Processes operating in the interior of the earth resulting in the formation of natural physical features or landforms.
They are caused by earth movements.
Examples of these processes are folding, faulting and Vulcanicity.
Formation of land forms by internal land forming processes is determined by:
- Nature and age of earth materials
- Type of movement involved
- Intensity and scale of movement involved
Crustal Earth Movements
Displacement of the earth’s crustal rocks.
They are brought about by tectonic forces which originate and operate in the interior of the earth e.g. tensional forces (which operate along horizontal plane moving away from each other), compressional forces (which operate along horizontal plane moving towards each other), shear forces (which move past each other with unequal strength) and gravitational forces (which attracts things to the earths centre).
Earth movements are of 2 types:
- Horizontal/lateral/orogenic movements
- Vertical/epeirogenic movements
Horizontal Earth Movements
Movements which act along a horizontal plane within crustal rocks.
They are caused by tensional and compressional and shear forces.
Effects
They cause:
- Strain and stretching of crustal rocks due to stretching caused by tensional forces which cause formation of cracks or faults.
- Squeezing and shortening of crustal by compressional forces rocks which cause them which also cause formation of faults.
- Crustal rocks to shear by slipping past each other or by dividing into layers which is caused by shear forces.
Results of Horizontal Earth Movements
results in the formation of the following features:
- Faults Escarpments
- Rift valleys Basins
- fold mountains Tilt blocks
- Block mountains
Vertical Earth Movements
Movements which occur along the earth’s radius or towards the earth’s surface or towards its centre.
Effects Causes:
- Subsiding/sinking/downwarping or pulling of crustal rocks downwards.
- Uplifting/upwarping or pushing of crustal rocks upwards
- Tilting of crustal rocks or shearing in vertical direction due to grater uplift on one side.
Results of Vertical Earth Movements
- Raised cliffs Plateaus
- Tilt blocks basins
- Rift valleys
- Fault scarps/escarpments
Causes of Earth Movements
- Magma movement within the earths crust.
- Gravitational force
- Convectional currents in the mantle
- Isostatic adjustment
1. Magma Movement within the Earths Crust
- When magma moves with force pushing crustal rocks horizontally or vertically.
- When magma moves from reservoir and leaves empty spaces onto which crustal rocks are pulled inwards.
2. Gravitational Force
When the attractive force of the earth pulls crustal rocks into empty spaces left after magma escaping from the reservoir.
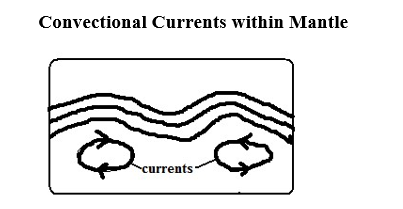
When convectional currents in magma in mantle drug crustal rocks by friction. Horizontal movement of currents cause horizontal movements while vertical cause vertical movements.
Isostatic Adjustment
Rising of continental masses to restore the upset state of balance between sial and sima layers.
Isostacy is the state of balance between sial and sima layers.
It can be disturbed by erosion on continents and melting of continental ice sheets.
The reduced weight causes continental masses to rise.
Theories Explaining the Earths Movements
A theory is reasoned ideas intended to explain facts or ideas. There are 2 theories which explain the earth’s movements namely the Continental Drift Theory and the Plate tectonics theory.
Theory of Continental Drift
Its proponent was A. Wegener.
It explains the origin of 6 continents.
It states:
- The earth was a single sialic land mass called Pangaea surrounded by a huge ocean called Panthalasa whose floor was a mass of sima.
- Pangaea broke into two parts called Laurasia (N. Hemisphere) which lay around equator and Gondwanaland (S. Hemisphere) which lay around south pole which were separated by a narrow ocean called Tethys (the present Mediterranean Sea).
- Laurasia broke into Laurentian Shield and Fennoscandia (Europe, Asia and N. America) and moved northwards to their present positions.
- Gondwanaland broke into Africa, Australia, S. America and Antarctica and India subcontinent.
- Africa and India drifted northwards.
Evidences Supporting the Theory
- Fitting of western coast of Africa and S. America into a jigsaw.
- Discovery of coal 40◦N and 55◦N which was formed by burying of tropical vegetation.
- Considerable displacement of rocks along some faults e.g. along the Great Glen Fault of Scotland.
- Cape and Buenos Aires folds resemble one another by having east west trend.
- Red sea shores show evidence of having undergone lateral displacement an indication that it was formed by movement of the earth’s crust.
- Evidence of ancient Glaciation to the south of equator in Africa in Madagascar and India where there is presence of ancient glacial deposits suggesting these areas were once around south pole.
Plate Tectonics Theory
It states that:
The earths crust is made of blocks called plates.
7 Large Ones
- Eurasian plate N. American plate
- Australian plate S. American plate
- Africa plate Pacific plate
- Antarctic plate
Smaller Ones
- Indian
- Arabian
- Caribbean Nazca
- Cocos Philippine
- Somali plates Scotia
- Juan de Fuca
- These plates are two types : tectonic plates:
- Oceanic plates which form major areas of the ocean floor including coastal lowland.
- Continental plates which form the bulk of the continental land mass.
- The plates float on molten mantle layer called
- The plates move relative to each other due to convectional currents in the mantle.
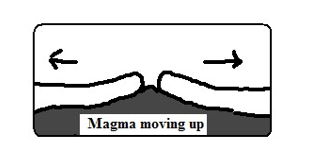
- They move away from each other forming extension or constructive boundary called so because magma fills the space between.
- They move towards each other forming compressional or destructive boundary called so because materials between are crushed. The movements of those two types of plates have the following effects:
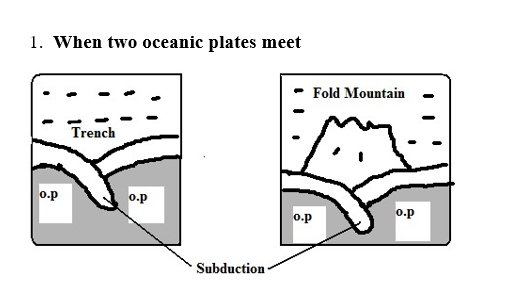
- There is subduction and the ocean floor is pulled inwards forming a trench e.g. Java Trench .
- Subduction is the passing of edge of one plate beneath the edge of another.
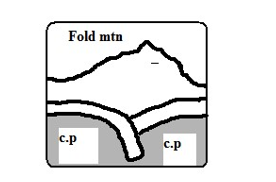
- Sediments on the sea floor in the region of subduction are compressed to form Fold Mountains.
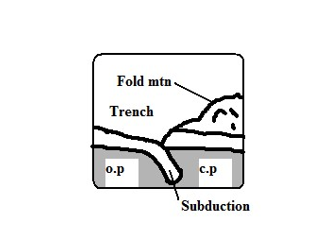
When an oceanic plate meets a continental plate the edge of the oceanic plate slides beneath the continental plate in a movement called subduction.
- Sediments on the sea floor in the region of subduction are compressed to form Fold Mountains.
- Fold Mountains are also formed at the edge of the continent when the sial layer is compressed.
- The edge of the oceanic plate bends into the mantle forming a trench.
When two continental plates collide the sial layer is folded into mountains.
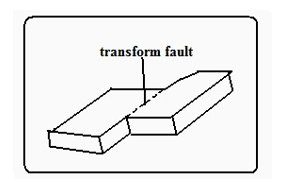
- They move past each other forming transform or conservative boundary called so because there is neither construction nor destruction which occurs where the plates are separated by a major fault.
Significance of Plate Movements
- Are sources of earthquakes and Vulcanicity.
- Causes formation of land forms such as Fold Mountains and ocean trenches.
- Spectacular landscapes formed are a tourist attraction.
- Eruption of magma can result in formation of valuable minerals.
