Once the project has been planned and the project proposal has been developed and accepted and required funds or resources obtained the challenges ahead is project Implementation.
The challenge is to undertake project activities with the budget time schedule and the scope ‘’’ the objective have been achieved and these objective can be sustained after the project is terminated.
The activities in project implementation include building deliverable monitoring , controlling , time management , cost management, procurement management , risk management and quality management.
Steps
- Prepare for project formulation and implementation involves the following
- Obtaining approval of the project proposal document g. donor , government.
- Selecting and appointing the project team leader who will assume responsibility for subsequent for the following steps of implementation.
- Recruit the staff g. secret a project and recruit member staff.
- Prepare operational budget for the first phase of the project.
- Order equipment and supplies which are known to take a long time to procure.
Importance of keeping records for implementation purpose.
- Account of programs kept in an orderly way. To measure the progress of the concern or to find our certain other facts , a history of the firm is needed . the past record , history of the project , recount the dealings.
- Proper study of the position of the project . the preserved record are the contributory factors without which a good proper study of the position of the firm cannot be made and statement cannot be prepared.
- Comparison of project. past record make it easy and possible to compare the performance of one period with that of another period by comparison , one can know there is progress or not.
- Policy making. Past record , events , progress etc are very necessary to decide future policies and lans . in the absence of record the policies and plans may not be successful.
- Legal requirement. Certain records are to be kept for a number of years from the legal point of view.
- Evidence . records are good evidence in the court of law, in the case of suit.
Revision questions.
- What is project implementation?
- Describe project implementation process?
- Explain the importance of keeping records for implementation purpose.
- Importance of keeping records for implementation purpose.
- Account of programs kept in an orderly way. To measure the progress of the concern or to find our certain other facts , a history of the firm is needed . the past record , history of the project , recount the dealings.
- Proper study of the position of the project . the preserved record are the contributory factors without which a good proper study of the position of the firm cannot be made and statement cannot be prepared.
- Comparison of project. past record make it easy and possible to compare the performance of one period with that of another period by comparison , one can know there is progress or not.
- Policy making. Past record , events , progress etc are very necessary to decide future policies and plans in the absence of record the policies and plans may not be successful.
- Legal requirement. Certain records are to be kept for a number of years from the legal point of view.
- Evidence records are good evidence in the court of law, in the case of suit.
Implementation purpose.
PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS
1. Organizing
In order to implement the plans a sound organization structure is required. Organizing is the process of allocating tasks among the members of the group, establishing authority-responsibility relationships among them and integrating their activities towards the common objectives.
Job description
The data is collected through job analysis provides the basis for preparing job description and job specification. Job description is a functional description of what the job entails. It is descriptive in nature and defines the purpose and scope of a job.
Job description is a written record of the appropriate and authored contents of a job, it is a factual and organized statements describing the job in terms of its title, location duties, responsibilities , working conditions, hazards and relationship with other job.
The main object of a job description is to differentiate it from other jobs and to set out its outer limits.
Uses of Job description
- Job grading and classification.
- Placement of new employees on a job.
- Orientation of new employees towards basic duties and responsibilities.
- Promotion and transfer.
- Definition and outlining care paths.
- Redressed of grievances relating to duties and responsibilities.
- Work measurements and work improvement.
Contents of Job description
- Job identification- Job title, code number of the job, department or divisions where the job is located.
- Job summary – It describes the contents of a job in terms of the activities or task performed.
- Job duties and responsibilities. – It is the heart of job description. It describes the duties performed along with frequency of each major duty.
- Working condition- The physical environment of the job is described in terms of heat, light, noise level, dust and fumes.
- Social environment – size of work group and inter-personal interaction required to perform the job given.
- Machines, tools and equipment – the names of major machines, equipments and materials used in the job are described.
- Supervision – The extent of supervision given or received is stated in terms of number of persons to be supervised along with their job
Relation to other jobs – the jobs immediately below and above is mentioned. It provides an idea of vertical workflow and channels of promotion
2. STAFFING
RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION
Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating and encouraging them to apply for jobs in an organization.
Features of recruitment
- Recruitment is a process or a series of activities rather than a single act or event.
- Recruitment is a linking activity as it brings together those with jobs (employer) and those seeking jobs (employees)
- Recruitment is positive functions as it seek to develop a pool of eligible persons from which most suitable ones can be selected.
