
TOPIC
CONTROLLING
Specific Objectives
By the end of this sub-module unit, the trainee should be able to:
- explain the meaning of controlling function
- describe various systems and processes of control
Control is that function of management that involves monitoring, measurement and correcting performance of employees and other organizational resources according to the plan.
The aim of control is to develop a feedback and to establish any deviations from the plan so as to take corrective action.
IMPORTANCE OF CONTROL
- To ensure that resources are optimally utilized
- To ensure the organization objectives are met
- It limits accumulation of error as they are corrected on time
- Control has a positive physiological impact on the subordinate i.e. when employees know they are being monitored, they become
- Control facilitate the decision making process. The organization can verify the quality of various
- Enables the organization to adopt to environmental changes ie properly designed control system can help managers anticipate, monitor and respond to charging environmental
- It can be used as an evaluation tool
- It enables an organization achieve an optimal level of productivity
- It ensures tasks are completed within the given time
- It improves communication in the organization
- Facilitates decentralization of authority duties can be delegated when there is effective control
ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENT FOR A GOOD CONTROL SYSTEM/FEATURES
- Economy
A good control system should be affordable and worth the cost.
- Simplicity
It should be understandable and simple to administer. It should not be complicated.
- Suitability
It should be suitable to the nature and requirement of the activities being controlled.
- Promptness
It must detect and report deviations as soon as possible, thus should have time reporting of deviations.
- Flexibility
It should be able to adjust according to changes in need and circumstances.
- Suggestive of remedial action.
A good control system should disclose where failures are occurring, who is responsible and what should be done about them.
- Organizational pattern
It should conform to the basic structure of organization.(authority responsibility relationships of the organization)
- Objectivity
Control should be objective verifiable and specific it shouldn’t be influenced by personalities.
THE CONTROL PROCESS
The control process involves four major steps.
- Establishing the standards
The setting of standards against which actual performance/results are to be evaluated is essential in managerial control. The standards should be clearly and precisely stated, accurate acceptable and attainable as they serve as the criteria against which the results are evaluated. They should also be communicated effectively.
- Measurement of actual performance.
The actual performance is measured against the set standard. That is comparing the performance with the standards. The major question here is what have we achieved.
- Compare the performance
Deviation/gaps from the expected standards are established through comparing the results and the expected performance. Critical deviation should be identified and diagnose their causes and their impacts on the organization.
- Taking corrective
This implies taking a remedial action in order to bring back actual results in the line wit the standards. This may involve review of the plan/standards or putting in place steps to prevent deviations.
TYPES OF CONTROL BUDGETARY CONTROL
A budget is a plan expressed in numerical terms for a specific period of time in future. There are several types of budgets. They include:-
- Sales budget – this shows the volume of sales expected
- Production budgets – shows the quantity and quality of goods to produced
- Material budgets – quantity & quality of raw materials
- Labour budgets – labour requirements
- Capital expenditure budgets – capital investment in assets
- Overhead budget – shows the estimates of overhead costs expected
- Master budget –shows the expected expenditure for the whole
Budgetary control is therefore the process of defining desired performance through the preparation of budgets, measuring and comparing actual results with the corresponding budget data and taking appropriate actions to correct any deviations.
The use of budgets to coordinate, evaluate and control day to day operations in accordance with the specified goals in the budget.
The following are characteristics of budgetary control
- Establish a budget or target performance
- Record the actual performance
- Compare the actual performance with the budgeted
- Calculate the differences and analyze the reasons for them
- Act immediately, if necessary for corrective actions to be taken
- Follow up
ADVANTAGES OF BUDGETARY CONTROL
- Improved planning – expression of plans and policies in quantitative terms gives an overall view of operations and the relative importance of different
- Budgetary controls promote efficiency by eliminating wasteful
- Budget provides useful information for preparing quotations and filling
- Budgeting promotes cooperation and team spirit since all activities of various departments
- Budgets serve as a yardstick with which performance of employees can be evaluated and
- Helps management to delegate authority more freely over specified
- It helps in determination of capital requirements and controlling the cash position of the
- It indicates where executive action is necessary in order to secure desired performance.
