic, tactical or operational.
Planning and controlling are related:-
1. Strategic Planning;
The purpose of this planning is to develop long-term objectives for the entire organization and for its major business units and more so to specify the general strategies for acquisition of resources needed to accomplish these objectives.
It includes the following:-
a) The establishment of broad long-term objectives for an enterprise.
b) Accessing the company’s current position relative to these objectives and in particular considering the threats and opportunities provided by the environment.
c) Considering alternative strategies for reaching the objectives in the competitive business environment.
d) Outlining the organizational structure and the total resources needed to implement the plan.
e) The planning for the implementation process.
The MIS strategic plan includes:-
ii) Statement of the objectives to be achieved.
iii) Projection of the future MIS environment.
iv) Projection of the future user environment.
v) Projection of the future industry environment.
vi) Definition and evaluation of strategic alternatives in relation to the organization strategic plan and the selection of the preferred alternative.
vii) The establishment of the required infrastructure plans and the personnel
requirements.
viii) The plan for the organizational structure of the MIS department.
ix) A detailed financial plan indicating the benefit and the cost to be incurred.
x) The plan for the implementation of the strategic plan.
2. Tactical and Operational Planning
This involves the prioritizing and laying out in detail the acquisition of hardware, software and telecommunication equipment. This planning is expressed in terms of the budgets which specify the resources committed to a given plan for a given project or time period. Budgets can be fixed or flexible, and an organization can use spreadsheet as the main budgeting tool.
Planning can be TOP-DOWNS whereby the process starts with the senior management. This may ignore what is going on at the bottom.
It can also be BOTTOM-UP where the junior staffs are encouraged to come up with their own departmental plans. However this may not align well with the strategic objectives of the organization.
The role that information systems play in the planning process is to be used in developing plans such as forecasting and identifying and comparing alternative causes of action. There is need therefore to make use of financial ratios to justify our various plans.
FINANCIAL RATIOS:
Information System Project Manager Technique
Planned financial projections produce ratios that indicate the performance of the business unit. They include;-
1. Payback method
2. Net present Value (NPV)
3. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
4. Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) or Return on Investment (R.O.N)
5. Cost benefit ratio
6. Profitability Index etc.
These are used to justify new systems, explain old systems and to develop quantitative support for the adoption of various alternatives. The major limitation is to assume that all the relevant alternatives have been examined and that all cost and benefits are known.
However in quantifying these in monetary terms, there are needed to classify whether the cost and benefits are tangible or intangible.
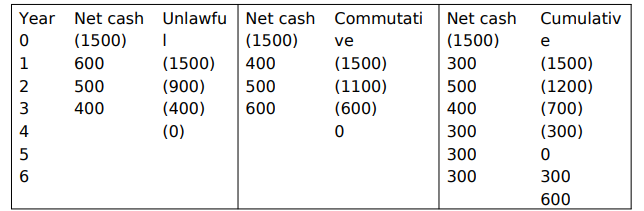
a) Pay Back Method
These measures the time required to pay back the initial investment of a project.
Calculate the payback period for the following project.
![]()
Advantages
1. It’s simple to calculate and understand.
2. It uses the project cash flow rather than the accounting profit and hence its more objectively used.
3. It favors quick return projects which may produce faster growth for the company and enhance liquidity.
4. Tends to minimize the risks to a company related to time.
Disadvantages
1. It ignores the time value of money.
2. It ignores the cash flows after the payback period.
3. It ignores the profitability of project or system in the long run.
Net Present Value (N.P.V)
This is the amount of money an investment is worth taking into account its cost, earnings and time value of money.
The present value is the value in the current currency of a stream of payments to be received in the future. From the following formula

