 UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2013/2014
UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2013/2014
ORDINARY EXAMINATION FOR THE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
BIT 1309 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT FOR IT
DATE: AUGUST, 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS: Answer Question ONE and any other TWO
QUESTION ONE
a) Describe any Six users of financial statements. Within your description, comment on
the needs of each user. (12 marks)
b) Discuss the limitations of financial accounting (6 marks)
c) Computer technology has greatly improved the way financial information is prepared
and saved. This has also improved the internal control systems all the same,
information technology can potentially weaken the control systems. Explore the
positive and negative impacts of computers on the internal control systems of an
organization. (8 Marks)
d) Central machine tools purchased an industrial lathe to be used in its manufacturing
process. The purchase price was Kshs 6,200,000. The company incurred kshs
1,000,000 to transport the machine to its plant location plus Kshs. 300,000 shipping
insurance. In addition the machine had to be installed and mounted on a special
platform at a cost of Kshs. 1,200,000. After installation, several trial runs were made
to ensure proper operation. The cost of these trials including waste materials was
Kshs 600,000. At what amount should the Company capitalize the lathe machine?
(4 marks)
QUESTION TWO
(a) Mama Gatimu opened a general grocers shop on 1 January 2014. She had shs.112,000
cash out of which she deposited shs.100,800 into her bank account. She completed the
following transactions during the month of January.
January 3: Purchased goods from Kirika for shs.16,800 on credit
4: Paid half-year’s rent by cheque shs.67,200
5: Cash sales for week amounted to shs.82,200
Paid cash into bank shs.56,000
8: Purchased goods from P. Pundo on credit for shs.12,880
Purchased goods on credit from K. Kiige for shs.8,456
10: paid Kirika’s account by cheque in full settlement shs.15,120
12: Cash sales for the week amounted to shs.81,984
Paid cash into bank shs.67,200
Cash drawings by Mama Gatimu amounted to shs.11,200
18: Paid K. Kiige by cheque shs.8,456. Paid P. Pundo by cheque on account
shs.5,600
19: Made sales to Mukaria on credit shs.3,360
Cash sales for the week amounted to sshs.54,175
Paid cash into bank shs.56,000
22: Purchased goods from P. Pundo for shs.19,745 on credit
23: Bought a cash register from BuruBuru Printers on credit for shs.19,265
24: Mukaria settled his credit balance by cheque less 10% discount
30: Cash sales for the week amounted to shs.64,100
Drawings by Mama Garimu by cheque amounted to shs.2,240
Paid cash into bank shs.78,000
Required:
(i) A three-column cash book to record the above transactions. (13 marks)
b) The balancing of the trial balance is not an absolute proof of accuracy in the books of
accounts. Give examples of accounting errors that the trial balance may not help to
disclose. (7 marks)
QUESTION THREE
The following trial balance is extracted from the books of Earnest Mutembei, a sole
trader, at the close of business on 31 December 2013:
Shs Shs
Capital 16,700,000
Purchases 4,500,000
Sales 9,850,000
Purchase returns 27,000
Sales returns 80,000
Discount allowed 90,000
Discount received 68,000
Wages and salaries 3,051,000
Rates 240,000
Insurance 175,000
General expenses 405,000
Trade debtors 1,840,000
Trade creditors 1,605,000
Bank balance 381,500
Cash in hand 35,000
Stock in trade 1 January 2013 605,000
Land and building (cost) 8,500,000
Plant and equipment (cost) 6,100,000
Motor vehicle (cost) 3,000,000
Drawings 835,000
Loan from Small- Finance Co. 1,000,000
Loan interest 150,000
Bad debts ___25,500 _________
29,631,500 29,631,500
The following additional information is provided:
1. Stock at 31 December 2013 amounted to Shs 741,800.
2. Rates paid in advance on 31 December 2013 amounted to Shs 30,000.
3. Wages and salaries owing on 31 December 2013 were as 150,000.
4. Earnest Mutembei took goods worth Shs 200,000 for personal use.
5. The loan from small – Business Finance Co. attracted interest at 20% per annum.
The interest for the last three months of the year was not paid by 31 December 2013
6. Depreciation is to be provided on straight line basis as follows:
Plant and equipment – 25%
Motor vehicles – 20%
Assume that the above assets were acquired at the beginning of the financial year.
Required
a) Income Statement for the year ended 31 December 2013. (10 Marks)
b) Statement of Financial Position as at 31 December 2013. (10 Marks)
QUESTION FOUR
(a) (i) Define the term “depreciation” (2 marks)
(ii) Explain any two factors considered in allocation of depreciation (4 marks)
Jabali established his Hardware business and started trading on 1 January 2011. His
purchases and disposal of fixed assets over a period of three years Subsequent to
establishing his business were as follows:
Asset Date of purchase Cost (Sh) Date of Disposal Proceeds of Disposal
(Sh)
MSIE 1 1 January 2011 2,800,000
MSIE 2 1 January 2011 1,400,000 1 January 2013 504,000
MSIE 3 1 January 2013 3,920,000
Required:
Prepare the following as they would appear in the books of Jabali for the years ended 31
December 2011, 2012 and 2013 assuming that the firm charges depreciation at 20% per
annum calculated on the straight line basis:
a) Fixed assets account. (at cost) (4 Marks)
b) Provision for depreciation account (5 Marks)
c) Disposal of fixed assets account. (5 Marks)
QUESTION FIVE
a) Discuss the main differences between income and expenditure account and receipts
and payments accounts. (8 Marks)
b) Kenya-real wine manufacturers presented the trial balance below
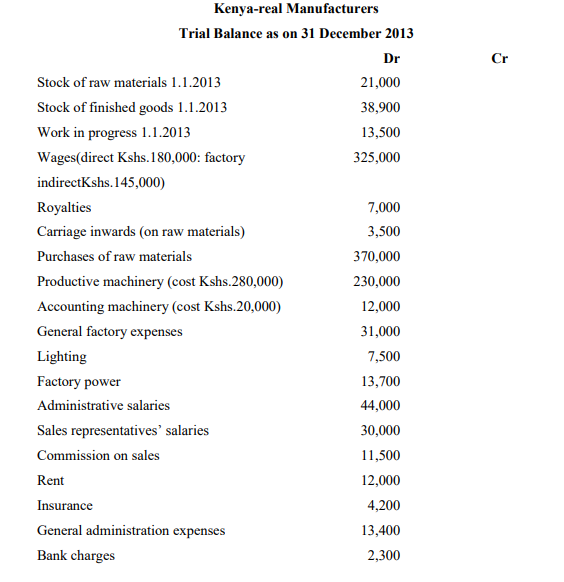
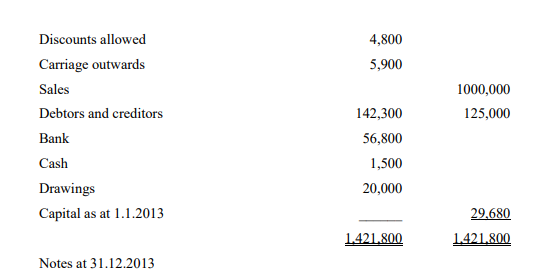
1. Stock of raw materials Kshs.24,000, stock of finished goods Kshs.40,000, work in
progress Kshs.15,000.
2. Lighting, and rent and insurance are to be apportioned: factory 5/6ths, administration
1/6th
.
3. Depreciation on productive and accounting machinery at 10 per cent per annum on
cost.
Required:
Prepare a manufacturing account and income statements for the year ended 31
December 2013. (12 Marks)
