Public Entities are responsible for carrying out all the procedures pertaining to the complete procurement cycle. It is important to be familiar with the complete procurement cycle and to ensure that there are effective management procedures in place to properly manage each step. The complete Procurement Cycle shall include:
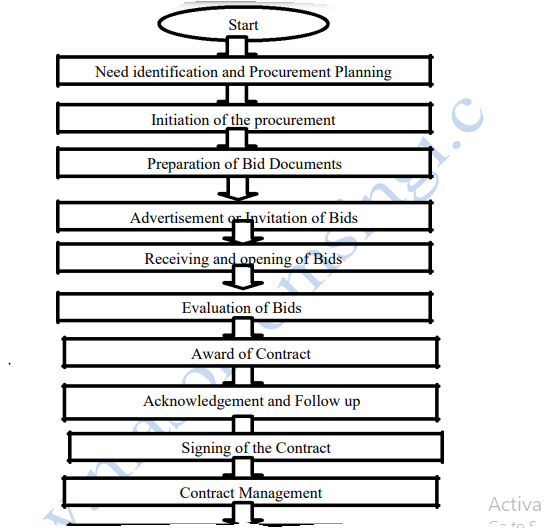
Identification of Requirements/Needs (Procurement Planning): Every purchase transaction originates with the recognition of need for an item by someone in the organization, that is, user departments. The users must identify materials and service requirements in order for purchasing to satisfy that need. Purchasing requirements are expressed in a variety of ways including
purchasing requisitions from internal users, forecasts and customer orders, routine reordering systems, stock checks, and materials identified during product development. The procurement plans are prepared as part of the annual budget preparation process as they are necessary to inform the cash flow preparation. The annual procurement planning is an integral part of the budget processes. It can be based on indicative or approved budgets, as appropriate. A procurement plan is not static; Organizations will need to revise and to update their procurement plans. For example and importantly, once the budget process is completed and the budget has been approved, the Procurement Plan has to be reviewed in order to take into account the exact votes as the basis for procuring the required goods, works and services
Initiation of procurement : After preparation and approval of the Procurement plan, the next important issue to consider is the preparation of specifications for each procurement package to be procured. Organization has the responsibility to prepare the specific requirements relating to the goods, works, services or consultancies. The specifications must be clear to give the correct and complete description of what is to be procured and thus allow fair and open competition among the candidates. In case of works, the specifications are to include bills of quantities, designs and drawings. In case of technical specifications for equipment reference should not be made to particular trademarks, names, brands, patents, design, type, product or service provided or to a specific
origin unless it is unavoidable in which case there shall be a statement allowing equivalents of what is referred to.
Preparation of Tender or Bid documents: This involves selecting the method of procurement to be adopted, either open national or international tendering, selective tendering, direct contracting or request for quotations depending on the prevailing circumstances of that particular procurement. The supply sources that can be used include registered suppliers, existing suppliers, trade sources or the website. Open Tender may sometimes be costly to administer as it requires review of all bids with fairness and equality in order to select the winning bid. In cases where the procurement requirement is large but simple, this may mean dealing with a large number of bids. It is thus better to first identify potential bidders on the basis of compliance criteria to determine their
qualification and then to conduct the tender on a short-list of pre-qualified bidders having demonstrated their capacity and intention to respond. This procedures permits reducing the number of bids to be evaluated technically and financially as this is a complex and costly task without reducing the level of competition as the prequalification stage is open to all competitors but simply seeks to evaluate the technical and financial capabilities of competitors.
Advertisement or Invitation of bids: This is done when an organization decides on method to use and two possibilities exit:
Invitation through the publication of an announcement of tendering proceedings in the case of open tendering, where no pre-qualification has been conducted; or Invitation from the list of pre-qualified bidders established where a pre-qualification stage has been conducted
The content of the invitation to tender notice should be sufficient to inform all the bidders on the procurement requirements, key specifications and conditions of execution so as to allow the bidders make an informed decision in order to be responsive and competitive. The document will indicate the specific requirements of the goods, works or services being procured and the time limit for delivery or completion; if works are being procured, relevant drawings and bills of quantities; the general and specific conditions to which the contract will be subject to, instructions for the preparation and submission of tenders including the forms for tenders; the
number of copies to be submitted with the original tender; any requirement that tender security be provided and the form and amount of any such security; and any requirement that if works are being procured, relevant drawings and bills of quantities; the general and specific conditions to which the contract will be subject to, instructions for the preparation and submission of tenders including the forms for tenders
Receiving and Opening Bids: Tenders are submitted in writing, signed in original and in a sealed envelope. Other forms of tender may be accepted in special circumstances, but this must be stated in the tender documents and should be an exception.
In the Public Sector, the submission and receipt of tenders is strictly regulated in order to ensure fairness and equal treatment of all the bidders as well as securing the bids to avoid any collusion. The following criteria must be verified when receiving a tender:
- A tender must be in writing, signed by an authorized officer of the bidder and it must be sealed in an envelope;
- A tender and the envelope it is sealed in must bear the tender number assigned by the organization and any other reference as specified in the bidding documents;
- A tender must be submitted before the deadline for submitting tenders and any tender received after that deadline is returned unopened or marked ―late‖ and stored unopened. It will be important for the tender documents to state how late tenders shall be treated but whatever the case they shall be rejected.