- Recruitment is an important faction as it makes it possible to acquire the number and type of persons necessary for the continued functioning of the organization.
- Recruitment is a pervasive function as all organization engages in recruiting activity.
- Recruitment is a two way process.
Steps in Recruitment process
- Recruitment process generally begins when the personnel department receives requisitions for recruitment form any department of the company. The personnel requisition contain details about the position to be filled, number of persons to be recruited , the duties to be performed, qualification required from the candidate, terms and condition of employment and time by which the person should be availed for
- Location and developing resources of required number and type of employees.
- Identifying the process drive employees with required characteristic.
- Communicating the information about the organization, the job and the terms and condition of service.
- Encouraging the identified candidates to apply for jobs in the organization.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of recruitment process.
Source of Recruitment
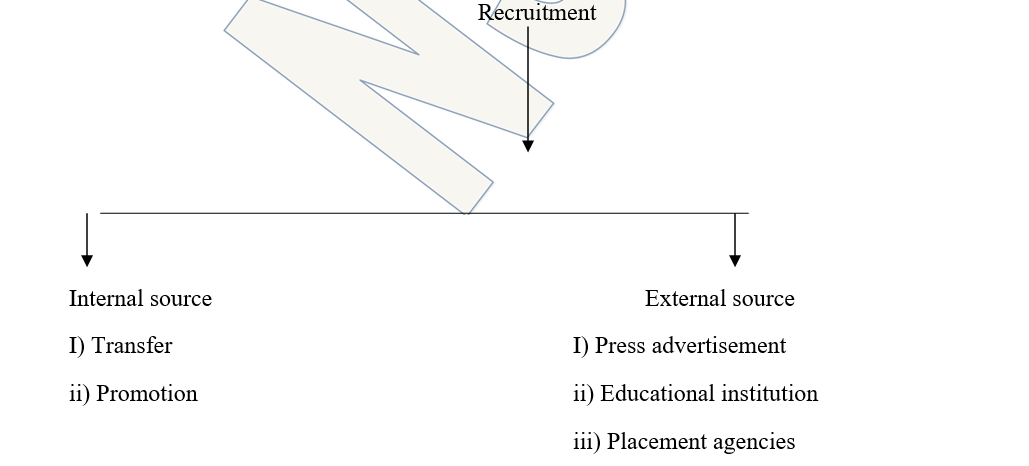

Internal sources
- Present employees – Permanent, temporary and casual employees, vacancies may be filled up from such employees through promotion, transfer, upgrading and even demotion.
- Retired and retrenched employees who want to return to the company may be retired.
- Dependent and relatives of deceased and disabled employees.
Advantages of internal source
- Morale and motivation of employees improve when they are assured.
- Suitability of existing employees can be judged better as records of their qualification and performance is already available in the organization.
- It promotes loyalty and commitment among employees due to sense of job security and opportunities for advancement.
- Present employees are already familiar with the organization and its policies.
- The time and expenditure of recruitment are reduced as there is little need for advertising vacancies.
- Relation with trade unions remains good because union prefer internal recruitment.
- Filing of higher levels job through promotions within the organization helps to retain talented and ambitious employees.
Disadvantaged of internal recruitment
- It may lead to inbreeding
- It discourages flow of new blood into the organization.
- If promotion is based on seniority, really capable persons may be left out.
- Choice in selection is restricted more talented outsiders may not be employed, mobility of labour is restricted.
- Chances of favoritism are higher and growth of business is restricted by the limited talents of insiders.
- This source of recruitment is not available to a newly established enterprise.
Internal sources
- Educational and training institutions- Various institutes like Aims, Its engineering colleges, medical colleges. They provide facilities for campuses interviews and placement.
- Recruitment Agencies – Several private consultancy firms perform recruitment function on behalf of clients companies by charging fee.
- Employment exchange- these exchanges provide information about job vacancies to the job seekers and help employers in identifying suitable candidates.
- Press advertisement- Advertisement in newspaper and journals is a wide source of recruitment.
Advantages of External recruitment
- People having the requisite skills, education and training can be obtained.
- As recruitment is done from a wider market best selection can be made irrespective of caste, sex or religion.
- Expertise and experience form other organization can be brought.
