Nature and Purposes of Budgets
A budget is a plan of action relating to a defined period of time expressed in financial and quantitative terms.
Budgetary control is the process by which financial control is exercised within an organization where budgets are used to set priorities and implemented.
Objectives of Budgets and Budgetary Controls.
1. Coordination
There is need for integration of all activities of the organization towards a common objective. This is only possible when the effort of one department’s budget is related to the budget of another department.
2. Communication
The budget itself may also act as a tool of communication of what is expected of the departments and managers.
3. Control
This is the process for comparing actual results with the budgeted results and reporting upon variances. Budgets set a control gauge, which assists to accomplish the plans set within agreed expenditure limits.
4. Motivation
Budgets set targets, which have to be achieved.
Where budgetary targets are tightly set, some individuals will be positively motivated towards achieving them. Involvement of managers in the preparation of budgets motivates them towards achieving the goals they have set themselves.
5. Provide a framework for assigning responsibilities
Budgets prepared have to be achieved and responsibility for their achievement will be assigned to a manager.
Each manager manages those items directly under his or her control.
6. Planning
It is by Budgetary Planning that long-term plans are put into action. Planning involves determination of objectives to be attained at a future predetermined time. When monetary values are attached to plans they become budgets.
7.Ensure achievement of company objectives
- Objectives are quantified in budgets.
- Objectives have targets which will be achieved within the time scale of the budgets
8.Measure of efficiency
- By comparing actual with budgets efficiency will be measured .
- In efficient activities will be identified and the necessary action taken to improve on the inefficiency
PREPARATION OF BUDGETS
In preparation of budgets, the management should:
Step 1:Set Plans
It involves establishment of objectives, formulation, evaluation of policies and strategies to achieve given plans
Step 2:Set budget period
This is the period in which the budget is prepared and used.
Step 3:Prepare Budget Manual
This is a document of instructions, responsibilities governing persons preparing budgets and the procedures, forms and records relating to the preparation and use of
budgetary data. It’s a guide on budget preparation process.
Contents of a budget manual
- Objectives of budgetary planning and control
- Objectives of various stages of budgetary processes.
- Organization chart showing how the organization is managed.
- List of individuals holding budget responsibilities.
- Types of their budgets and their interrelationship.
- Budget timetable and budget committee.
Step 4:Budget Committee
This is the coordinating body in preparation and administration of budgets.
Functions of budget committee include:
- Coordination of budget preparation.
- Issue of budget preparation timetable.
- Allocation of responsibility in budget preparation.
- Provision of information to assist in budget preparation.
- Communication of final budgets to appropriate managers.
- Comparison of actual with budgets and investigation of variances
Step 5:Appointment of budget officer
This is the person who assists the budget committee in the budgeting process .
Step 6:Determination of principal budget factor.
This is a factor or a resource that limits the activities of the organization e.g. cash availability
Step 7: Negotiation of budgets with superiors
Once a manager has prepared his draft budget he should submit it to his superior for approval and harmonization.
Step 8: Final acceptance of the budget
When all the budgets are in harmony with one another they are summarized into a master budget consisting of a budgeted income statement, budgeted statement of financial position and cash budget.
FUNCTIONAL BUDGETS
- Functional budgets are prepared for an individual function. For each operation in the organization a budget is prepared Sales budget, purchases budget, production budget, cash budget etc. are examples of functional budget.
- This budget are consolidated to arrive at a master budget
Problems of functional Budgets
- As the functional manager prepares the functional budget, the target may not be in line with the strategic objectives or may conflict with the organizational objectives or inter departmental objectives.
- Functional budgets are based on forecasts. There are many external as well as well as internal environmental factors (such as a change in demand for a product,)that affect the functional budgets. If these factors behave differently than predicted, this may render the budgetary system ineffective
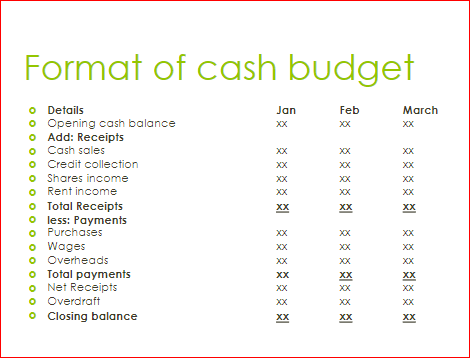
CASH BUDGET
It shows the expected receipts and payment of money for a given period.
A cash budget is a detailed budget of estimated cash inflows and outflows incorporating both revenue and capital items.
A cash budget is useful because :
- Shows the expected surplus in the short run and long run so that the amounts can be invested in a profitable venture
- Shows the expected deficit in the short run and long run so that the necessary arrangement can be made to finance the deficit
Functions of cash budget
- It ensures that cash is available for revenue expenditure
- Helps to indicate where, when and how cash will be needed and whether this permanent or temporarily.
- Helps to preserve liquidity throughout the year
- It reveals surplus cash for investment
- It guides management on financial capital expenditure both internally and externally
2.Sales Budget
This is a budget of forecasted demand in sales quantities and value analyzed as per product being produced and sold. Sales forecasting is complex and involves the consideration of a number of factors.
- Production capacity
- Current demand
- Level of competition
- Sales trend
3.Production Budget
It summarizes the production requirements for the forthcoming period to match the forecasted sales above. Factors to consider are:
- Production capacity.
- Budgeted sales.
- Availability of resources.
- Finished good stock level
Material Usage Budget
It is a budget of material requirements during production. It is stated in quantities for each type of material used. Factors to consider include:
- Material requirement per unit.
- Units to be produced.
- Availability of raw materials
5.Material Purchases Budget
It is prepared to determine the quantities of materials that will be purchased during the period to meet all production requirements. It shows the quantities of each material and costs to be incurred on quantities purchased.
Factors to be considered:
- Usage in production.
- Availability of materials .
- Stocks to be maintained .
- Types of raw materials.
6.Labour Budget
This is a budget of labour requirements during production. Factors to be considered include:
- Availability of labour.
- Units to be produced .
- Labour requirement per unit.
NON- PRODUCTION BUDGETs
7.Selling and Distribution Cost Budget:
It is the forecast of all costs incurred in selling and distributing the company’s product during the budget period. It is closely concerned with the sales budget in that it is
mainly based on the volume of sales projected for the period. Expenses included are selling office costs, salesmen salaries and commission, advertising expenses, etc.
8.Administration Costs Budget:
It represents the costs of all administration expenses.
Management, Secretarial, Accounting and Administration costs, which cannot be directly related to the production, are included here
9.Research and Development Cost Budget:
Research cost is the cost of original investigation undertaken in order to gain new scientific or technical knowledge and directed towards a specific practical aim objective.
Development cost is the cost of using scientific or technical knowledge in order to produce new or substantially improved materials, devices, products, processes systems or services prior to the commencement of commercial production.
10.Capital Expenditure Budget:
It represents the expenditure on all fixed assets during the budget period which increases the production capacity, efficiency, lifespan or economy of existing fixed assets are also incorporated
MASTER BUDGET
Master budget has two major sections which are the operational/functional budget and the financial statements.
They have following components:
a) Functional Budgets
b) Income Statement
c) Balance Sheet.
BENEFITS OF BUDGETING
- It is the major formal way in which the organizational objectives are translated into specific plans, tasks and objectives related to individual management and supervisors.
- It is an important medium of communication for organizational plan, objectives and of the progress towards meeting those objectives.
- The development of budgets helps to achieve co-ordination between the various departments and functions of the organization.
- The involvement of all levels of management with setting budgets help to promote coalition of interest and to increase motivation
