Introduction
● Change can be simply defined as a transition from one state to another with focus on being different.
● Change is the only constant in today‘s life – for individuals and organizations
● Some changes can be reversible while others are not hence the risk involved in managing change.
● There are both objective and subjective conditions in making the transition in organizations.
Definition
- Change management is the use of systematic methods to ensure that an organization change can be guided in the planned direction, conducted in a cost effective manner and completed within the targeted time frame and with the desired results” (Davis and Holland 2002)
- Focus is on the process
- Change management is a structured and systematic approach to achieving a sustained change in human behavior within an organization‖ (Todd A. 1999)
- Focus is on the people aspects of change
UNDERSTANDING STRATEGIC CHANGE
- Strategic change is one that involves fundamental changes in the business of the organization and its future direction
- Successful strategic change is built on an overall strategic management system of the organization
- The strategy of the organization legitimizes the change programme
- The goal of strategic management is to build and maintain sustainable competitive advantage and to maximize shareholder value.
- Organizations have to change to align themselves to changes in their environments.
- Purpose of strategic change is to ensure that organization is heading in the right direction (effectiveness).
- Key pre-occupation is anticipation
McKinsey Survey on Change Management (2006)
Why change?
- Reducing costs
- Moving from good performance to great performance
- Completing or integrating a merger
- Turning around a crisis situation
- Catching up to rival companies
- Splitting or divesting part of the organization
- Preparing for privatization or market liberalization
Source: The McKinsey Quarterly Jan 2007
Operational change
- Is the type of change aimed at ensuring that the organizational activities are being performed in the best way possible?
- Focuses on excellence in whatever the organization does.
- Purpose of operational changes is to ensure the organization is efficient.
- Strategic change informs operational change.
CONTEXT AND FORCES OF CHANGE
In a fast paced global economy, change can not be an occasional episode in the life of a corporation. Companies with rigid structures will be swept away. Corporate cultures that can adapt will survive and thrive‖
Source: Business Week – Reinventing America, 1992.
Introduction
- At the beginning of the twenty first century, change is everywhere.
- The reality of yesterday is different from that of today and possibly that of tomorrow
- Social, political and economic changes have greatly compromised individuals and organizations ability to respond.
- Organizations just like individuals follow a certain logic or system and sometimes react irrationally.
- Some are fairly successful while others are failing
- How can we – as individuals, as well as organizations, prepare for the uncertain future?
- Change management is empowering organizations and individuals for taking over responsibility for their own future.
- Creating a learning organization is an example of one such form of empowerment
Context for change
- The forces that operate to bring about change are many and varied.
- Some forces are gentle while others are strong and can cause devastation to structures and operations in an organization.
Multiple Causes
- Identifying the causes of change (PESTEL analysis, Internal analysis etc.)
- Analyzing the causes of the change is a good beginning point in change management
Driven by Environmental Turbulence
- Predictable
- Forecastable by extrapolation
- Predictable threats and opportunities
- Partially predictable opportunities
- Unpredictable surprises
Varieties of Change
Arising from the various levels of turbulence in the environment, there are varieties of change in organizational Changes.
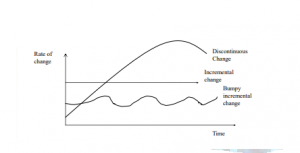
Forces of change
- Most of the forces of change can be traced to some fundamental forces of change.
- Growth of capital intensive manufacturing.
- Accelerated tempo of new technology
- The concentrated patterns of consumption
- Neo-protectionism era.
What are the implications of these forces to change in Kenyan organizations today? Technical Obsolescence and Technical Improvements
- Stems from competitors or availability of new technologies
- Internally from R & D e.g. replacing product models every short time (shorter PLC and persuade customers to replace these products as frequently.
Accelerated diffusion of new technology
Political and Social events
- Changes in political ideologies and inclinations over time
- Changing political systems e.g. in 1980 – pressure not to trade with South Africa – now?
- Convergence of cultures and social systems
Globalization of markets and operations
- Improved communication
- Similarities in technological infrastructure
- Similarities of consumer demand and life style patterns
- These have led to growing incidence of strategic alliances and joint ventures.
Increases in size, complexity and specialization of organizations
- Most organizations have grown in size and increasingly utilizing specialized technology.
- These changes require new organization structures and skills for cooperation and coordination.
Greater strategic awareness and skills of managers and employees
- These require changes in the scope of their jobs and call for strategic development and growth of the company
Neo-protectionism
- World trade has been fairly liberalized
- Competitive power of the corporation is no longer in the monopolistic status
- Competition has eroded the abilities of corporations.
- Global competition as opposed to localized competition
- Free flow of resources in the world
All these pose challenges and change in the way of doing things is inevitable.
Types of change
- There appears to be four basic types of change, which affect organizations.
Technology changes
- Production processes
The product or service changes
- Concerned with output of the business
Administrative changes
- Structures, policies, budgets rewards systems
People changes
- Attitudes
- Expectations
- Behaviors
- A change in one of these changes will place demands for change on one or more of the others.
- Major changes in the strategic perspective forces changes in the structure which forces change in jobs and consequently on behaviors.
Implications
- The approach to management of change will need to be context dependent.
- Managers have to balance different approaches to management of change according to circumstances they face.