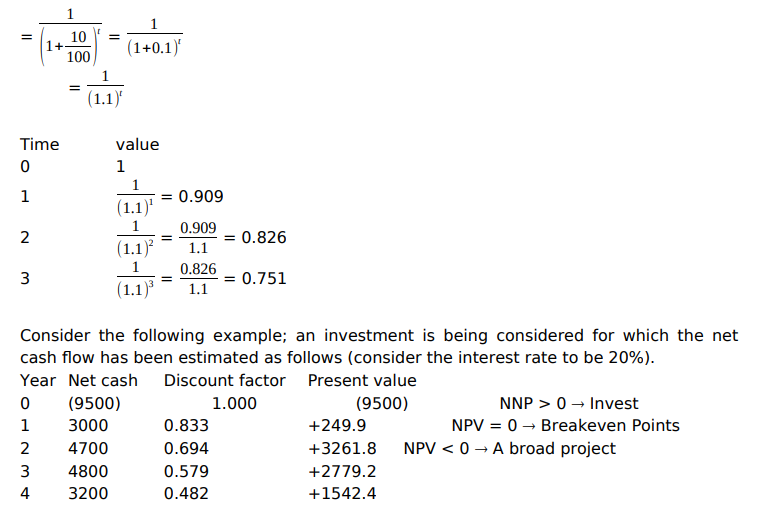
Advantages of N.P.V
1. It takes into account the time value of money
2. One can easily use the spreadsheet to calculate it.
3. It considers the whole project life and calculate the returns at expected times.
Advantages
1. It involves estimates of future returns and is thus subject to error.
2. It doesn’t set possible targets against which evaluations can be made.
Internal Rate of Return
This is the variation of NPV that takes into account the time values of money. This is the rate of Return on profit that on investment is expected to earn. It’s the discount on interest rate that will equate the present value of the project into the future cash flows to the initial cost of the project. This value can be determined graphically or by interpolation.
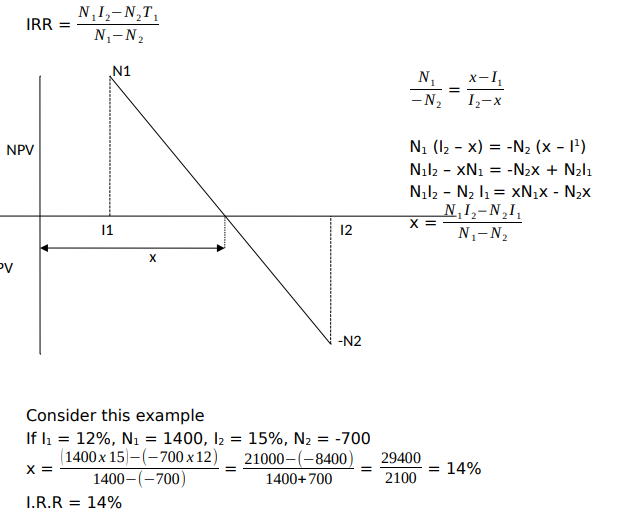

