
Exam focus
There will usually be one question in the exam that will test your ability to apply your knowledge to a non-audit engagement. The question could cover any area of the engagement process – acceptance, planning, procedures or .
- Audit-related services
Audit-related services are those services that professional accountants offer which are not statutory audits, although they are conceptually related and use similar skills.
An assurance engagement is an engagement in which a practitioner obtains sufficient appropriate in order to express a conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the intended users other than the responsible party about the outcome of the evaluation or measurement of a subject matter against criteria.
[International Framework for Assurance Engagements, 10]
Agreed upon procedures require the accountant to report on factual findings based upon the procedure agreed with the client and any appropriate third parties, hence no assurance (conclusion) is expressed. [International Framework for Assurance Engagements, 37]
Non-audit engagements include:
Assurance engagements
Review of interim financial statements Due diligence review
Examination of prospective financial information
Social and environmental information review.
Agreed upon procedures
Forensic audit: Fraud investigation
Forensic audit: Verifying an insurance claim Due diligence.
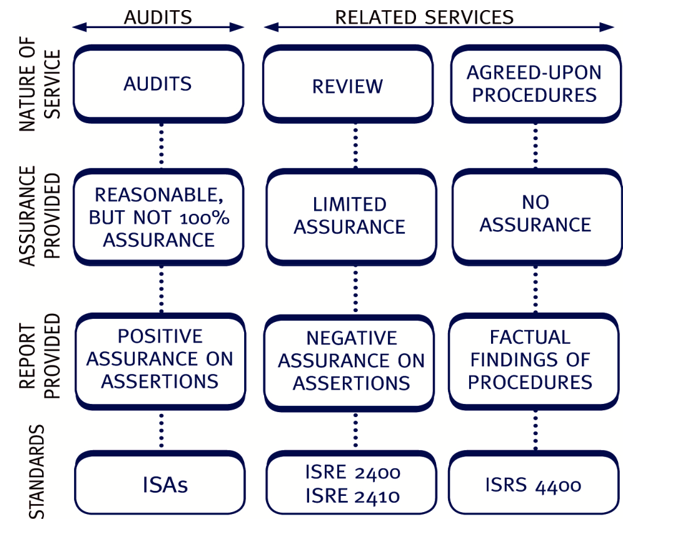
Differences between an audit and audit-related services
| Audit | Audit-related Services | |
| Level of assurance | Reasonable assurance | Either limited or no assurance |
| Scope of work | Established by the | Established in consultation with |
| auditor in accordance | client, in accordance with | |
| with auditing standards | assurance and related services | |
| standards | ||
| Wording of | Positive assurance | Negative or no assurance |
| assurance/other | ||
| reports | ||
| Required by | Law in many countries | Usually not required by law |
The elements of an assurance engagement
The five elements of an assurance engagement are:
A 3 party relationship between the practitioner (i.e. accountant), the responsible party (usually the directors) and the users of the report.
A subject matter (the items about which assurance is being sought, e.g. the financial statements).
Suitable criteria (the benchmarks against which the subject matter is being evaluated, e.g. compliance with International Financial Standards).
Sufficient appropriate . A written assurance report.
[International Framework for Assurance Engagements, 26]
The engagement process usually involves:
Agreeing the terms of the engagement in an engagement letter.
Deciding on a methodology for gathering to support a conclusion.
Agreeing on the type of report to be produced at the end of the engagement and expressing the opinion in the written report.
Professional standards for audit-related services
IAASB issues specific guidance for other services:
International Standards on Review Engagements (ISREs)
International Standards on Related Services (ISRSs)
International Standards on Assurance Engagements (ISAEs) Specific examples include:
ISRE 2400 (Revised) Engagements to Review Historical Financial Statements.
ISRE 2410 Review of Interim Financial Information Performed by the Independent Auditor of the Entity.
ISAE 3000 (Revised) Assurance Engagements Other than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Statements.
