
2016 Agriculture Paper 1
No. 1.Name four rabbit breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
❖ New Zealand white/ Kenya white;
❖ California white;
❖ Flemish giant;
❖ Chinchilla;
❖ Rex;
❖ Angora;
❖ Ear lops;
No.2.Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock health: a) Disease (1 mark)
❖ Any deviation or alteration in the state of animal body or its organ which interferes with proper performance of its functions
b) Vaccination (1 mark)
Is the administration of a weakened or killed disease causing agent into the animal to induce production antibodies for immunity against the disease
No.3.State four advantages of artificial calf rearing in dairy cattle management.(2 marks)
❖ Farmer is able to keep accurate records of milk yield
❖ Easy to regulate the amount of milk taken by the calf
❖ cows produce milk even in the absence of the calves
❖ allows for maintenance of high standard of hygiene during milking
❖ There is a possibility of the farmer selling more milk thereby maximizing profits.
No.4.List four materials that can be used in constructing a Kenya Top Bar Hive.(2 mark)
❖ Timber
❖ Nails
❖ Plain wire
❖ Iron sheets
No.5.Give four features of housing that help to control livestock diseases (2 marks)
❖ Well ventilated
❖ Well lit
❖ Easy to clean
❖ Free from droughts
❖ Spacious
❖ Leakproof
❖ Proper drainage
No.6.State four characteristics of the Duroc Jersey pig. (2 marks)
❖ Long body
❖ Black in colour
❖ Drooping ears
❖ Is hardy;
No.7.Give four characteristics of a good site for a fish pond. (2 marks)
❖ Topography/ slope of land should be gentle sloping.
❖ Reliable water source.
❖ Area with cracks/ anthills should be avoided.
❖ Soil type/ site should be free of gravel/ stone/ sand/ preferably clay soil.
❖ Secure from predators and thieves.
❖ The site should be accessible.
No. 8.Name four systems of a tractor engine. (2 marks)
❖ Fuel systems,
❖ Lubrication system.
❖ Electrical system.
❖ Ignition system,
❖ Cooling system,
❖ Hydraulic system
❖ Power transmission system
No.9.What is dry cow therapy? (1 mark)
❖ The application of antibiotics into the teat canals of the cow’s udder after drying off the cow to prevent mastitis/ bacteria infection.
No.10. Give two reasons for steaming up in dairy cattle management. (2 marks)
❖ Ensures birth of a healthy calf
❖ Provides nutrients for maximum foetal growth
❖ Build up energy for parturition
❖ Increases and maintains high milk yield after birth/ stimulates development of alveoli
❖ Promotes good health of the cow / mother
❖ Accustoms the cow to concentrate feeding
No.11.State four maintenance practices for a disc plough. (2 marks)
❖ Cleaning after use
❖ Painting the frame
❖ Greasing the moving parts.
❖ Repair/ replace broken/ worn out parts.
❖ Metal parts on long storage.
❖ Proper storage
No.12. List four preventive measures for livestock diseases. (2 marks)
❖ Vaccination
❖ Proper feeding
❖ Quarantine imnposition
❖ Use of prophylactic drugs e.g. coccidiostaf
❖ Proper hygiene/ use of antiseptic/ disinfectants
❖ Treatment of sick animals; all aspects eg deworming. drenching
❖ Isolation of sick animals
❖ Proper selection and breeding
❖ Control of vectors
❖ Slaughtering sick animals /culling
No.13.Give two reasons for using litter in a poultry house. (1 mark)
❖ To keep the house warm.
❖ To absorb moisture from poultry droppings.
❖ Keeps birds busy scratching, thus reducing cannibalism.
No.14.State four disadvantages of fold system in poultry rearing (2 marks)
❖ Few birds per unit area.
❖ Laborious in moving the folds.
❖ Difficult to keep individual bird production records.
❖ Produces dirty eggs.
❖ Fold breaks easily due to constant movement.
No.15.State four practices that come immediately after complete milking in a milking shed (2 marks)
❖ Teat dipping to control mastitis
❖ Weigh and record milk yield
❖ Sieve/ strain/ filter milk
❖ Application of milking jelly on teats
❖ Store milk in a cool place
❖ Clean the milk shed
❖ Release the animal
❖ Clean the milk equipment
No.16.List four tools that are used when laying concrete blocks during construction of a wall. (2 marks)
❖ Plumb bob/ plumb line
❖ Mason’s trowel
❖ Spirit level/ pipe level
❖ Wood float/ steel float
❖ Masons square
❖ String/ masons line/ line
No.17 Below is a diagram illustrating an instrument used in cattle breeding.