The opening of tenders should take place as soon as possible after the deadline for submission and only tenders received prior to the deadline are eligible for evaluation. Tenders received late are not considered for evaluation process and are returned to the tenderers unopened. At the opening, the following details are announced.
1) Tenderer‘s name
2) Tender price
3) Total amount of each tender
4) Details of tender modifications
5) Details of any discounts offered, discounts not announced at the opening should not be taken into consideration in the evaluation process.
Minutes of the proceedings of the tender opening are prepared and all tenders opened are submitted promptly to evaluation committee.
Evaluation of Bids: The tender evaluation committee is composed of a minimum of at least three and a maximum of five members, appointed by the Managing Director or his designate. The evaluation is on a common basis to determine the lowest evaluated cost. The evaluation has to be consistent with the criteria laid down in the tender documents. Evaluation committee initially checks tender for arithmetic errors and also ensures that bid securities are in correct form for the correct amounts. Tenderers may be asked to provide
clarification to assist with the evaluation process; however tenderers should not be allowed to respond with changes to their technical and /or financial proposals. Determination of a tender‘s responsiveness is based upon the information included in the tender documents. A substantially responsive tender is one that conforms to the terms, conditions and specifications of the tender documents without material deviation or reservation.
Award of Contract and Notification: The evaluation report is presented to the relevant authority that may after review, approve the recommendations and award the contract in the form provided with the tender documents, or refuse to accept any of the recommendations and instruct committee to re-evaluate the offers or re-tender the requirement. Acceptance of the tender is issued promptly to the successful bidder. The contract is signed within the stipulate period after the issuance of the acceptance tender notice. Should a bidder refuse to accept an award of contract, the organization may select another supplier, whose bid is still valid, and is
awarded the contract.
For simple procurements, an order is placed with the selected supplier after agreeing on the terms of supply. Purchase order is a commitment made by the buyer to pay for goods/services ordered. Likewise it gives the supplier authority to dispatch the goods and charge the buyer for them. A purchase order is a contractual document and all precautions, must, therefore be taken by buyer to safeguard his interests. When a purchase order is issued, various terms and conditions pertinent to the contract are spelt out in the purchase order itself. The terms and conditions appearing on the purchase order, usually on the reverse side are considered part of the
contract. Acceptance of order is conditional on the acceptance of all terms and conditions.
Acknowledgement and follow-up of the order: In most cases, the original copy of the purchase order that is sent to the supplier constitutes a legal ―offer‖ to buy. No purchase contract exists, however, until the seller accepts the buyer‘s offer. The seller‘s acceptance can take one of the two forms:
1) Performance of the contract or
2) Formal notification that the offer is accepted.
The purpose of the supplier acknowledgement form along with the purchase order is twofold, first, it is a form that can be completed conveniently and returned to the buyer, acknowledging acceptance of the order. At the same time, the supplier can indicate whether or not it is able to meet the desired delivery date. Acceptance is communicated to buyer and some suppliers normally prefer using their own forms stating their terms and conditions of sale. The purchasing department‘s responsibility for an order does not terminate with the making of a satisfactory contract. Follow-up communication with the supplier is done (expediting) to ensure on time delivery. To ensure that all material is available when needed, firm track critical purchases by having travelling follow-up representatives personally visit suppliers‘ plants. These personnel have additional responsibility of attempting to speed up or even delay (deexpedite) delivery as the buyer‘s timing requirements undergo changes.
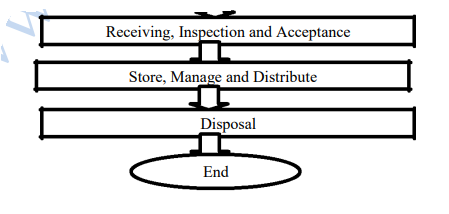
Receiving and Inspection: On receipt of the materials in stores, the receipt section checks the quantity with that mentioned in the invoice. Sometimes the inspection for quality is carried out at the supplier‘s premises at different stages of production. The buyer has to be satisfied about the quality of materials through an independent quality control inspection department which checks the conformance. Acceptances of items that have passed the quality test usually cause no problem. The necessary entries will have to be made on acceptance and items are taken on stock for consumption. The inspection note, wherein the inspection has indicated the acceptance of materials becomes the basis for the payment of these items.
Bill/Invoice Settlement; The role of the purchasing executive does not end with the acceptance of quality goods. He/she has to maintain good relations with supplier, because the transaction might be repeated. Therefore he/she has to see that payment is made for the supplied goods within the due date. The payment is usually made by the accounts department on the basis of purchase order, seller‘s invoice, the goods inspection note and goods received note.
Documentation: The job is not finished until paper work is done, is the motto behind the purchase cycle. Therefore documentation is the last stage of the purchasing cycle and this is essential to ensure adequate accountability and to prevent misunderstanding.
End Contracts: After all work is complete, or if the contract is terminated, the contract is formally ‗closed. ‗Contract closure involves the formal notification of all parties regarding the status of the contract. In addition, a contract archive is created that documents exactly what work was completed and what payments made. Records are kept of all correspondence generated during the life of the contract.