ISAE 3420 Assurance Engagements to Report on the Compilation
of Pro Forma Financial Information Included in a Prospectus.
ISRS 4400 Engagements to Perform Agreed-Upon Procedures Regarding Financial Information.
ISRS 4410 (Revised) Compilation Engagements.
Attestation and direct engagements
The framework also permits assurance engagements to be performed as either an attestation engagement or a direct engagement.
In an attestation engagement, the accountant’s conclusion relates to an assertion made by the party who is responsible for the subject matter. The accountant can either express a conclusion about this assertion, or can provide a conclusion about the subject matter.
In a direct engagement , the accountant expresses a conclusion on the subject matter based on identified criteria, regardless of whether the responsible party has made a written assertion on the subject matter. [ISAE 3000 (Revised), 2]
For example: a professional accountant may be engaged to report on a company’s internal financial controls.
| Attestation engagement | Direct engagement | |
| Management would first | The accountant would simply | |
| make a written assertion | report directly on the effectiveness | |
| about the effectiveness of | of the control structure in | |
| the company’s control | accordance with predetermined | |
| structure. | performance criteria. | |
| The accountant would then | ||
| give an opinion on | ||
| management’s assertion. | ||
Care must be taken to ensure that management’s assertion is clearly understandable and is not subjective. For example, an assertion that the control structure is ‘very effective’ would be unacceptable since this is a subjective opinion.
2 Levels of assurance
The Framework provides the overall guidance for carrying out assurance engagements such as audits and reviews. It permits only two types of assurance engagement to be performed: either a ‘reasonable assurance’ or a ‘limited assurance’ engagement.
Reasonable assurance
The objective of a reasonable assurance engagement is where the practitioner reduces engagement risk to an acceptably low level to conclude that the subject matter conforms in all material respects with identified suitable criteria.
The accountant expresses their conclusion in a positive form, giving an opinion on whether the subject matter is free from material misstatement, e.g. statutory audit.
Limited assurance
The objective of a limited assurance engagement is to obtain sufficient appropriate to be able to state whether anything has come to the practitioner’s attention that causes them to believe the subject matter is materially misstated.
In other words the subject matter ‘appears plausible’ in the circumstances.
The accountant expresses their conclusion in a negative form, stating that their procedures have not identified any material misstatement of the subject matter, e.g. a review engagement.
The procedures for a limited assurance engagement are therefore less comprehensive than for a reasonable assurance engagement.
No assurance (agreed upon procedures)
The objective of an agreed upon procedures engagement is to perform the procedures requested by the client and report the findings on a factual basis.
The client forms their own conclusion based on the results of the work.
The assurance report should include the following elements:
Title – clearly indicating the report is an independent assurance report. Addressee – identifies the intended user.
Identification and description of the subject matter including period of the information, name of the entity to which the subject matter relates.
Identification of the criteria.
Description of any significant, inherent limitations.
Restriction on the use of the report to specific users.
Statement of responsibilities of the responsible party and practitioner.
Statement that the engagement was performed in accordance with professional standards.
Summary of the work performed. Practitioner’s conclusion.
Date.
Name of the firm or practitioner and location.
[ISAE 3000 (Revised), 69]
Assurance conclusion Unmodified
The conclusion of an assurance report will be unmodified if nothing has come to the practitioner’s attention to suggest the subject matter has not been prepared in accordance with the criteria. [ISAE 3000 (Revised), 72]
If the practitioner wants to highlight a matter to the intended user, this can be done using an Emphasis of Matter paragraph or Other Matter paragraph in the same way as the auditor’s report. [ISAE 3000 (Revised), 73]
Modified
A modified conclusion will be expressed if:
There has been a scope limitation which means the practitioner has not obtained sufficient appropriate to be able to form a conclusion on the subject matter.
The subject matter is materially misstated.
The modifications are the same as for an auditor’s report:
Qualified – if the effects of the matter are not pervasive.