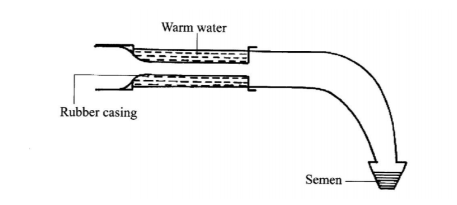
(a) Identify the instrument (1 mark)
❖ Artificial vagina
(b) State the role of the instrument in cattle breeding. (1 mark)
❖ Collection of semen from bulls
(c) When would it be appropriate to serve a cow after the onset of heat? (1 mark)
❖ Between 12-18 hours/at standing heat
(d) Apart from the method in which the above instrument is used, name two other methods of serving a cow. (2 marks)
❖ Natural mating
❖ Embryo transplant;
No.18.The diagram below is an illustration of an egg. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.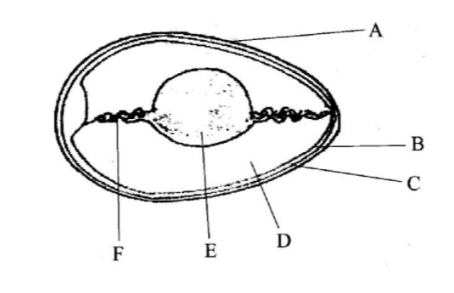
a)Name the parts labeled B,C,D and F
❖ B -Inner shell membrane
❖ C -outer shell membrane
❖ D -Albumen/ egg white
❖ F – Chalaza
(b)State two qualities of the part labeled A that should be considered when selecting eggs for incubation.
❖ Texture/ smoothness of the shell
❖ Absence of cracks on the shell
❖ Cleanliness/ absence of the shell
❖ Cleanliness/ absence of blood stains
❖ Oval in shape.
(c)What is the function of the part labeled E in a fertilized egg? (1 mark)
❖ Provides nutrients for the developing embryo/ chick.
No.19 .The photograph below illustrates a method of identification labeled X in cattle.

a) Name the identification method (1 mark)
❖ Branding
b) Explain three disadvantages of the identification method. (3 marks)
❖ Reduces quality of hides/ skins/ because the heat damages the skin/ hide
❖ Causes the animal a lot of pain because it uses heat
❖ Causes wounds which can result in infections
No.20 .Below is a diagram illustrating a farm implement. Study it and answer the uestions that follow.

a) Identify the implement illustrated above
❖ A Ridger/ mould board ridger.
b) State the use of the:
i) Implement on the farm
❖ To make ridges/ furrows
ii) Part of the implement labelled j
❖ used to attach the implement to a tractor.
❖ Adjusting the depth of operation.
No.21.Below is a diagram of a knapsack sprayer. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow

(a)Name the parts labeled N, P, Q and R.
❖ N – Tank
❖ P – Delivery note rej.
hose pipe/ hose alone
❖ Q – trigger
❖ R – Lance (2 marks)
(b) State one function of the part labelled S (1 mark)
❖ Breaks the liquid chemical into desired size of droplets/ spray form/ fume droplets/jets
No.22(a).(i)Describe short-term tractor servicing. (10 marks)
❖ The engine should be checked daily by use of dip stick and oil level maintained;
❖ The fuel level should be checked at the start of everyday’s work and added if necessary;
❖ Water level in the radiator should be inspected and if low topped up;
❖ The level of electrolyte should be checked daily and topped up with distilled water if low
❖ The nuts and bolts should be tightened every day;
❖ Grease should be applied regularly to the moving parts;
❖ Large sediments from the sediment bowl should be removed;
❖ Tyre pressure should be checked every morning before the day’s work and
❖ adjusted accordingly;
❖ The fan-belt tension should be checked to ensure that it deflects between o cm – 2.5 cm when pushed;
❖ The brake shaft bearing should be greased and break fluid level maintained;
❖ Lost bolts and nuts are replaced.
(ii) Explain the maintenance practices that should be carried out on an ox-cart.(5 marks)
❖ Moving parts should be oiled/ greased regularly to reduce friction (tear and wear);
❖ The yoke should be properly maintained eg. repair when worn out, replaced if not repairable, properly padded;
❖ Tyre pressure should be checked daily before the start of work;
❖ Broken trailer bodies should be repaired;
❖ Loose nuts and bolts should be tightened;
❖ Paint it if to be stored for long to avoid rusting;
❖ Clean after use;
❖ Store under shed;
❖ Replace lost nuts and bolts;
No.22b.State five indicators that can be observed on a goat to confirm sickness. (5 marks)
❖ By checking the appetite and feeding – if low or excessive it indicates that the goat is sick
❖ Defaecation – inconsistency in texture, colour, smell, frequency and posture, presence of arasite segments, egg, larvae or blood
❖ Urination – irregular posture, colour and and frequency;
❖ Change in temperature above or below the normal range;
❖ Respiratory rate – irregular respiration shown by non-rhythmic inspiration and expiration indicates ill health.