- It helps to bring new bulled and new ideas into the organization.
- This source of recruitment never dries up it is available to even enterprises.
Disadvantages of eternal recruitment
- It is more expensive and time consuming to recruiter people from outside.
- The employee being unfamiliar with the organization their orientation and training is necessary.
- If higher levels jobs are filled from eternal sources motivation and loyalty of existing staffs are affected.
Sources of recruitment can be evaluated and the most appropriate source can be chosen on the basis of the following criteria.
- Time lag between personnel requisition and placement.
- Field rationale number of applications divided by the number of persons selected.
- Employee reaction towards different sources of recruitment.
- Correlation between source of recruitment and job success of the persons selected.
- Data on labour turnover.
- Cost per for different sources of recruitment.
Methods of Recruitment
- Direct Method – Under direct recruitment scouting employee contacts, manned exhibits and waiting list are used. In scouting representatives of the organization are sent to educational and training institutions. These traveling, recruiters exchange information with the student clearly their doubts, stimulate them to apply for jobs conduct interview and shortlist candidates for further screening.
- Indirect method – Advertisement in newspapers journals on the radio and television are used to publicize vacancies. A well thought out and clear advertisement enables candidates to assess their suitability so that only those possessing he requisite qualification will apply.
- Third party method – Various agencies can be used to recruit personnel
SELECTION
Selection is the process of choosing the most suitable person out of all the applicants. In this process relevant information about applicants is collected through a series of steps so as to evaluate their suitability for the job to be filled.
Selection is a process of matching the qualification of applicants with the job requirements.
Selection procedure
- Preliminary interview- Initial screening is done to weed out totally undesirable/unqualified candidates at the outset.
Preliminary interview is essentially a sorting process in which prospective candidates are given the necessary information about the nature of the job and the organization.
- Application Blank- Application form is a traditional and widely used devise for collecting information from candidates. The applicant form should provide all the information relevant to selection…
- Selection test- Psychological test are being increasingly used employee selection- a test is a sample of some aspect of an individual‘s attitudes, behavior, and performance.
It also provides systematic basis for comparing the behavior, performance and attitudes of two more persons.
- Employment interview- an interview is a conversation between two persons. In selection it involves a personal observational and face to face appraisal of candidates for employment.
Selection interview serves three purposes.
- Obtaining information about the background, education, training work history and interest of the candidates.
- Giving information to candidates about him specific job and personnel policies.
- Establishing a friendly relationship applicant to work for the organization.
- Medical examination- applicants who have crossed the above stages are sent for a physical examination either to the company’s physician or to a medical officer approved for the purpose.
- Reference Checks- The applicant is asked to mention in his application form the names and addresses of two or three persons who know him well.
- Final approval – In most of the organizations selections process is carried out by the human resource department. The decision of this department is recommendatory. The candidates short listed by the department are finally approved by the executives of the concerned departments.
TRAINING AND DEVELOPING STAFF
Training is the process of increasing the knowledge and skills for doing a particular job . It is an organized procedure by which people learn knowledge and skills for a definite purpose. The purpose of training is basically to bridge the gap between job requirement and present competence of an employee.
Need for training
Training is requiring on account of the following reasons:
- Job requirement- Employees selected for a job might lack the qualification required to perform the job effectively. New and inexperienced employees require detailed instructions for effective performance on the job.
- Technological changes – Technology is changing very fast. Now automation and mechanization have are been increasingly applied in offices and service sector.
- Organisational viability – In order to survive and grow, an organization must continually adopt itself to the changing environment. With increasing economic linearization and globalization, business firms are experiencing expansion growth & diversification.
- Internal mobility – Training becomes necessary when an employee moves from one job to another due to promotion and transfer.
Advantages of training
- Higher productivity- Training helps to improve the level of performance. Trained employees perform better by using better method of work.
- Better quality of work – Informal training , the best methods are standardized and taught to employees.
- Cost reduction – Trained employees make more economical use of materials and machinery .
- Reduced supervision– Well trained employees tend to be self –reliant and motivated.
- Low accident-rate – Trained personnel adopt the right work method and make use of the prescribed safety devices
Reasons for training
- The installation of new equipment or techniques which require new or improved skills.
- A change in working method.
- A change in product , which may necessitate training
- A realization that performance is inadequate.
- Labour shortage, necessitating the upgrading.
- A desire to reduce the amount of accidents.
- Promotion or transfer of individual employees
Benefits of training
Training is useful to employees in the following ways.
- Self confidence- Training helps to improve the self confidence of an employee.
- Higher earnings- Trained employees can perform better and herby earn more .
- Safety – Training helps an employee to use various safety devices. We can handle the machines safety and become less prone to
- Adaptability- Training enables an employee to adopt to changes work procedures and methods.
- Promotion – Through training employees can develop himself and earn promotions.
Types of Training
- Orientation training
Induction or orientation training seeks to adjust newly appointed employees to the work environment. Every new employees need to be made fully familiar with his job, his superior and subordinates.
- Job training – It refers to the training provided with a view to increase the knowledge and skills of an employee for improving performance on the job.
- Safety training – Training provided to minimize accidents and damage to machinery. It involves instruction in the use of safety devices and in safety consciousness.
- Promotion training – It involves training of existing employees to enable them to perform higher-level job.
- Refresher training – When existing techniques become absolute due to the development of better techniques employees have to be trained in the use of new methods and techniques with the passage of time employees may forget some of the methods of doing work. Refresher training is designed to revise and refresh the knowledge and to update the skills of the existing employees.
- Remedial training – Such training is arranged to overcome the shortcoming in the behavior and performance of old employees.
Identifying training needs
- Organisational analysis– It involves a study of the entire organization in terms of its objectives, its resources allocation and utilization, growth potential and its environment. Its purpose is to determine where training emphasis should be placed within the organization
- Tasks or role analysis
It is a systematic and detailed analysis of job to identify job content the knowledge, skills and aptitudes required and the work behavior. On the art of the job holder particular attention should be paid to the tasks to be performed, the methods to be used, the way employees have learnt these methods and the performance standards required of employees.
- Manpower analysis.
In this analysis the persons to be trained and the changes required in the knowledge, skills and aptitudes of an employees are determined . First, it is necessary to decide whether performance of an individual is substandard and training is needed. Secondly it is determined whether the employees are capable of being trained. Thirdly the specific areas in which the individual requires training will improve the employees performance or not is determined.
Objectives of training
- To impart to new entrants the basic knowledge and skills required for efficient performance of definite
- To assists the employees to function more effectively in their present position by exposing them to the latest concept, information and techniques & developing skills they would require in their particular
- To build up a second line of competent officers and prepare them to occupy more responsible
- To broaden the minds of senior managers through interchange of experience within and outside so as to correct out loaded caused to over specialization
Training methods & Techniques
- On-Job-Training (OJT)- In this method the trainee is placed on a regular job and taught the skills necessary to perform The trainee learns under the guidance and supervision of the superior or an instructor.
Advantages of On Job Training
- The trainee learns on the actual machine in use and in the real environment of the job thus he is better motivated to learn and there is no problem of turnover of training skills to the job.
- This method is very economical because no additional space, equipment, personnel or other facilities are required for training .
- The trainee learns the rules and regulation and procedures by observing their day to day
- This is the most suitable method for teaching knowledge and skills which can be acquired through personal observation in a relatively short time
- Line supervisors take an active part in training their subordinates .
Disadvantages of On-Job training
- The learner finds it difficult to concentrate due to noise of the actual workplace.
- This method is often haphazard due to noise of the actual work-place.
- In this method the trainee may cause damage to costly equipment and materials.
Vestibule training–
In this method a training centre called vestibule is set up and actual job conditions are duplicated.
Advantages of vestibule training
- Trainee can concentrate on learning without disturbance of the work place noise.
- The interest and motivation of the trainee are high as the real job conditions are duplicated.
- This method is essential in cases, where on the job training might result in a serious injury, costly event or the destruction of valuable equipment and materials.
- Correct method can be taught effectively by the trained instructor who knows how to teach.
- It permits the trainee to practice without the fear of being observed and indicated by the superior .
- It is very efficient method of training a large number of employee works.
Disadvantages vestibule training.
- It is the most expensive method because of additional investment in classroom,, equipment and experts trainers.
- Training situations is somewhat artificial and the trainee does not get a feel of the real job.
- Separation of training from the supervisory responsibilities may lead to problems in the organization.
