OVERVIEW OF INFORMATION SYSTEM
Information system, an integrated set of components for collecting, storing, and processing data and for providing information, knowledge, and digital products. Business firms and other organizations rely on information systems to carry out and manage their operations, interact with their customers and suppliers, and compete in the marketplace.
An information system can also be defined as a set of interrelated and interdependent components working together to collect (or retrieve), process, store, and distribute information to support decision making in an organization.
It is a combination of hardware software and telecommunication networks to collect create and distribute
useful data typically in an organization setup.
Information system may also help managers and workers to analyze problems, visualize complex subjects and create new products.
Business System – A business system is defined as a combination of related subsistence consisted of a series of operations arranged in a logical sequence to achieve a particular purpose.
As information systems enabled more diverse human activities, they exerted a profound influence over society. These systems quickened the pace of daily activities, enabled people to develop and maintain new and often more-rewarding relationships, affected the structure and mix of organizations, changed the type of products bought, and influenced the nature of work. Information and knowledge became vital economic resources. Yet, along with new opportunities, the dependence on information systems brought new threats. Intensive industry innovation and academic research continually develop new opportunities while aiming to contain the threats.
A system can be defined as a collection of procedures, activities working together to achieve a common objective. Can also be defined as an organized interactive and interdependent set of components working together to achieve the same goal.
Data – Raw facts and figure about a particular subject or entity. It needs to be processed before it can be turned to something useful. Data comes in many forms-numbers words, symbols. Data relates to transactions, events and facts.
Information -Information is data that has been processed in such a way as to be meaningful to the person who receive it.
Qualities of good information
i. It should be relevant i.e. it should be applicable for the purpose intended.
ii. Completeness- Information should contain all important facts.
iii. Accuracy – Information should be correct and without errors.
iv. Cost Effective – Benefit of particular information must exceed the cost of collecting information.
v. Timeliness – It should be available when required.
vi. Secure – Information should be protected against unauthorized users;
vii. Availability- It should be accessible to those who need it.
viii. Flexibility-Information should be applicable in a number of ways.
1. Structured or Programmed Decision: These are decision made on the basis of predetermined set of rules and procedures. I.e. rules and procedure are known in advance. No human judgment is required and they apply to the low-level operational managers.
2. Non-Programmed / unstructured Decisions: These are non-routine decisions which are not made based on predetermined rules and procedures. They require the use of human judgment and are made
by the top-level managers. Decisions made in this case are long term decisions.
3. Semi-structured decision: These are partially programmed and partially non-programmed decision. They involve the element of human judgment and sometimes use predetermined or predefined set of procedures. An example would be pricing would be pricing, production etc.
Level of Management
There four levels of management
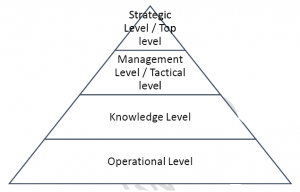
Strategic Level Management / top level Systems
They require Strategic information which they use to determine the resources the organization employs and how they have been employed. They are mainly concerned with long term planning and making strategic decision. They help managers to tackle and address strategic issues of long-term values within the organization and the external environment.
Management level / Tactical level System
They require tactical information which they use to determine how the resources of an organization should be employed and to monitor how they have been employed. They serve controlling, monitoring, decision making and administrative function within an organization. Their duty is to oversee supervisor and to make tactical decisions.
Knowledge level system
They support organization knowledge and data workers. They help businesses to integrate new knowledge and help control the flow of paperwork.
Operational level systems
They keep track of elementary or basic activities in an organization e.g. Sales, periodic decisions, flow of money in and out, production schedules, order processing etc.

One thought on “INFORMATION SYSTEM IN AN ENTERPRISE”
Comments are closed.