PLANNING A PROSPECTING STRATEGY
Prospecting is the searching for and calling upon customers who have not previously purchased from the company. This activity is not of uniform importance across all the branches of selling. It is obviously far more important in industrial selling than retail selling.
Prospecting begins the process of converting prospects into repeat customers. A suspect or lead is a potential prospect, i.e. a person or an organization that might have a need for a salesperson’s product or services. If a salesperson determines the suspect has a real need for the product, then that person or organization becomes a prospect. The next step is for the salesperson to qualify the prospect to find out if that person has both the ability and authority to make a purchase. Once a qualified prospect is located process begins.
The following are some of the prospecting strategies commonly used:
- Direct mail marketing – Have a direct mail marketing, planning and tracking system, keeping in mind parameters such as age, income, occupation location and so on. Decide the frequency and number of mailers to be sent and the enclosures therein. Remember to follow-up.
- Trade shows – Professionals who effectively work trade shows, keep the following in mind:- they define very clear goals, as to what they want to accomplish through shows. The ultimate aim here is to translate presentations into sales.
- Customer referrals (endless chain) – this is a very effective method to for finding customers. Customers and customers are the best sources of future sales, with repeat sales from customers being better. You ask customers whether they know any other individuals or organizations who may be interested in finding out about your product or service. If the customer hesitates on communicating with other individuals about your product ask for names and promise to call them and ask them to give brief description of what you do.
- Orphaned customer – these are the customers left by the salespeople. These are great prospects. As a salesperson you should quickly contact such customers to begin developing relationships.
- Sales lead club – organize a group of salespeople in related but non-competitive fields to meet twice a month to share leads and prospecting tips.
- Observation
- Networking
- Center of influence
The prospect pool
The referrals come from prospects and customers. Different sources of prospects form prospect pool. The prospect pool is a group of names gathered from various sources. Your source, for example may be mailing list, telephone book, referrals, orphans or existing customers. A prospect pool is usually created from the main sources such as:
- Leads – people or organizations you know nothing or very little about.
- Referrals – you frequently know very little about these people or organizations other than what you learned from the referrals.
- Orphans – company records provide your only information about these past customers.
- Your customers – the most important prospects for future sales
Obtaining referrals is a continuous process without beginning or end. The salesperson is always looking for the right opportunity to find a referral. The referral cycle provides guidelines for a salesperson to ask for referrals in four commonly faced situations experienced by salespeople as shown below.
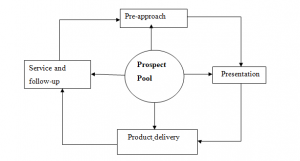
If you have a sales presentation at 10:00 am you can begin the referral cycle in the presentation phase. If you are delivering a product to a client you can start the cycle in the product delivery phase. If you are planning on making telephone calls to leads, referrals, orphans, or customers you can begin pre-approach phase. Referral cycle can begin at any point.
Salespeople must sell the product, plus sell the prospect on providing referrals. Equal emphasis must be given to both product sales and referral sales. You must nurture a parallel referral sale from the time of the initial contact, such as when making appointment. The referral sale should receive equal importance, effort and emphasis as the product sale. This is the key to referral cycles.