Adverse – if the subject matter is not prepared in accordance with the criteria and the effects are pervasive.
Disclaimer – if the practitioner has not been able to obtain sufficient appropriate to form a conclusion and the effect is pervasive.
[ISAE 3000 (Revised), 74]
Basis for conclusion
If the conclusion is modified, a basis for qualified/adverse/disclaimer of conclusion will be included to explain the circumstances causing the modification.
Illustration 1 – Example of an unmodified review report
A company which does not require a statutory audit may decide to have a review of its financial statements in order to provide some assurance over, and improve the credibility of, those financial statements.
ISRE 2400 Engagements to Review Historical Financial Statements states that:
‘The objective of a review of financial statements is to enable an auditor to state whether, on the basis of procedures that do not provide all the that would be required in an audit, anything has come to the auditor’s attention that causes the auditor to believe that the financial statements are not prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with an identified financial framework.’
The following report illustration is taken from [International Standard on Review Engagements 2400 (Revised) Engagements to Review Historical Financial Statements, Appendix 2, Illustration 1]
INDEPENDENT PRACTITIONER’S REVIEW REPORT TO … … …
Report on the Financial Statements
We have reviewed the accompanying financial statements of ABC Company, which comprise the statement of financial position as at December 31, 20X1, and the statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity and statement of cash flows for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory information.
Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation of these financial statements in accordance with International Financial Standards, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
Practitioner’s Responsibility
Our responsibility is to express a conclusion on the accompanying financial statements. We conducted our review in accordance with the International Standard on Review Engagements 2400 (Revised) Engagements to Review Historical Financial Statements. ISRE 2400 (Revised) requires us to conclude whether anything has come to our attention that causes us to believe that the financial statements, taken as a whole, are not prepared in all material respects in accordance with the applicable financial framework. This standard also requires us to comply with relevant ethical requirements.
A review of financial statements in accordance with ISRE 2400 (Revised) is a limited assurance engagement. The practitioner performs procedures primarily consisting of making inquiries of management and others within the entity, as appropriate, and applying analytical procedures, and evaluates the obtained.
The procedures performed in a review are substantially less than those performed in an audit conducted in accordance with International Standards on Auditing. Accordingly, we do not express an audit opinion on these financial statements.
Conclusion
Based on our review, nothing has come to our attention that causes us to believe that these financial statements do not present fairly, in all material respects, (or ‘do not give a true and fair view’) the financial position of ABC Company as at December 31, 20X1, and of its financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended, in accordance with International Financial Standards.
Signature
Date
Address
Illustration 2 – Example of a modified conclusion
Based on our review, except for the effects of the matter described in the Basis for Qualified Conclusion paragraph, nothing has come to our attention that causes us to believe that the financial statements of ABC Company are not prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with the Financial Framework.
[International Standard on Review Engagements 2400 (Revised) Engagements to Review Historical Financial Statements, Appendix 2, Illustration 2]
Provision of other assurance services
The auditor is in a strong position to carry out additional assurance services for their clients as they are already familiar with the company, its operations and systems and controls in operation at the.
In practice, the skills required to offer a comprehensive range of assurance services means that only the largest firms can offer a complete range of services to clients. Other firms still offer these services and many specialise in certain areas.
The implications of assurance services being provided by auditors are wide-ranging:
There will be further pressures on the audit firm to maintain its independence as the proportion of fees earned from non-audit work continues to grow and the self-review threat increases.
Practitioners specialising in a range of disciplines (e.g. IT systems, public sector specialists, etc.) will be needed in the firm as well as traditional financial auditors.
Many assurance services involve on risk (operational, financial, environmental, etc.). on such matters will increase the auditor’s exposure to professional liability claims.
Clients may be willing to pay for value-adding assurance services but correspondingly less willing to pay for the statutory audit where they perceive less value for their money putting pressure on audit fees.
4 summary

