Demand forecasting constitutes an important part in making crucial business decisions.
The objectives of demand forecasting are divided into short and long-term objectives, which are shown in Figure-1:
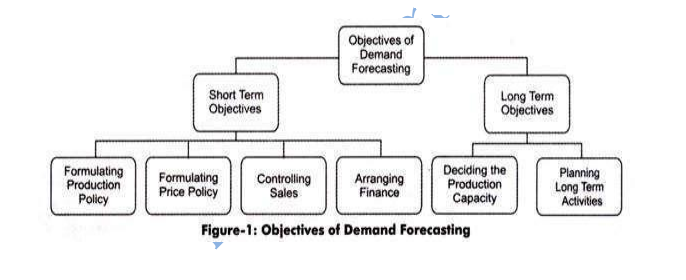
1.Short-term Objectives:
Include the following:
- Formulating production policy:
Helps in covering the gap between the demand and supply of the product. The demand forecasting helps in estimating the requirement of raw material in future, so that the regular supply of raw material can be maintained. It further helps in maximum utilization of resources as operations are planned according to forecasts. Similarly, human resource requirements are easily met with the help of demand forecasting. - Formulating price policy:
Refers to one of the most important objectives of demand forecasting. An organization sets prices of its products according to their demand. For example, if an economy enters into depression or recession phase, the demand for products falls. In such a case, the organization sets low prices of its products. - Controlling sales:
Helps in setting sales targets, which act as a basis for evaluating sales performance. An organization make demand forecasts for different regions and fix sales targets for each region accordingly. - Arranging finance:
Implies that the financial requirements of the enterprise are estimated with the help of demand forecasting. This helps in ensuring proper liquidity within the organization.
2.Long-term Objectives:
Include the following:
- Deciding the production capacity:
Implies that with the help of demand forecasting, an organization can determine the size of the plant required for production. The size of the plant should conform to the sales requirement of the organization. - Planning long-term activities:
Implies that demand forecasting helps in planning for long term. For example, if the forecasted demand for the organization‘s products is high, then it may plan to invest in various expansion and development projects in the long term.
Share this:
