FRIDAY: 17 December 2021. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
Answer ALL questions. Marks allocated to each question are shown at the end of the question. Show ALL your workings.
QUESTION ONE
1. Blade Ltd. manufacturers a range of electronic products. The supplier of component X has informed Blade Ltd. that it will offer a quantity discount of 1% if Blade Ltd. places an order of 10,000 components or more at any time.
Details of component X are as follows:
Cost per component before discount Sh.20
Annual purchases 150.000 components
Ordering costs Sh.360 per order
Holding costs Sh.3 per component per annum
Required:
Economic order quantity (E0Q). (2 marks)
Annual ordering cost and holding costs of inventory of component X using the economic order quantity ( EOQ ) computed in (a) (i) above. (4 marks)
Advise the management of Blade Ltd. whether the discount should be accepted. (4 marks)
2. Usenge Products Ltd. manufactures and retails products A. 13 and C. The company has 120 workers who work under a group bonus scheme. The workers are categorised into three grades and arc paid a bonus of the excess of time allowed over time taken. The bonus paid is 80% of the workers’ base rate and is shared by the workers in the proportion of time spent on the job. The following production data has been extracted from the company’s records for the month of November 2021.
Product Units produced Time allowed per unit (Minutes)
A 640 63
B 1,280 120
C 2,400 100
Grade of worker Number of direct workers Basic rate per hour flours worked per worker
1 40 300 30
2 16 270 64
3 64 240 50
Required:
Percentage of hours saved to hours taken. (3 marks)
Bonus due to the group. (3 marks)
Gross earnings due to the group. (4 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION TWO
1. Using relevant examples, distinguish between a joint product” and a -by-product”. (4 marks)
Zaidi Industries Ltd. produces two products branded A and B from the same material. The cost of material is Sh.9.50 per kg and the two products appear after Process I.
Product A can be sold directly to the market but product B requires further processing in Process II. The following data relate to the month of October 2021:
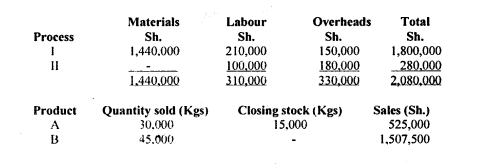
Additional information:
There were no materials on hand at the end of the month of October 2021.
The company uses the sales value method of apportionment for joint costs.
Required:
Determine the total cost of Products A and B. (8 marks)
2. The following data was provided by the cost accountant of Miradi Ltd. relating to marketing expenses and sales for a period of first eight months of the financial year ending 31 December 2021.
Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Total marketing expenses (Sh.”000″) 265 302 222 240 362 295 404 400
Sales units (000) 20 24 16 18 26 22 32 30
Preliminary calculations have established the tbllowing analysis using the equation in the form of y = a + bx

Required:
Predict the total marketing expenses for the ninth month when planned sales are 44,000 units. (8 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION THREE
1. The Cost Accountant of ABC Ltd. has provided the following information relating to production of a single product branded -Zed”:
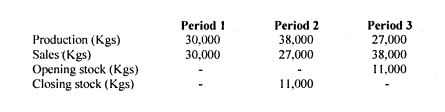
Additional information:
- The financial details for one unit of product ”Zee, based on a normal activity level of 30.000 Kgs is as follows:
Cost per Kg (Sh.)
Direct material 1.50
Direct labour 1.00
Production overheads (300% of labour) 3.00
Total cost 5.512
- The selling price of product “Zed” is Sh.9 per kg
- Administrative overheads are fixed at Sh.25,000 per period whereas one third of production overheads are fixed.
Required:
Prepare operating statement using:
Variable costing. (6 marks)
Absorption costing. (6 marks)
2. Summarise four assumptions of cost-volume profit (CVP) analysis. (4 marks)
3. Britkon Ltd. makes a single product branded “P- with a sales price of Sh.100 and a variable cost of Sh.60. Fixed costs are Sh.600,000 per annum.
Required:
Assuming the taxation rate is 40%. determine the number of units to be sold to make a profit after tax of Sh.200,000 per annum. (2 marks)
As a result of increasing costs, the variable cost is expected to rise to Sh.65 per unit and fixed costs to Sh.700,000 per annum.
Assuming the selling price cannot be increased, determine the number of units required to maintain a profit of Sh.200,000 per annum. (Ignore inflation). (2 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION FOUR
1. Outline six benefits that might accrue to an organisation as a result of preparing budgets. (6 marks)
2. You are in charge of making forecasts and preparing budgets for Kondele Ltd. You have been supplied with the following cost and revenue forecast and details of payments:
Forecast for revenue and costs for half year 2022
January February March April May June
Sh.”000″ Sh.•000″ Sh.•000″ Sh.”000″ Sh.”000″ Sh.”000″
Direct material purchases 112,000 100.000 135,000 90,000 67,000 79.000
Wages 90,000 80.000 100,000 72,000 54.000 63.000
Overheads
Production 34.000 32,000 40.000 45.000 36,000 40,000
Administrative 22,000 20,000 27.000 24,000 25,000 27.000
Selling and distribution 13.000 11.000 18.000 13.000 11,000 16,000
Sales 360,000 350.000 440,000 350,000 360.000 360.000
Additional information:
- Cash balance on 1 April 2022 is expected to be Sh.90 million.
- Period of credit allowed by suppliers averages two months.
- Debentures worth Sh.125 million are expected to be issued in May 2022 and the amount will be received in the same month.
- A new machine will be installed in March 2022 at a cost of Sh.150 million and payment is expected in May 2022.
- Sales commission of 3% is payable after one month of sale.
- A dividend of Sh.100 million is to be paid in June 2022.There is a delay of one month in the payment of overheads and wages.
- Twenty percent of the debtors pay cash, receiving a cash discount of 4% and seventy per cent of debtors pay within one month and receive 2.5% discount while the remaining debtors pay within two months without a discount.
Required:
A cash budget on a monthly basis for the months of April 2022 to June 2022. (14 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
QUESTION FIVE
1. Describe four factors that could influence a company’s demand for management accounting information. (8 marks)
2. Highlight four purposes of standard costing. (4 marks)
3. Describe two advantages and two disadvantages of using activity based costing (ABC). (4 marks)
4. Explain the following terms:
Relevant cost. (2 marks)
Sunk cost. (2 marks)
(Total: 20 marks)
