CHAPTER 6
INFORMATION SYSTEMS ACQUISITION
Evaluating MIS Applications
The I.T. investment management process begins with the project selection process. Projects being proposed for funding are put through a screening process to:-
1. Eliminate proposals that fail to pass minimal acceptance criteria.
2. Ensure that projects are being reviewed at the most appropriate organizational level. Proposals that pass this screening process have their cost, benefits and risks analyzed in-depth. Once this is accomplished, all fo the projects are compared against some common decision criteria and ranked based on their relative benefits, cost and risks. This process is appropriate in most projects and is the essence of I.T. portfolio analysis. The organization should have a process that outlines how to introduce projects for funding and how these projects would be severed for relevancy to the business sand its objective. Specify the organization should:-
i. Identity initial requirements that projects must meet before funding can be released.
ii. Explain how the screening would be conducted.
iii. Establish roles and responsibilities for conducting the screening.
The screening criteria serves the following functions;-
1. Identity whether the project meets its initial acceptance requirements.
2. Ensure that the project is being reviewed at the most appropriate organizational
level.
3. Identify what level of management scrutiny is appropriate given the projects type, size and risks. On the basis of this screening process projects will either move or for more in-depth
analysis or will be rejected.
Analyzing And Ranking MIS Applications; Based On The Benefits, Cost And Risks Criteria.
Each application should have a business case developed that provides the management justification for the system. The business case should identify the organizational needs that the application is meeting or proposes to meet, provide information on the benefits,
costs, and risks of the application and establish proposed project development time frame and delivery schedule.
The organization should have an audit function that is responsible for verifying and validating the various analyses including cost/benefit analysis and risk assessment. This
validation should include;-
1. Accessing all the alternatives that were analyzed and determining whether others should have been included.
2. Reviewing cost and benefit estimates to ensure that they are accurate and
realistic.
3. Evaluating risks identified and determine whether others may be applicable.
4. Evaluating the sensitivity analysis that was conducted.
The organization should have the management information system that collects all the applications information. Their mechanism for collecting and maintaining applications
will also be essential during the control and evaluation phase in order to:-
1. Help assess whether projects are still aligned with mission needs and organizational objectives.
2. Determine whether applications are meeting planned performance goals etc.
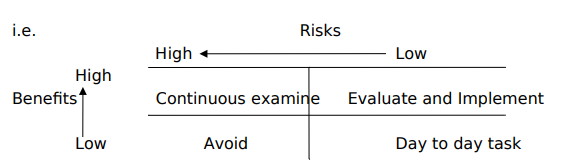
Decision should rarely be made based on only one factor such as the project cost. Using an assortment of decision criteria an organization can compare a number of factors. The organization may assign weight for each category inorder to help prioritize a
particular application. An important point for an organization in developing such a scoring model or decision
support tool is to define the scoring elements such as:-
1. Very poor
2. Poor
3. Average
4. Good
5. Excellent
The decision making process should help address difficulties associated with using different units of measure for analyzing different kinds of applications. No matter how vigorous or structured the organization’s decision making process is, the decision to take the particular application lies with the management. If managers select applications that score low when compared to other projects e.g. high risk, high return profits, the justification for this should be documented and the applications progress constantly be
monitored.
Cultural dimension of IS development
When designing and understanding I.S the following check list should be considered:-
1. The environment in which the organization must function.
2. The structure of the organization, areas of specialization, standard operating procedures (SOPs), cultural and politics of the organization.
3. The type of organization type of ownership, nature and style of leadership.
4. The extent of support and understanding of the top management.
5. The level in the organization at which the system resides.
6. Principle interests groups affected by the system, decision and business processes
that the information system is designed to assist.
7. Sentiments and altitudes towards workers in the organization who will be using the information system, history of the organization e.g. past investment in I.T., existing skills, important progress and human resource.
To design the above the developer must understand the hand and soft properties of the organization.
Hard Properties:
Characteristics
1. The problem can easily be defined.
2. The objective and data can be objectively addressed.
3. The problem is self-contained.
4. The information requirements are known.
5. The solution to a problem can be recognized.
6. Standard solution techniques are often available.
Soft Properties:
Characteristics
1. Often difficult to define the problem.
2. This involves taste, values, opinions and judgments.
3. The problem is fuzzy-edged (not clearly defined) i.e. we aren’t so sure of what the solution will look like.
4. Its people oriented.
5. It requires soft system methodology approach (SSM).
Soft system methodology (SSM)
This is a user driver methodology developed by check-land. It’s a way of analyzing unstructured and poorly defined problems in the real world. It recognizes that change is constant. It has the following assumptions:-
1. Its intended as an aid for managing complex organizational issues in a participative process. Its purpose is to enhance understanding of human situations that are perceived as problematic.
2. In organization there are many divergent perspectives on issues to be dealt with and each has to be considered.
SSM involves a process of enquiring which eventually leads to an action. It has seven steps.
1. The problem or situation must first be entered into.
2. The prevalent culture and power relations are used to express the problematic
expression.
3. This findings are represented in a set of predefined solutions i.e. systems that are thought to be relevant to the particular problem.
4. Conceptual models are built where the verbal concepts previously defined are logically structured.
5. The model and redelity are compared.
6. Possible changes to the real world are considered. One of the framework that is used in SSM is the CATWOE definition which attempts to give root definitions of the problem.
7. It deals with who is doing what, for whom they are answerable, what assumptions are made and in what environment this is happening.
C – Customer – The who or people who benefit or suffer from the system.