Apprenticeship Training
In this method theoretical instruction and practical learning are provided to trainees in training institutes.
Advantages of apprenticeship training.
- The main advantages of this method are that it combines theory and practice.
- The trainee acquires skills which are valuable in the job market.
- Apprenticeship programmed provide skilled workforce to industry.
Disadvantages of apprenticeship training
- Apprenticeship training is time consuming and expensive .
- Many persons leave the training programmed midway as the training period ranges from one year to five years.
- Apprenticeship training is the oldest method of training.
Principles of training
The following guidelines can help to make training more effective.
- Clear objective- The objective and scope of a training programmed should be clearly defined.
- Training policy a clearly defined training policy serves as a guide for designing and implementing training programmes.
- Motivation- employees tend to be most responsive to training programmes when they feel the need to learn . Therefore training must be related to the needs and problems of the trainees as well as to their abilities and aptitudes.
- Reinforcement – According to BF skinner’s behavior modification model – When behavior is repeatedly rewarded It becomes a permanent part of one’s personality. Learning is more effective when there is reinforcement in the form of rewards and punishment.
- Organized materials- Training material should be properly organized a complete outline of the whole course should be distributed in advance coming to the class.
- Learning period- Learning takes time and teaching in segments is better then in one go several short sessions spread over a long period enables the trainee to learn reinforce and review.
- Preparing the instructor – The instructor or trainer is the key figure in training programme. The trainer should not only be a good teacher but must know the subject and the job also.
- Feedback – Trainee should be provided with information on how much they learn and how they are doing.
- Practice- Practice makes a man perfect. Skills that are practiced often are better learned and less easily forgotten. Therefore, trainee should be allowed continuous practice.
REMUNERATION
Employee compensation is a vital part of human resource management. Wages, salaries and other forms of employee compensation constitute a very large component of operating costs. One of the biggest factors affecting industrial relations is the salary or wage compensation an employee receives for a fair day ‘s work.
Objectives of wage and salary administration
- To establish a fair and equitable remuneration there should be internal and external equity in remuneration paid to employees.
- To attract competent personnel – a sound wage and salary administration helps to attract qualified and hardworking
- To retain the present employees- By paying at competitive levels, the company can retain its personnel . It can minimize the incidence of quoting and increase employee loyalty.
- To improve cost – sound wage and salary administration labor and administration costs can be kept in line with the liability of the company to
- To improve productivity – Sound wage and salary administration helps to improve the motivation and moral of employees which in turn lead to higher
- To establish job sequences and line of promotion whenever
- To improve union management relations- Wages and salaries used on systematic analysis of jobs and prevailing pay levels are more acceptable to trade
- To improve public image of the company – Wage and salary programme also seeks to project the image of a progressive employer and to comply with legal requirement relating to wages and salaries.
Principles of wage and salary administration
The following guidelines should be followed in the administration of wages and salaries
- Wage policy should be developed keeping in view the interests of the employer, the employees, the consumers and the community.
- Wage policy should be stated clearly in writing to ensure uniform and consistent
- Wage and salary plans should be consistent with the overall plans of the company.
- Wage and salary plans should be sufficient flexible or responsive to changes in internal and external conditions of the organization.
- Management should ensure that employees know and understand the wage policy of the company.
- All wages and salary plans should simplify and expedite administrative process.
- All wage and salary decisions should be checked against the standard set in advance in the way policy.
- An adequate database and a proper organizational set up should be developed for compensation determination and administration.
- Wage policy and programme should be reviewed and revised periodically in conformity with changing
Essential s of a sound wage and structure
- Internal equity- It implies a proper relationship between wages paid for different jobs within the company.
- External competitiveness-0 Wages and salaries in the organization should be in line with wages and salaried for comparable jobs in other organization.
- Build in incentives – Wage or salary plan should contain a build in incentives so as to motivate employees to performs
- Link with productivity – Some part of the total pay should be linked to productivity.
- Maintain real wages- At least a part of the increase in cost of living should be neutralized so as to protect the real wages of labour.
- Increments – compensation policy can be good motivator if pay increases are linked with
Factors affecting wages
- Demand for supply of labour – Wages or salary is the price for the services rendered by a worker. Forces of demand and supply of labour determine the going wage rate.
- Ability to pay – an organization’s ability to pay its employees is unimportant determinant of wage level.
