
2019 Agriculture Paper 1
I. Name four aspects of rain fall that affects agriculture. (2 marks)
- Rainfall intensity
- Rainfall distribution/pattern
- Rainfall amount
- Rainfall reliability2. State four factors that determine the depth of cultivation. (2 marks)
- The type ot crop to be grown
- Type of implement used
- Soil moisture content
- Presence of hard pans
- Presence of underground obstacles
- Type of soil
- feed material eaten by the Animal3. State four factors that influence the quality of farmyard manure.(2 marks)
- Species of the Animal
- Type of bedding material/litter used
- Method of storage
- Age of the farm yard manure
- Age of the Animal which produces the waste materials
- Type of animal
- Per capita income4. State two factors that determine national income.(1 marks)
- Gross domestic product
- Gross national product
- Household firm relationship
- Natural resource endowment
- Shifting cultivation5. State four causes of land fragmentation. (2 marks)
- Inheritance of land
- Population pressure leading to purchase of small scattered pieces.
- Accumulation of land holdings by money lenders due to debtors failing to pay
- Settlement and resettlement6. Name two types of labour records.(2 marks)
- Muster roll
- Labour utilization analysis
- Storage pests7. State four ways in which crop pests are classified.(2 marks)
- Field pests
- Biting and chewing pests
- Piercing and sucking pests
- Rodents
- Insect pests
- Scientific classification
- Stage of development
- Stage of growth of the crop attacked8. What is the minimum number of people required to form a co-operative society in Kenya? (½ marks)
- Ten people9. Give two examples of fixed costs in maize production. (1 marks)
- Salaries of permanent workers
- Insurance
- Rent
- Standing charges of telephone
- Depreciation cost of farm machinery
- Cost of buying machinery10. What is meant by the term production function? (1 marks)
- It is the physical relationship between resource inputs and the corresponding output/product.11. State three characteristics of good trees for agroforestry.(1½ marks)
- Fast growth rates
- Deep rooted
- Nitrogen fixing
- Good in by product production
- Leafy
- Highly branched
- Hardy12. Name two varieties of sorghum grown in Kenya.(1 marks)
- Serena
- Dobbs
- Intama
- Humid
- Lulu13. State four reasons why agriculture is important to Kenya’s economy.(2 marks)
- Source of food
- Source of employment
- Provision of raw materials for industries Provide market for industrial goods
- Source of income14. Give two reasons why the use of fire is discouraged in land clearing.(1 marks)
- It kills soil micro-organisms
- Leads to loss of nutrients
- Destroys soil organic matter
- Leads to accumulation of ash that changes soil pH
- Destroys soil moisture
- Destroys soil structure15. State four ways in which mulching conserves water.(2 marks)
- Prevents splash erosion/intercepts rain drops Reduces speed of surface run offs
- Reduces evaporation
- Increases water holding capacity
- Improves water infiltration16. State four uses of fault records.(2 marks)
- Records help to compare the performance o1 different enterprises within a farm or other farms.
- They show the history of the farm.
- Guide a farmer in planning and budgeting of farm operations
- Help to detect losses or theft on the farm.
- Help in the assessment of income tax to avoid over or under taxation
- Help to determine the value of farm or to determine the assets and liabilities of the farm.
- Make it easy to share the profits and losses in partnerships
- Help in settling disputes among heirs to the estate when a farmer dies without leaving a will.
- Record help to show whether the farm business is making profits or losses.
- Help in insurance claims
- Provide labour information
- Help farmers to access credit17. State four characteristics of shifting cultivation.(2 marks)
- Movement/shifting when soil loses its fertility
- Practiced where land is plenty
- Practicable with annual crops not with perennials
- Agricultural output is low
- Inputs such as pesticides, fungicides are rarely used
- Simple hand tools are used
- Land communally owned
- Population is sparse
- Low number of livestock per unit area18. State the law of supply as used in agricultural marketing.(1 marks)As the price of a commodity increases the quantity offered for sale increases and as the price of commodity falls the quantity supplied declines.