A – Action – Who carries out the transformation process
T – Transformation – What is the conversion of input into output.
W – Welt a schaning – Assumption behind the root definition.
O – Owner – Who can stop the transformation.
E – Environment – What are to fixed elements outside the organization or system.
Methods for acquiring MIS applications
1. SDLC: This is a methodology for developing an information system that partitions the system development process into formal stages that must be completed sequentially with a very formal division of labor between the user and the specialists.
The characteristics of this method are;
i. The development is in stage.
ii. Its advantages for large organizational systems e.g. T.P.S.
iii. Supports project planning and control organization of team development effort and the production of a maintainable system.
iv. Relatively inflexible with respect to the user requirements that change
during the development cycle.
v. There is vigorous documentation.
vi. It can be costly and time consuming.
2. Prototyping: This is the provision of a model that is given to the users for them to clarify their requirements and gain a measure of confidence in the general approach. In some cases the prototype is upgraded through several iterations, thoroughly undergoing testing and documentation. In some cases the prototype may be thrown away once the user requirements have been captured.
Characteristics
1. Development by gradually modifying an initial prototype based on feedback from the users.
2. It’s a relatively fast development with early availability of the first model of the
system (the first version).
3. Its advantageous when user requirements are uncertain.
4. It works well for project that are limited in size and for systems that are being computerized for the first time. Typical application of this is the development of DSS.
5. Unless precautions are taken it may evolve into a quick and dirty system hampering maintenance.
3. Internal development via end-user computing;-
This is the development of I.S by end-user with little or no formal assistance from technical personnel.
Characteristics
i. It leads to increased user satisfaction and involvement.
ii. It reduces applications back-log (this is the queue of systems awaiting
implementation)
iii. It requires tools such as the fourth generation languages which are user friendly.
iv. It leads to improve requirements determination.
v. It requires the involvement of information centers /helpdesk /hotlines.
Information Centres /HELP DESK
This concept of an organization centre was developed in Canada in 1974 by IBM to support end-user. Its part and parcel of the corporate MIS function and its usually manned by technical people with extensive knowledge of the business. It has the following functions.
a) Assisting the end-users in evaluating, selecting, installing and maintaining
hardware and software i.e. ‘they help you choose the best’.
b) Provide assistance to end-users in accessing the data resource
c) It provides guidelines for system development and provides also modalities for preparing a prototype using a 4th Generation language.
d) It supports all the installed software’s within the organization.
e) Acts as a nit to provide standards of end-user systems.
f) It also provides a hotline or helpdesk in giving assistance to users. If thus help keeping track for the request and offer trouble shooting techniques.
g) Assist in setting standard and supports internal auditors in auditing the systems.
h) It trains end-users in operating systems that are to be introduced in the
organization.
4. Off-the-shelf package
This is actually the purchase of a license to use the package. At times these packages
may have to be tuned to fit the needs of the user company. When purchasing an off the-shelf package, requests for proposals are sent to potential suppliers. This document outlines the requirements of the organization and asks questions as to how the vendor systems may satisfy them. The selection is based on the characteristics of the software package and the requirements that the user organization wants.
Characteristics
i. They are more reliable and have better documentation than internally produced systems.
ii. They often need to adjust work within the organization to fit the needs of the package.
iii. It may cost the company to forego competitive advantages, if this was done internally.
iv. It satisfies most user requirements due to the fact that it has been developed by experts.
v. Due to its mass production its relatively cheaper to buyer and that the implementation is quick.
5. Outsourcing
This is the hiring of external firms known as the software houses or system integrators to develop and install systems that can easily be executed. They also perform other services i.e. developing strategic plans to carryout organizational functions. In the rather case we refer to this as facility management.
Outsourcing is necessary and appropriate in the following circumstances:-
1. When you want to reduce development cost.
2. Relief the firm from the burden of developing the system.
3. When the firms existing information systems capabilities are limited, ineffective or
technical inferior.
4. When the company needs to off-load some of pending workloads from the I.S.
department.
Problems of outsourcing
1. The firm may lose control over the I.S function i.e. No control over the type of software or hardware being used.
2. There is total vendor dependency i.e. the firm may have to pay whatever the
vendor charges and accept whatever he does.
3. If the firm lacks expertise to negotiate a sound contractor, this dependency may eventually lead to loose of control over the technical direction.
4. Trade secrets may leak to outsiders and the company may lose competitive advantage. Solutions to outsourcing problems
1. Organizations should manage the outsources as they would manage this over\ information systems departments by setting priorities and targets to be met by the outsourced company.
2. Establishment of criteria to evaluate the outsourcing vendor.
3. Designing outsourcing contracts carefully so that outsourcing functions can be
adjusted if the nature of the business changes.
4. A climate of trust should exist between both parties i.e. they should be in partnership.
Agents involved in MIS projects
Development of information systems will involve the following group:
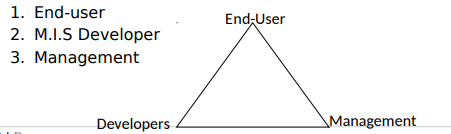
END-USERS:- It’s the function of the end-user to prepare their information requirement and to ascertain the working environment of the system developed by making sure that the system interfaces are proper.
M.I.S DEVELOPERS: – Their function is to implement system that satisfy user requirement as well as the objectives of the management by establishing that they have adequate resources, develop a quality system and meet the development constraints.
MANAGEMENT: – It’s the function of the management to control and allocate resources that go in the development of the system and to approve the various stages in the process.
