SYSTEM ACQUISITION METHODS
Acquiring Information Systems and Services
Information systems are a major corporate asset, with respect both to the benefits they provide and to their high costs. Therefore, organizations have to plan for the long term when acquiring information systems and services that will support business initiatives. Organization can adopt different approaches in acquisition of an information system. This includes: –
A. Purchasing
The Purchasing Information System can be used at a variety of levels in the decision-making process as an instrument for monitoring, controlling and planning your business operations. It is a flexible tool for collecting, aggregating and analyzing data from Purchasing The purchase order process consists of several compliance checkpoints and approval/input tasks to ensure timely PO processing. Here are the most common purchase order process steps:
a) PO creation: Purchase orders are created from approved purchase requisitions
b) Approval flow: POs are approved after budget and document verification
c) PO dispatch: Once approved, purchase orders are forwarded to the selected vendor
d)Binding contract: A legally binding contract is invoked once the vendor accepts the PO
e)Goods delivery: The vendor delivers goods, and the buyer does a quality check and notifies the sender in case of defects
f) Three-Way matching: Buyer performs three-way matching (with purchase request, PO, and invoice)
g) PO closure: After PO matching, if there are no discrepancies, purchase orders are closed
Purchase order process flow
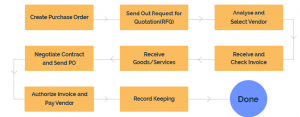
The purchase order process flow is the lifecycle of a purchase order from order creation to closure. A predefined purchase order process flow allows the purchasing team to process a PO without missing any steps, and follow it up easily to avoid delays. This purchase order process flow depicts the action steps in PO processing as follows:
1. Create a purchase order
2. Send out multiple requests for quotation (RFQ)
3. Analyze and select vendor
4. Negotiate contract and send PO
5. Receive goods/services
6. Receive and check invoice (3-Way Matching)
7. Authorize invoice and pay vendor
8. Record keeping
9. Purchase order closure
B. Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the process of engaging a third-party individual or organization outside of your company, either locally or internationally, to handle certain business activities for you. It is a common business practice that allows companies of all sizes to grow as and when they need it, without major risk or investment.
IT outsourcing is the practice of hiring resources outside of an organization to handle certain information technology functions. Companies often outsource data storage because it is cheaper to contract a third party than to buy and maintain their own data storage devices and facilities.
The most commonly outsourced IT functions are:
i. Web development
ii. Hosting
iii. Software and application development
iv. Website/application maintenance or management
v. Technical support
vi. Database development and management
vii. Telecommunications
viii. Infrastructure
IT Outsourcing Examples
The individual or company that becomes your outsourcing partner can be located anywhere in the world one block away from your office or on another continent.
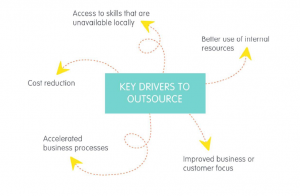
Why do companies outsource? Here are a few common reasons that can help explain the trend:
1. To reduce cost. More often than not, outsourcing means saving money. This is often due to lower labor costs, cheaper infrastructure, or an advantageous tax system in the outsourcing location.
2. To access skills that are unavailable locally. Resources that are scarce at home can sometimes be found in abundance elsewhere, meaning you can easily reach them through outsourcing.
3. To better use internal resources. By delegating some of your business processes to a third party, you’ll give your in-house employees the opportunity to focus on more meaningful tasks.
4. To accelerate business processes. When you stop wasting time on mundane, time-consuming processes, you’ll be able to move forward with your core offering a lot faster.
C. Development
Information Systems/Systems Development. Systems development is a process used in systems engineering, information systems, and software engineering for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system.
In the field of information systems where a systems specialist develops an information system to improve an existing system or develop a new system based on user requirements is called as Information Systems Development.
Participants in system Development
1. User Groups (Staffs)
The user plays the following roles in system development: –
i. They help to identify problem(s) to the current system.
ii. They define the requirements to be met by the new system.
iii. They are involved during testing and evaluation of the delivered system.
iv. They may provide necessary services required by the development team e.g. Accountants, Clerks, receptionists, librarians etc.
Benefits of user involvement
It has been found in numerous studies that effective involvement in system design produces the following benefits: –
i. Improved quality of the system arising from more accurate user requirements.
ii. Avoiding costly system features that the user did not want or cannot use.
iii. Improved levels of acceptance of the system.
iv. Greater understanding of the system by the user resulting in more effective use.
v. Increased participation in decision-making in the organization.
2. The Management
They Plays the following tasks: –
i. Provision of necessary resources i.e. finances, facilities, labour etc.
ii. Participating in identification process of the intended system.
iii. Participating in problem definition and definition of requirements
iv. Coordinating system development process examples CEO, Directors, Managers etc.
The Technical Staffs
Plays the following roles: –
i. Investigating and gathering facts on the existing system
ii. Analyzing facts collected to understand the organization requirements
iii. Identification and design of the proposed system
iv. Development and implementation of the system
NB/ Examples of technical staff: System analyst and Programmers.