DISADVANTAGES OF BUDGETARY CONTROL
- Budgeting is time consuming process and also
- Budgets may be used to hide efficiencies, as past precedents often become evidence for the present
- Rigid adherence to budgets discourages
- Budgets are estimates and can never be one hundred percent
- Budgets are only tools to efficient management and not a substitute for
NON-BUDGETARY CONTROLS
- BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS
Break-even analysis is frequently used in business and economics to analyze the implication of various pricing and production decisions. This is an important planning and control device as it depicts the relationship between revenue and the total costs (fixed
and variable). The break-even point is the point where the sales revenue is equal to the total costs.
Therefore below the break-even point losses occur and above it profits occur. The fixed and the variable costs are also indicated.
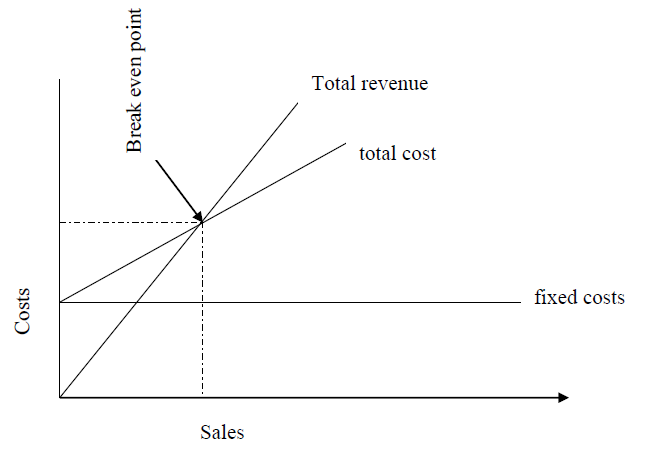
Sales Break-even chart
Although the break-even analysis is an important control tool, it ignores.
- Price changes
- Time gap between production and sales
- Plant size
- Technology
- PERSONAL OBSERVATION
Personal observation is a very important control tool as it supplements the other control devices such as budgets, audits reports etc. a manager who sits in his office and depend only on the scientific devices hardly realizes a thorough job.
Personal observation allows the manager a better involvement in all the operations of the organization.
However, personal observation suffers the following limitations,
- Manager has to be present thus it consumes a lot of
- There may be bias in the assessment of individual
- It requires to be supplemented by other devices personal observation cannot give all the
- Some critical areas in the organization cannot be effectively evaluated through observation.
- Hawthorne effect may affect the efficiency of personal
- AUDITING
Auditing can either be external or internal, external auditing is carried out by an external chattered accountant and is enforced by law in respect to all joint stock companies and cooperatives. It ensures that the stakeholders and any interested parties are safe guarded against any manipulations and malpractices of management. The external out for certifies that the profit and loss account and the balance sheet of the firm gives a true and fair picture of profit or loss and the picture of Financial state of affairs of the company respectively.
For internal audits and a member of staff is appointed specifically for this function in the organization to verify all financial transactions and records and also analyze the overall control system in the organization.
- REPORTS (Special)
Some complex operations in the organization require special analysis and reporting. This system of control can help supplement other control techniques especially where routine accounting and statistical reports falls to give adequate information.
SYMPTOMS OF INADEQUATE/ DEFECTIVE CONTROLS
- Unexplained declines in revenue and profits
- Degradation of services e.g. increase in customer complaints
- Employee dissatisfaction. This will be evidenced by increase in grievances
- Working capital shortage
- Idle facilities and personnel
- Disorganized operations
- Excessive costs
DISTINCION BETWEEN PLANNING AND CONTROL
Planning
- It’s deciding and present what is to be done
- Planning is a decision making activity
- Planning uses estimates
- Planning is less structured
Control
- Control rounds off the process of managing organizational resources by measuring results and checking them against previously agreed standards
- Controlling places more reliance on measured data from specific cases
- Control is a monitory process
- Controlling is highly
SIMILARITIES
- Both are concerned with identifying and quantifying standards of
- Measures used for planning purposes are frequently the same with one used for controlling purposes are frequently the same with one used for controlling purposes e.g. targets
- Both makes use of quantitative techniques
LEARNING RESOURSES
- Principles and practice of management by Saksena
- Management dynamics by Sagimo
- Management by Harold Koontz.
- Management principles by A Cole
EVALUATION
- Explain the purpose of control in business
- Describe the control
- “Planning is looking ahead while control is looking back” Discus
- Explain the advantages of budgetary controls in the
- Describe five forms of non-budgetary controls.
- Explain the limitations of personal observation as a control
- Explain the major requirements of an effective control system