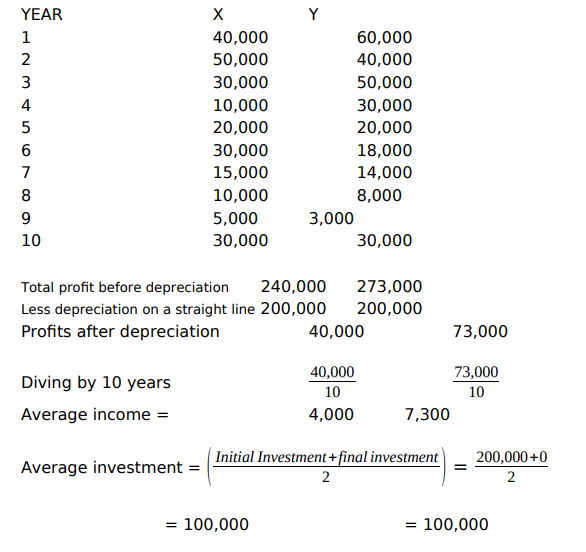
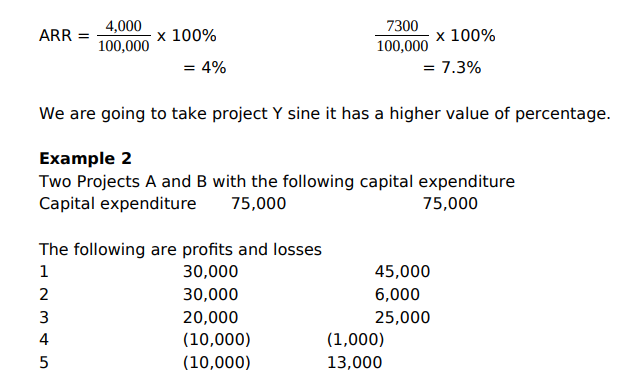
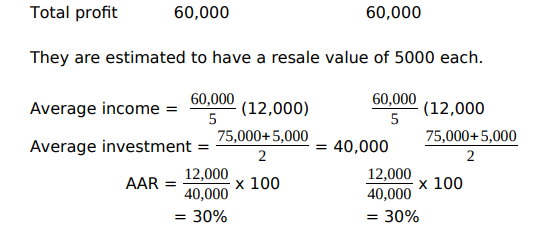
Advantages of ROI/AAR
1. Uses available accounting information
2. It’s understood by managers
Disadvantages
1. It deals with accounting profits rather than the cash flow.
2. It doesn’t take into account the time value of money.
3. For different types of deprecation method doesn’t work well e.g. it only works well in straight-line method because the depreciation is constant. Steps involved in Information system Planning:-
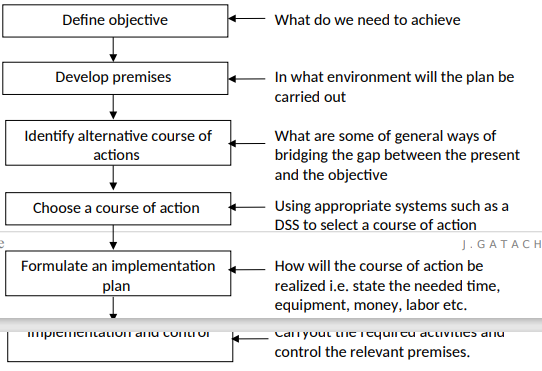
Elements of Good Planning
1. VISION: This is a view of what top management has for organization. It create model that represent what organization would look like and what it will achieve in future environment which it will operate.
2. MISSION: This is the bottom line purpose of organization i.e. what is why it exists.
3. GOALS: These are broad statement of the end results that organization intend to achieve in fulfilling its mission.
4. OBJECTIVE: These are specific and tangible measures of result that organization want to achieve.
5. STRATEGY: A statement on how to reach the vision and achieve the objectives taking care of environment available resources and constraints.
6. CONSENSUS AND COMMITMENT: The leadership must be dedicated to achieving the vision and mission.
Information system planning in a Business The next major step in planning process is the assessment of the organization from an information management perspective.
During these steps the major processes that are necessary to accomplish the mission successfully are needed to support the process. This can be done by the following:-
a) Development or validating business system plan
Business system planning (BSP) methodology was introduced by IBM in 1970s as a way to incorporate information system strategy into business strategy. This methodology has other different name such as Information System Planning (ISP), Information Requirement Studies (IRS).
Functions manager counter praising process of re-engineering will find that performing or updating a business or information system planning studies, provides valuable time saving information that will enhance process re-engineering. The objectives of business system planning are:-
1. To determine information system priorities
2. Plan long level information system based on business process.
3. Manage system resources to support business objective.
4. Assign system resources to high-return projects.
Implementation and control Carryout the required activities and control the relevant premises. MIS
5. Improve relationship between function and technique organization units.
Once the study has been conducted the following would be the benefit:-
1. Coordination of processes re-engineering plans.
2. Assurances that the date and application will be aligned with function process requirements.
3. It will be easier for the plan and resources to synchronize with implementation strategy.
The following task are performed in business system planning
i. Review /validate current business planning system architecture.
ii. Develop the business process or the organization maps.
iii. Prepare or validate information system architecture.
iv. Review and approve business system plan.
v. Identity major business process.
Review /validate current business plan
Many organizations has current business plan that should be reviewed and validated the important that this review take organization model into account. Identify major business process
Major process can be identified and defined from an enterprise wide perspective independent of process re engineering effort.
The rules of identifying process include;-
i) Processes are independent of organization structures.
ii) Processes are significant to the nature and purpose of enterprise.
iii) The naming convention for process are verb-name for e.g. Design-project, provide spare parts.
iv) Process redundancy is to be avoided.
Develop process plan/organization matrix
This is a chart or map that show the relationship between the business process sand various organization department.
![]()
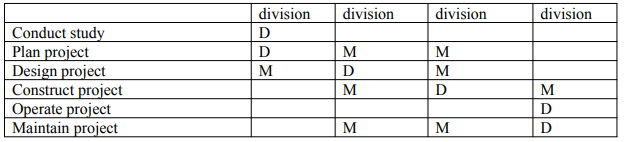
D – Decision making primary responsibility
M – Major involvements.
Prepare and validate architecture
This area involves preparation and validation of the following:-
i) Process and data entity
ii) Process /automated information system.
iii) The business strategy / process
iv) Business strategy /organization
v) Business strategy /data item.
Its importance to conduct the above so as;-
1. To understand how data is showed throughout the organization and between business processes.
2. To illustrate the process and information system interdependence.
3. To determine the relative important of data with respect to business strategy.
4. To identity organization responsibility and ensure optimum participation in the business process reengineering projects.
5. Understanding the legacy and migration system impact in process re-engineering effort.
Prepare review and approve business systems plan
A good plan report should have the following setting;
1. Executive summary
2. Background section explaining objectives of studies and the methods used.
3. Studies perceptive highlighting the objective and expressed in strategic plans
4. Findings with respect to IS needs, requirements and opportunities.
5. Potential constraints based on the information system infrastructure that may hinder process reengineering effort and suggested means of dealing with these constraints.
6. Information system strategy and recommendation based on implication of strategic plan.
7. Appendices of details architecture including application protocols and data structure.
The business system plan should be reviewed and approved by all functional managers in organization, once approved the plan is then passed into the next step that is process re-engineering.
