A product is like a human being. It is born, grows up fast, matures and then finally passes away. The product life cycle discusses the stages which a product has to go through since the day of its birth to the day it is taken away from the market.
However, the basic difference in case of human beings and products is that a product has to be killed by someone. Either the company (to bring better products) or by competition (too much external competition). There are several products in the market which have lived on since ages (Light Bulbs, Tubelights), whereas there are others which were immediately taken off the shelf
(HD DVD).Thus the Product life cycle deals with four stages of a products life. Products typically go through four stages during their lifetime. Each stage is different and requires marketing strategies unique to the stage.
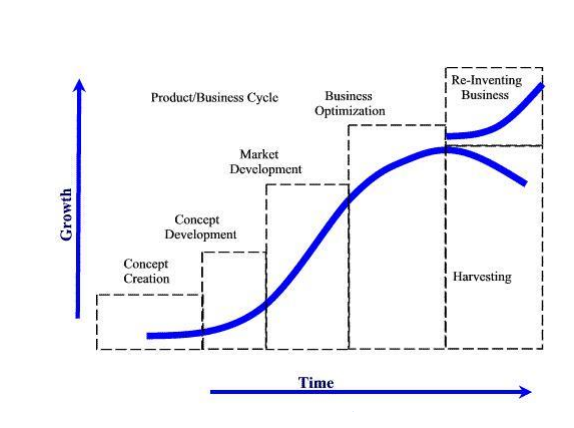
Stage 1 – Introduction of the product
The stage 1 is where the product is launched. A product launch is always risky. You never know how the market will receive the product. There have been numerous failures in the past to make marketers nervous during the launch of the product. The length of the introduction stage varies according to the product.
If the product is technological and receives acceptance in the market, it may come out of the introductory phase as soon as it is launched. Whereas if the product is of a different category altogether and needs market awareness, it may take time to launch.
This stage involves introducing a new and previously unknown product to buyers. Sales are small, the production process is new, and cost reductions through economies of size or the experience curve have not been realized. The promotion plan is geared to acquainting buyers with the product. The pricing plan is focused on first-time buyers and enticing them to try the product.
Characteristics of Introductory stages of Product life cycle
1. Higher investment, lesser profits
2. Minimal Competition
3. Company tries to Induce acceptance and gain initial distribution
4. Company needs Promotions targeted towards customers to increase awareness and demand for product
5. Company needs Promotions targeted towards channel to increase confidence in the product
Stage 2: Growth of the product
Once the introductory phases are over, the product starts showing better returns on investment. Your customers and channels begin responding. There is better demand in the market and slowly the product starts showing profits. This is a stage where competition may step in to squash the product before it has completely launched. Any marketing mistakes done at this stage affect the product considerably as the product is being exposed to the market and bad news travels fast. Thus special care has to be taken in this stage to ensure competition or bad decisions do not affect the growth stage of the product.
In this stage, sales grow rapidly. Buyers have become acquainted with the product and are willing to buy it. So, new buyers enter the market and previous buyers come back as repeat buyers. Production may need to be ramped up quickly and may require a large infusion of capital and expertise into the business. Cost reductions occur as the business moves down the experience curve and economies of size are realized. Profit margins are often large. Competitors may enter the market but little rivalry exists because the market is growing rapidly. Promotion and pricing strategies are revised to take advantage of the growing industry.
Characteristics of Growth stage of Product life cycle
1. Product is successfully launched
2. Demand increases
3. Distribution increases
4. Competition intensifies
5. Company might introduce secondary products or support services.
6. Better revenue generation and ROI
Stage 3: Maturity stage of the product
In this stage the market becomes saturated. Production has caught up with demand and demand growth slows precipitously. There are few first-time buyers. Most buyers are repeat buyers. Competition becomes intense, leading to aggressive promotional and pricing programs to capture market share from competitors or just to maintain market share. Although experience curves and size economies are achieved, intense pricing programs often lead to smaller profit margins. Although companies try to differentiate their products, the products actually become more standardized
One of the problems associated with maturity stages in a technologically advanced environment is the problem of duplication. Not only is the product available in duplicate markets, but also there are several competing products which arise with the same features and capabilities. As a Along with competition, Penetration pricing becomes a weapon for competitors. Competitors sell products with the same features at lesser prices thereby trying to penetrate in the market. Nonetheless, The sales of a product (especially sales from return customers) is at its peak point during the maturity stages. The growth of sales may be lesser, but the sales revenue of the
organization is maximum during the maturity stage of product life cycle.
Characteristics of Maturity stages of Product life cycle
1. Competition is high
2. Product is established and promotion expenditures are less
3. Little growth potential for the product
4. Penetration pricing, and lower profit margins
5. The major focus is towards extending the life cycle and maintaining market share
6. Converting customers product to your own is a major challenge in maturity stage
Stage 4: Decline Stage
1 product, 10 competitors, minimum profits, huge amount of manpower and resources in use – A typical scenario which a product might face in its last stage. In this stage the expenditures begin to equal the profits or worse, expenses are more than profits.
Thus it becomes a typical scenario for the product to exit the market. It also becomes advantageous for the company as the company can use resources it was spending on the declining product on an altogether different project. In this stage buyers move on to other products and sales drop. Intense rivalry exists among competitors. Profits dry up because of narrow profit margins and declining sales. Some businesses leave the industry. The remaining businesses try to revive interest in the product. If they are successful, sales may begin to grow. If not, sales will stabilize or continue to decline.
Characteristics of Decline stages of Product life cycle
1. Market is saturated
2. Sales and profits decline
3. Company becomes cost conscious
4. A lot of resources are blocked in rejuvenating the dead product.
5. There are only three options left with the company
- Re positioning or Rebranding of the product to extend product life cycle
- Maintain the product as it is and reduce costs to get minimum profits till the product can produce profits
- Take the product off the market.
