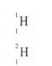CHEMISTRY (233)
4.5.1 Chemistry Paper 1 (233/1)
1. The set up below can be used to prepare oxygen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
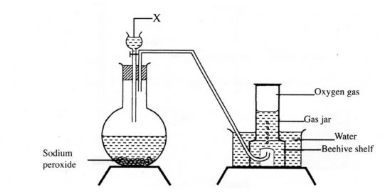
(a) Identify gas x ? (b) What property of oxygen makes it possible for it to be collected as shown in the above set up? (1mark)
(c) State two uses of oxygen. (1mark)
2 Write equations to show the effect of heat on each of the following: (a) sodium hydrogen carbonate; (1mark)
(b) silver nitrate; (1 mark)
(c) anhydrous iron (ll) sulphate. (1 mark)
3 Describe an experimental procedure that can be used to extract oil from nut seeds. (2 marks)
4 In terms of structure and bonding, explain the following observations: (a) the melting point of aluminium is higher than that of sodium: (1 /2 marks)
(b) melting point of chlorine is lower than that of sulphur. (1 % marks)
5.The diagram below illustrates a method of preparing salts by direct synthesis.

(a) This method can be used to prepare either aluminium chloride or iron (III) chloride. Explain why it cannot be used to prepare sodium chloride. (1 mark)
(b) Describe how a sample of sodium chloride can be prepared in the laboratory by direct synthesis. (2 marks)
6.(a) A student electroplated a spoon with copper metal. Write an equation for the process that took place at the cathode. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate the time in minutes required to deposit 1.184g of copper if a current of 2 amperes was used. (1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs, Cu = 63 .5). (2 marks)
7.Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
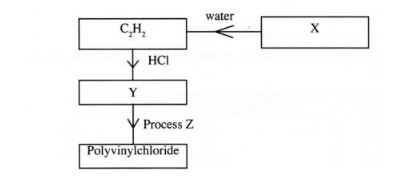
(a) Identify:
(i) X (1mark)
(ii) Y (1 mark)
(b) State two uses of polyvinylchloride. (1 mark)
8.Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate how alpha, beta and gamma radiations can be distinguished from each other. (3 marks)
9.Aqueous hydrogen chloride reacts with potassium manganate (VII) to produce chlorine gas, while a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene has no effect on potassium manganate (VII). Explain this observation. (2 marks)
10.The table below gives the solubilities of substances T and U at 10°C and 40°C. Substance Solubility g/100g water

When an aqueous mixture containing 55g of T and 12g of U at 80°C was cooled to 10°C, crystals formed.
(a) Identify the crystals formed. (1 mark)
(b) Determine the mass of the crystals formed. (1 mark)
(c) Name the method used to obtain the crystals. (1 mark)
11.Hydrazine gas,

burns in oxygen to form nitrogen gas and steam.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
(b) Using the bond energies given below. calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction in (a) above. (2 marks

Bond Bond energy (k/ per mole)
12 (a) What would be observed if sulphur (IV) oxide is bubbled through acidified potassium manganate (VII)? (1 mark)
(b) In an experiment, sulphur (IV) oxide was dissolved in water to form solution L.
(i) What would be observed if a few drops of barium nitrate solution were immediately added to solution L? (1 mark)
(ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction that occurred between solution L and aqueous barium nitrate in (b)(i) above. (1mark)
13 The scheme below shows some reaction sequence starting with solid N. Study it and answer

(a) Write the formula of the complex ion in solution Q. (1mark)
(b) Write an equation for the reaction in step IV. (1 mark)
14 (a) State the Charles’ law. (1 mark)
(b) A certain mass of gas occupies 146 dm’ at 291 K and 98.31 kPa.
What will be its temperature if its volume is reduced to 133 dm’ at 101.325 kPa? (2 marks)
15 The chromatogram below was obtained from a contaminated food sample P. Contaminants

Q, R, S and T are suspected to be in P. Use it to answer the following questions. Solvent front
P Q R S T (b) Which is the most soluble contaminant in P? (1 mark)
16 The curves below represent the change in mass when equal masses of powdered zinc and zinc granules were reacted with excess 2M hydrochloric acid. Study them and answer the question below.
Which curve represents the reaction with zinc granules? Explain your answer. (3 marks)
17 When fuels bum in the intemal combustion engine at high temperature, one of the products formed is nitrogen(ll) oxide.
(a) Write the equation for the formation of nitrogen(ll) oxide. (1 mark)
(b) Give a reason why nitrogen(ll) oxide is not formed at room temperature. (1 mark)
(c) Describe how formation of nitrogen (II) oxide in the internal combustion engine leads to gaseous pollution. (1 mark)
18 The set-up below was used to investigate the products of buming biogas (methane). Study it and answer the questions that follow.
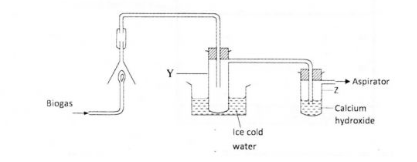
(a) What product will be formed in test-tube Y? (1 mark)
(b) State and explain the observations which would be made in Z. (2 marks)
19 (a) Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. What is meant by an allotrope? (1 mark)
(b) Explain why graphite can be used as a lubricant while diamond cannot. (2 marks)
20.The plots below were obtained when the atomic radii of some elements in groups I and II were plotted against atomic numbers.

Explain:
a)the trend shown by Li, Na and K. (1 mark) b)why the atomic radii of elements Be, Mg and Ca are lower than those of Li, Na and K. (2 marks)
21. On heating a pale green solid K, carbon (IV) oxide gas and a black solid M were formed. On reacting K with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon (IV) oxide gas and a green solution S were formed. When excess aqueous ammonia was added to solution S. a deep blue solution was formed.
a)Identify the cation in solid K. (1 mark)
b)Identify the two anions in solution S. (2 marks)
22. a) Name two ores from which copper is extracted. (1mark)
b)During extraction of copper metal, the ore is subjected to froth flotation. Give a reason why this process is necessary. (1mark)
c c)Name one alloy of copper and state its use. (1mark)
Alloy
Use
23. When l5cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, P, was burnt in 100cm-‘ of oxygen, the resulting gaseous mixture occupied 70cm-‘ at room temperature and pressure. When the gaseous mixture was passed through potassium hydroxide solution, its volume decreased to 25cm’.
a)What volume of oxygen was used during the reaction? (1mark)
b)Determine the molecular formular of the hydrocarbon. (2 marks)
24. A solution was made by dissolving 8.2g of calcium nitrate to give 2 litres of solution. (Ca = 40.0: N = 14.0; O = 16.0).
Determine the concentration of nitrate ions in moles per litre. (3 marks)
25) State and explain what would happen if a dry red litmus paper was dropped in a gas jar of dry chlorine. ( 2 marks)
26. By using aqueous sodium chloride. describe how a student can distinguish calcium ions from lead ions. ‘ (2 marks)
27. A student investigated a property of acids M and N by reacting equal volumes of acid M and N of the same concentration with equal volumes of 2M potassium hydroxide. The results were recorded in the table below.

(a) Which of the acids is likely to be a weak acid? Explain. (2 marks)
(b) Write the equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and potassium hydroxide. (1 mark)
28. A student investigated the effect of an electric current by passing it through some substances.

The student used inert electrodes. and connected a bulb to the circuit. The table below shows the substances used and their states.
Experiment: Substance State
1:Potassium Carbonate Solid
2 :Copper (II) sulphate Solution
:Sugar Solution
:Lead (II) iodide Molten
(a) In which experiments did the bulb not light? (1 mark)
(b) Explain your answer in (a) above. (2 marks)
29. A sample of hydrogen gas was found to be a mixture of two isotopes, ‘1-1and IH. I I Determine the relative molecular masses of the molecules formed. when each of these isotopes is burnt in oxygen. (O = l6.0)