❖ Pulse rate – Abnormal pulse rate under normal physiological status indicates ill- health.
❖ Production level – Loss of weight, emaciation and reduced production rate. Abnormal discharges
❖ Posture – while standing or lying.
❖ Behaviour eg. abnormal sound, aggression, excitement.
❖ Appearance – eg. dullness, restlessness, pot belly, bloated.
❖ Movement eg. gait, eg, standing or limping when walking.
❖ Mucuors membranes (abnormal) eg. bright red colour, yellowish, blueish depending on disease.
❖ Skin/ animal coat – (abnormal) starring hair, coat, sores/ wounds on skin.
No.23a.Describe the uses of fences on the farm. (10 marks)
❖ Mark boundaries.
❖ Help to avoid boundary disputes
❖ Keep off wild animals and intruders from outside the farm.
❖ Enable the fanner to practice mixed farming.
❖ Facilitates rotational grazing
❖ Controls movement of animals and people preventing formation of unnecessary paths in the farm.
❖ Control the spread of parasites and diseases by keeping off wild and stray animals the farm.
❖ Help the farmer to isolate or confine animals requiring special attention.
❖ Enable the farmer to control breeding by rearing different animals in different paddocks.
❖ Hedges act as windbreakers.
❖ Adds beauty to the farm,
❖ Add value
❖ For privacy
No.23b Give five harmful effects of liver flukes in sheep rearing. (5 marks)
❖ Digestive upsets due to blocking of bile duct.
❖ Emaciation/ recumbency leading to death
❖ Anaemia due to destruction-of-liver tissues
❖ Swollen lower jaw/ Oedema in the jaws.
❖ Swollen abdomen.
❖ Destruction of liver tissues /haemorrhage
No.23c.Explain the factors considered when culling livestock. (5 marks)
❖ Poor health;
❖ Old age;
❖ Physical deformities;
❖ Hereditary defects;
❖ Infertility;
❖ Poor mothering ability
❖ Poor quality products
❖ Low production;
❖ Bad temperament.
❖ Avoid inbreeding
No.24a .Combs and wattles – small/shrivelled/shrunken. Dry scaly and place.
❖ Eyes – dull and pale yellow.
❖ Beak – yellowish in colour.
❖ Abdomen/ breast – hard and full
❖ Vent – round, dry and less active
❖ Space between kee and pelvic bone – small and fits only one or two fingers
❖ Plumage – preened & glossy (smooth) beautiful
❖ Moulting – early moulting
❖ Shanks/ feet – Yellowish in colour
❖ Broodiness – Is common/ early moulting
❖ Temperament – easy and dull
No.24bi. Outline three characteristics of clean milk.
❖ Free from disease causing micro-organisms/pathogens
❖ Free from hair, dirt or dust.
❖ Free from bad odours and tastes/ has good flavours.
❖ Chemical composition within expected standards.
No.24bii . Explain seven factors that affect milk composition in dairy farming. (7 marks)
❖ Age of animal – Butter fat in milk becomes less as an animal grows old thus young animals produce milk with higher BF than older animals.
❖ Breed differences e.g. Species of the animal
❖ Different breeds of cattle produce milk with differing percentage composition e.g Jersey produce higher BF than Friesian.
❖ Type of wood eaten by an animal – Roughage feeds produce link with higher fats, lactose and protein compared to grains.
❖ Diseases – Diseases such as mastitis reduce the lactose composition in milk because bacteria attack milk sugars.
❖ Physiological condition of the animal – Sick/ extremely emaciated animals register low percentage of BF/ during late pregnancy, cows produce milk with low BF content.
❖ Stage of lactation – The BF content in milk is highest at the middle phase of the lactation period and lowers towards end of lactation.
❖ Completeness of milking – Milk drawn last from udder during contains high BF content/ last drop milk has BF content produce in the milk.
❖ Season of the year – accept environmental condition. BF content increases during cold seasons.
❖ Time of milking – Milk produced in the morning has a lower BF content than milk produced in the evening 1/2 factor method
