
SECTION A (40 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1. The diagram below illustrates a blood capillary surrounding a structure for gaseous exchange in human beings.
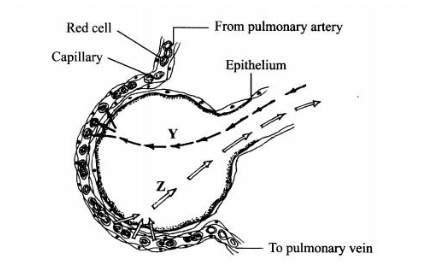
(a) Name the gaseous exchange structure.(1 mark)
………………………..
(b) Identify the gases labelled Y and Z.
Y……………………………(1 mark)
Z…………………………….(1 mark)
(c) How does the gas labelled Y reach the inside of the blood capillary?(3 marks)
……………………………..
(d) How does cigarette smoking lead to lung cancer?(2 marks)
……………………………
2. The diagram below illustrates the structure of the female part of a flower.
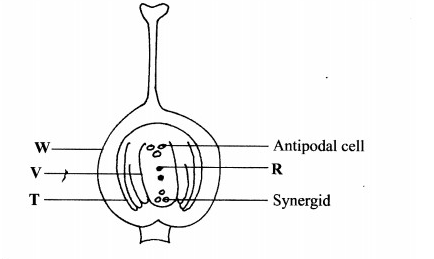
(a) Name the part labelled W. (1 mark)
…………………………….
(b) Describe what happens when the pollen tube enters the structure labelled V. (5 marks)
………………………………………
(c) What do the structures labelled R and T develop into after fertilization?
R……………………………….(1 mark)
T……………………………….(1 mark)
3. (a) What is meant by the term genetics? (1 mark)
………………………….
(b) State two examples of discontinuous variation. (2 marks)
…………………………………
(c) A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for sickle cell is Hbs and the normal allele is HbA. Deternine the probability that their first born will have the sickle cell trait. Show your working. (5 marks)
……………………
4. In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was treated as shown in the diagram below and exposed to light.
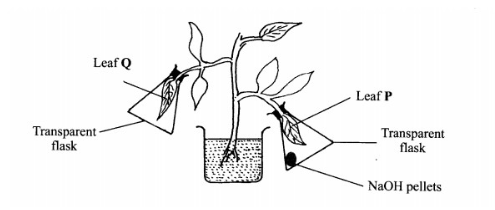
(a) Why was the potted plant kept in the dark overnight? (1 mark)
………………………..
(b) Which factor was being investigated in the experiment? (1 mark)
………………………
(c) (i) Which test did the students perform to confirm photosynthesis in the leaves labelled P and Q? (1 mark)
………………………..
(ii) State the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q.
P …………………… (1 mark)
Q……………………. (1 mark)
(iii) Explain the results obtained in the leaves labelled P and Q.
P …………………….(1 mark)
Q……………………..(l mark)
(d) What was the purpose of leaf Q in the experiment? (1 mark)
………………………
5. In an experiment to investigate a plant response, the set up shown in the diagram below was used.
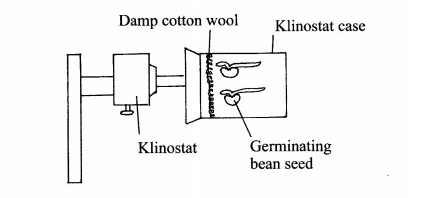
(a) Name the type of response that was being investigated. (1 mark)
……………………
(b) If the Klinostat was not rotating:
(i) state the observations that would be made on the seedlings after three days; (2 marks)
…………………………..
(ii) explain the observations in (b) (i) above, (3 marks)
…………………………..
(c) If the experiment was repeated with the Klinostat rotating:
(i) state the observation that was made on the seedlings after three days; (1 mark)
……………………
(ii) give a reason for the observation made on the seedlings. (1 mark)
………………………
SECTlON B (40 marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8. 6. The graph below shows the relative numbers of three main species of organisms in a pond.
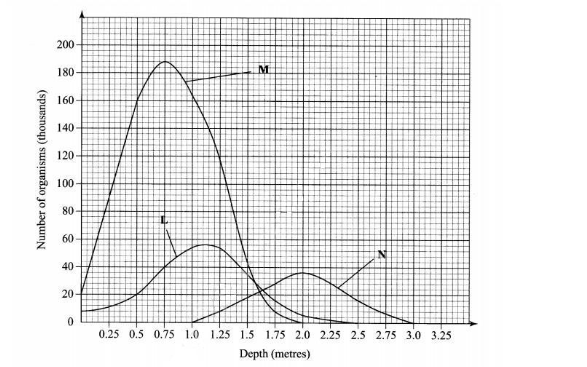
(a) Giving a reason for your answer, which of the species is a
(i) producer?…………………………. (1 mark)
Reason …………………….. (1 mark)
(ii) secondary consumer………………… (1 mark)
Reason……………………….. (1 mark)
(b) State the depths at which each of the populations labelled L, M and N is at its optimum. L …………………………………… (1 mark)
M……………………………………. (l mark)
N……………………………………. (1 mark)
(c) (i) Which method may have been used to deternine the population of organisms labelled N in the pond? (1 mark)
……………………
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i) above. (1 mark)
……………………
(iii) State the assumptions made when using the method in (c) (i) above. (4 marks)
…………………….
(d) State two reasons why primary productivity in the pond decreases with depth. (2 marks)
………………………
(e) Explain the ecological importance of fungi to plants. (2 marks)
……………………….
(f) Why is flooding likely to lead to a cholera outbreak? (3 marks)
………………………..
7. Explain the various ways in which seeds and fruits are adapted to dispersal. (20 marks)
……………………….
8. How is a mammalian heart structurally adapted to its function? (20 marks)
…………………………….
