Planning the flow of materials is important in a warehouse. This is because with a plan, we would most likely be aware of the location of items in the store and also the status and location of the handling equipment. With this information, better control of the store can be achieved. There are two main approaches of the plan of material flows. They are the ‘U’ flow and ‘Through’ flow.
‘U’ flow
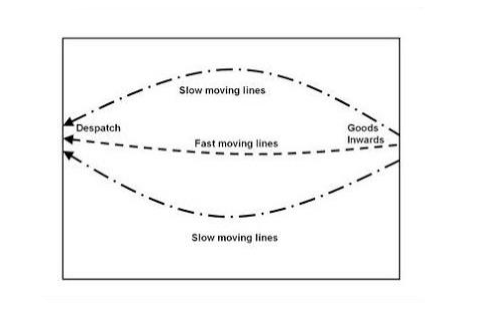
A ‘U’ flow occurs when the goods receipt and dispatch functions are located at the same end of a store building. Products flow in at receiving, move in to storage in the back of the store, and then to shipping, which is located at the adjacent to receiving on the same side of the building. Items with higher throughput level are located closer to the loading bays. An example of a ‘U’ flow design can be seen in the diagram below.
Advantages of ‘U’ Flow
- Excellent utilization of dock resources because the receiving and shipping processes can share dock doors
- Facilitating cross-docking because the receiving and shipping docks are adjacent to one another and may be co-mingled
- Excellent lift truck utilization because put away and retrieval trips are easily combined and because the storage locations closest to the receiving and shipping docks are natural locations to house fast moving items
- Yields excellent security because there is a single side of the building used for entry and exit
‘Through’ flow
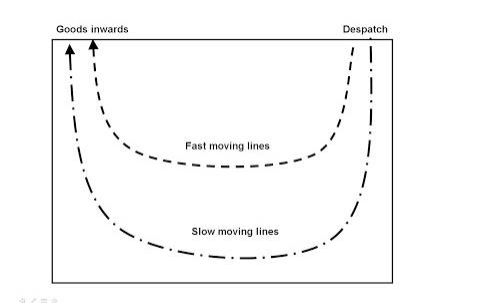
‘Through’ flow happens when separate loading bay facilities for outbound and shipping are provided, often at opposite end of store.
Products flow in at receiving, move into storage, picking area and then the marshaling and dispatch area in a straight line. Items with a higher throughput level are located at the center of the store because the total distance travelled would be shorter. An example of a ‘Through’ flow layout design is shown on the diagram below.