19. State four ways in which trees improve soil productivity.(2 marks)
- Conserve moisture
- Improve soil structure
- Control soil erosion
- Contribute plant nutrients/organic matter
- Is a combination of chemical, physical, biological and cultural20. What is meant by the term integrated pest management? (2 marks)Pest control methods.
Section B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section
21. The diagram below illustrate a tomato fruit infested by a field pest

- (a) Identify the pest. (1 mark)American-bollworms(b) State two ways in which the pest is economically important. (2 mark)
- Reduces the quality of produce by boring holes on fruits
- Increase the cost of production by purchase of pesticide(c) State two cultural ways of controlling the pest. (2 mark)
- Early planting
- Field hygiene/Removal and destruction of affected crop residues
- Plant Mexican marigold in the field
- Destruction of alternate host
- Close season Crop rotation
- Intercropping22. The diagram below shows a weed

- (a) Identify the weed. (1 mark)Nut grass/sedge/Cyperus rotundus(b) Using features on the diagram, give two reasons why it is difficult to eradicate the above weed. (2 marks)
- It has underground nuts which regenerate.
- Produces many seeds to enhance survival chances(c) State two ways in which the weed is economically important. (2 marks)
- Competes for nutrients with crops greatly reducing yield
- Increases production costs
- Reduces quality of pastures/can damage the teeth of livestock
- Blocks irrigation channels23. The diagram below represent soil structures

- (a) Identify the soil structure labelled M, N and P.
- M — Prismatic structure
- N — Platy structure
- P — Granular structure(b) Name the type of soil where each of the structures labelled N and Q is found.
- N — Clay soil
- Q — Sandy soil24, The diagram below shows an illustration of a crop field practice.
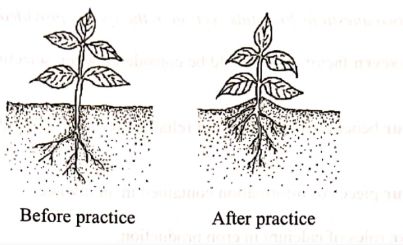
- (a) Identify the field practice illustrated above.(I mark)Earthing up;(b) Name two crops which require the practice illustrated.(2 mark)
- Groundnuts
- Potatoes
- Irish potatoes
- Sweet Potatoes
- Maize(c) Give two reasons for carrying out the practice on one of the crops you have named in (b) above. (2 marks)
- To improve tuber formation in Irish/sweet potato
- To encourage/improve seed formation in groundnuts
- To improve drainage and provide support in tobacco
- To provide support/prevent lodging in cereal crops like maize
- To prevent greening in root/ tuber crops;SECTION C (40 marks)Answer any two questions from this section
25. (a) Explain seven factors that should be considered when selecting seeds for planting. (7 marks)
- Adaptability — should be adapted to local ecological conditions
- Physical deformities/damages — should be free from physical deformities/damages Should be free from pests/diseases Viability/high germination percentage — should have high viability/ germination percentage
- Should be from high yielding/healthy plant early maturing
- Purity; should be clean/free from impurities
- Maturity; should be of correct maturity stage
- Age/storage period; seeds stored for long periods have low viability/germination percentage hence should not be selected
- Size of seeds; seeds should be of correct size(b) State four benefits of adequate and reliable rainfall in vegetable crop production. (4 marks)
- Ensures adequate supply of water to the crop Production/growing of vegetables is done throughout the year
- Controls pests in crop production
- Maximizes the utilization of available resources
- Increases yields and ensure a steady supply of food throughout the year
- Ensures a steady and reliable source of income and employment(c) State four pieces of information contained in an invoice.(4 marks)
- Date of the transaction
- Type of goods
- Quantity of goods
- Price of goods
- Total amount of money involved
- Invoice number
- Terms of payment
- Name of supplier
- Signature/stamp of supplier(d) State five roles of calcium in crop production.(5 marks)
- Calcium acetate strengthens plant cell wall
- Calcium is necessary in protein synthesis
- Promotes soil aggregate formation thus improving soil aeration, water infiltration and retention
- Calcium compounds when added to acidic soils they raise soil pH
- Increases cation exchange capacity
- Makes phosphorus and potassium available for plant uptake.
- Controls blossom end rot in tomatoes;26. (a) Describe how sugar cane is harvested.(5 marks)
- Harvest at the correct age 13 — 22 months for plant crops months for ratoon crop
- Take sugar cane samples for testing to determine maturity
- Cut the mature cane at the base/near the ground
- Cut off the green tops
- Strip off green leaves/using machete/bum before harvesting
- Deliver the cane to the factory within 48 hours/ immediately after cutting(b) Explain four factors that determine the nutrient content of hay.(4 marks)
- Stage of growth at harvesting time- cut when 50% has flowered
- Species of the forage crop used- rich in nutrients Duration of storage- long storage lowers the quality Weather conditions during drying- dry and sunny conditions produce high quality hay
- Length of drying period- rapid drying produces high quality Pest/disease attack on the crop- free from diseases
- Method of storage- store in a dry place under shade(c) State seven roles of a farm manager.(7 marks)
- Short term planning/making quick decisions in order to carry on t e activities in appropriate time and hence avoid a crisis
- Long term planning/making decisions which are linked to the future plans and operations on the farm
- Gathering and analyzing information related to the enterprises
- Detecting weaknesses and constraints and finding ways and means of overcoming them.
- Keeping farm records or accounts
- Guiding and supervising the farm management
- Bearing consequences/responsibility of plans/decisions
- Making predictions of the likely outcome of possible alternative courses of action
- Comparing ones enterprise with the set standards(d) Describe four methods used to reclaim a swampy land for agricultural production. (4 marks)
- Open ditches — U shaped, V-shaped, trapezoidal ditches are dug for excess water to flow away by gravity
- Underground drain pipes/perforated pipes are laid underground, excess water then seeps from the surrounding area into the pipes and flows to a water way
- French drains — ditches are dug, filled with stones and gravel and then covered with soil. Excess water from the surrounding area seeps into these drains and is carried away.
- Cambered beds — Raised beds are constructed to allow excess water to flow away in furrows.
- Pumping — is draining excess water from the swampy area using mechanical force.
- Planting of trees — e.g. Eucalyptus absorbs a lot of water from swampy areas.27. (a) Describe the production of carrots under the following subheadings:(i) land preparation (3 marks)
- land preparation
- Clear the bush/using a panga/slasher Remove stump
- Primary cultivation is done using jembe/ploughs
- Secondary cultivation/harrow to a fine tilth
- Avoid manure application to prevent forking(ii) planting (4 marks)
- Make drills 30cm apart and lcm deep
- Apply phosphates/DSP/DAP/MAP fertilizer during planting Sow seeds along the drills Cover with top soil
- Apply fertilizer at the rate of 90kg of DSP/DAP
- Plant at the onset of rains/when the soil has enough moisture
- Firm the soil after planting;(b) Describe six ways in which grass cover helps in soil and water conservation. (6 marks)
- Grass cover reduces the speed of run off which lowers the erosive power of run off
- Grass cover reduces/intercepts the impact of rain drops which reduces splash erosion
- Grass cover protects soil surface hence reducing wind erosion
- Gross cover holds soil particles together from being carried away by erosive agents The grass improves soil structure
- Grass cover improve infiltration rate of water
- Grass cover reduces the rate of evaporation of soil moisture.
- Grass filters trap soil(c) Explain seven nursery management practices. (7 marks)
- Mulching — A light mulch is applied on the nursery bed before seedlings emerge to conserve moisture and control erosion
- Watering — nursery bed is watered regularly in the morning and evening to ensure adequate water supply.
- Weed control- weeds are removed through uprooting to minimize competition with the crop
- Pricking out- overcrowded seedlings are removed and planted in a second nursery bed/seedling bed
- Shading — A light shade is erected over the nursery bed to protect young seedlings from excess sunlight/ rain drops that damage them.
- Pest and disease control – controlled through application of appropriate chemical/fungicides
- Hardening off — is gradual reduction of shade and watering 1 — 2 weeks before transplanting seedlings to acclimatize them to seed bed conditions
- Root trmming- cut at the tips to encourage lateral root development
- Application of foliar feed fertilizer to boost growth
- Removal of mulch after emergence to prevent etiolation
Share this:
