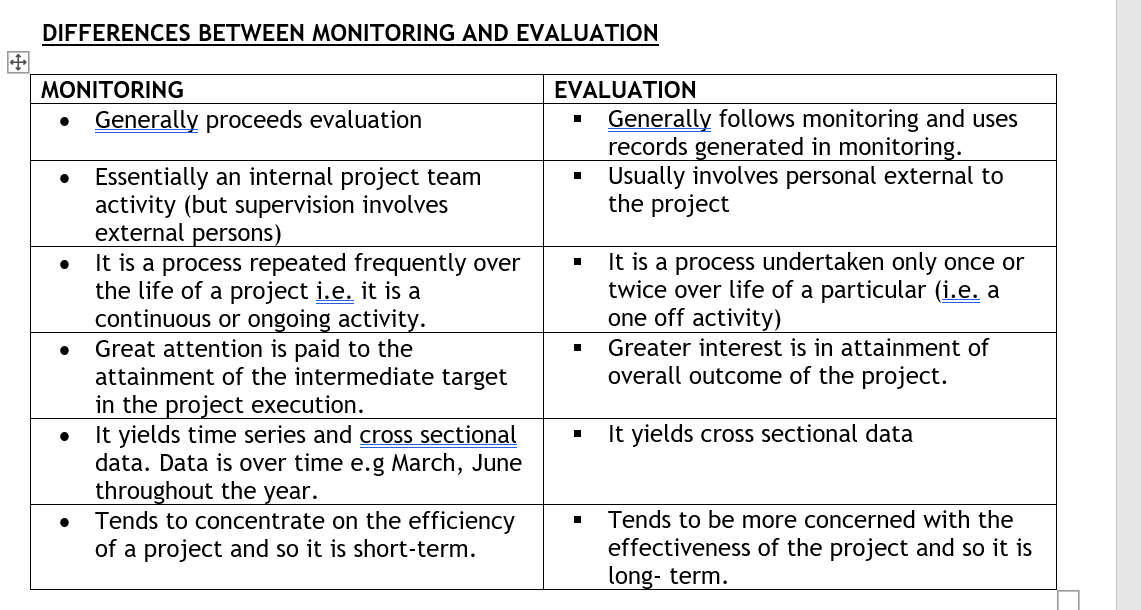
- Project evaluation is a process of determining the extent to which objectives have been achieved.
- It is a set of procedures to appraise a projects merits and information about its goals, objectives, activities outcomes and costs
- An evaluation can be done during implementation at its end or afterwards
Aims of Evaluation
- To determine the efficiency of which project interventions are
- To assess the effectiveness of a project
- To measure the sustainability of a project
- To determine the relevance of a project
- To determine the relevance of a project
- To measure the impact of an intervention/project
Scope of Evaluation/Key Evaluation Question
Efficiency
- This is the measure of the relationship between output and input. It answers the questions:
- How economically have the output been achieved
- How much have been put to get what
Effectiveness
- It is the measure of the relationship between project output and objective and the outcomes. It is the extent to which the development intervention objectives are expected to be achieved.
Relevancy
- It measures the relationship between project output to the needs that were identifies. It investigates the extent to which outputs of a project have met the needs of the beneficiaries.
Sustainability
- It estimates the extent to which a project will continue after external funding has terminated.
Types of Evaluation
- Baseline survey/feasibility survey
- Formative/ongoing evaluation
- Summative/final evaluation
- Impact evaluation
Baseline Survey/Feasibility Survey
- This is carried out before project implementation to assess and determine development needs and potential of the target population in the area.
- It also checks on the proposed approaches and planned project activities
Primary users of feasibility survey are:-
- Donors
- Implementing agencies
- Beneficiary community
- Researchers
- Institutions of higher learning
Formation/On-Going Evaluation
- This is a continuous evaluation during project implementation. It enables the implementing personnel to check on different aspects of the project and their effects as well as detect problems or shortcomings in good time to make necessary changes.
- Components of formative evaluation
- Implementation evaluation
- Progressive evaluation
- Implementation evaluation – its main purpose is to assess whether the project is being conducted as planned. It is also called process evaluation and occur several times during the project implementation period.
Progressive Evaluation
It assesses the progress of meeting the goal of the programs/project. Information is collected to determine the impact of activities/strategies on beneficiaries.
- Primary users
- Donors
- Project management
- Target group
Summative/Final Evaluation
This is done at the end of project implementation. It is used to examine the projects effectiveness in achieving its objectives and its contribution to the development of the area. Final evaluation is concerned with all aspects of the project. The main purpose is:
- To assess results and effects of the intervention
- To draw lessons
- To assess the impact to justify resources
- To justify replication
Primary Users of Summative Evaluation
- Donors project planner
- Government
- Target group
- Who carried out summative evaluation
- External evaluators
- Internal evaluators
- Project staff
- Beneficiary communities
Impact Evaluation
- It is done 1-10 years after project implementation. Its main purpose is to establish sustainability of the results of the project.
- It is used to ensure direct and indirect changes and draw lessons from the project.
Main beneficiaries
- Donors
- Planners
- Government
- Researchers
- Academics
Types of Evaluation
- Internal evaluators
- External evaluators
Internal Evaluators
- They include people who have been included in the project i.e. Project team, target group and beneficiaries. They assess whether the project outcome achieved its intended purpose and if not they recommend areas of improvement or next cause of action
Advantages of Using Internal Evaluators
- They have internal knowledge of the project
- They have personal commitment to the project
- Their evaluation results are easily accepted and used
- It gives them a learning experience they can use in future activities
Disadvantages
- They are likely to be more subjective and blind to their own faults
- They can be inexperienced and lack evaluation skills and technique
- If they lack integrity, they might ignore negative aspects of the project and emphasize on the positive ones only.
External Evaluators
- They include professional evaluators, donors, headquarter staff
Advantages
- Their findings seem to be more objective and more acceptable to funding agencies
- They have more refined skills and evaluation techniques
Disadvantages
- They are expensive
- They lack first hand knowledge of project operations
Evaluation involves
1. Measuring
Evaluations will 1st measure what has been done in relation to what should have been done. If the evaluating agency is observing the work continuously, the performance evaluation is to be done.
2. Reviewing
The purpose of a review is basically participative problem solving. It is also keeps the implementing team informed and alerted that their performance is closely checked.
3. Reporting
All information related or collected during evaluation must be presented in form of a report that is represented to respective bodies’ i.e. the donor agency.
4. Deciding and Taking Corrective Measures
This involves determining the cause of action possible to deviate from an undesired cause of action if any.
PROJECT PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
- An indicator is something that points to or signifies the condition of something else. It is used to determine whether something is on some scale of measurement.
- It indicates the degree of progress that is being achieved towards some goals or objectives or meeting some standard.
Types of Indicators
Direct indicators
- These are pieces of information that express and relate to what is being measured e.g if information on crop yields is measured.
Indirect indicators
- These are essential pieces of information chosen amongst many possible pieces of information to serve as substitutes of proxies to answer question or respond to statements that are difficult to measure. Organization instead of direct indicators of income, indirect indicators of poverty are chosen.
Elements of Indicators
- Observer – has intentions/motives or skills in using apparatus
- Apparatus/instruments
- Object of observation
- Actions performed by the observer with the apparatus
Sources of Information Commonly Used By Indicators
- Direct observation of conditions or performance by the monitor
- Project records e.g finance records, committee minutes etc
- Project committee members, community leaders, project staff and others
- Community members (both direct and indirect beneficiaries)
Tools and Techniques Used In Project Evaluation
- Tools required for evaluation include:
- Project document papers i.e. Legal papers, registration, agreement etc
- Financial records and guidelines
- Director’s articles
- Concept papers and initial profiles
- Funding proposals
- Project initial plans and designs
Techniques for monitoring and evaluating a project vary from one situation to another. Whichever technique used, their main aim is to measure for efficiency and effectiveness of system and competencies that exist in individuals overseeing the systems and ensure conformity to project goals, objectives and purposes.
Steps in Evaluation
- Specifying the objectives of evaluation
- Decide on scope of evaluation
- Select indicators and performance standards
- Choosing information source and develop data collection procedures
- Collect data
- Tabulate and analyze data
- Present findings
- Take appropriate action, based on evaluation
Reasons for Evaluation
- To determine the impacts of the project
- To determine the effectiveness and efficiency of the project
- To come up with corrective measures
- To determine the sustainability of the project
Challenges
- Lack of skills and knowledge
- Lack of 1st hand information and knowledge especially for external evaluation
- Inadequate financial resources
- It is expensive with concern to external evaluation
- Lack of personal commitment to the project