- Labour unions – Well organized trade unions exert pressure for higher wages and allowance. This pressure is exercised through collective bargaining strikes and other
- Cost of living – Due to inflation the real wages decline affecting the purchasing owner of workers. Therefore clearness allowance is given according to changes in consumer price
- Prevailing wage rate- While fixing wages prevailing wages in the particular industry region are taken into
- Job requirement – Basic wages depend largely on the difficult level and physical and mental effort required in particular job.
- Productivity- There is an increasing trend towards linking wage increases to gain in productivity or performance or workers.
- State regulation- Wage policy and laws of the government exercise a significant influence on wage levels government has enacted laws to protect the interest of the working class.
Method of wage payment
- Time wage system
Under this system, wages are paid on the basis of time spent on the job irrespective of the amount or work done.
Advantages of time wage system
- It is the simplest and the oldest method, it is easy to understand and compute .
- Earnings of worker are regular and fixed.
- The land is economical as no detail records of output are required.
- Union prefers time wage as it does not differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers.
- It is an objective
- The employer can calculate the wage bill in
Disadvantages of time wage system
- The method provides no incentives for better performance as
- Guaranteed remuneration makes workers in different and complacent.
- Calculating of labor cost per unit is different as the total wage bill does not change in volume of reduction.
- In the absence of an incentive to handwork, productivity of labour becomes low unless close supervision is used.
- Control over labour cost become difficult and more payment may be made for the lesser amount of work
Piece wage system
Under this system, remuneration is based on the amount of work done or output of a worker.
Advantages of piece wage system
- There is a direct relation between effort and reward workers who work hard and produce more get more wages.
- Ambitious and efficient workers are provided ample opportunity to utilize their talent and increase their
- This method is just and fair to all.
- Management can distinguish between efficient and inefficient workers for the purpose of promotion .
- The cost of labour per unit of output can be easily calculated as the wage varies in direct proportion to the output.
Disadvantages of piece wage system
- It is difficult to fix piece wage rates .
- The earnings o f workers are not stable and they may suffer due to temporary delay or difficulties
- In order to maximize their earnings, workers work with excessive
- This system may create jealously between efficient workers .
- The method may lead to industrial dispute.
Process of wage determination
- Job analysis – the data collected through job analysis is used to prepare job descriptions and job On the basis of these statement standards of job performance are laid down.
- Job evaluation – the relative value of every job is determined thorough job The relative job value is then covered into money value so as to fix basic wage for the job .
- Wage survey – Wage or salary surveys are conducted to find out wage/salary levels prevailing in the region or industry for similarly jobs.
- Developing wage structure- While determining such structure several points need to be considered.
- Legislation relating towages.
- Payment equal to more or less than prevailing wage
- Number and width of pay grades
- Jobs to be placed in each pay grades.
- Provision for merit
- Differentials between pay plans
- Dealing with wages/salaries that are out of line with the
- Wage administration rules – rules are regulated to determine the degraded to which advance will be based on length of service rather than merit.
- Employee Appraisal – In order to reward merit and performance, it is necessary to evaluate the performance of individual
INCENTIVE PLANS AND PROFIT SHARING
Meaning of wages incentives
Incentives wages refer to performance linked compensation paid to improve motivation and productivity of employees. It implies to monetary inducements offered to employees to perform beyond acceptance standards.
Advantages of incentive plans
- It helps to make improvement in work flow, work method and man machines relationship.
- It provides an opportunity for hardworking and ambitious workers to earn more.
- Employees are encouraged to become innovative.
- It helps improve discipline and industrial relations.
- The cost of supervision is reduced as workers themselves are motivated to work.
- A spirit of mutual cooperation and teamwork is created. Among.
- Wage incentives are a sound techniques of improving
Disadvantages
- Introduction and administration of incentives plans increase the cost and time of clerical work.
- Whenever production flow is disrupted due to the faults of management, workers insist on
- Jealousy and conflict s among workers may arise when some workers earn more than others
Essential of a sound incentives plans
- Proper climate – In the absence of mutual trust and understanding between management and workers , a wage incentive system maybe viewed as an attempt on the part of management to coerce for production.
- Workers participation- A wage incentive plan should be installed in consultation with workers and their union.
- Scientific standard – The standards of performance for payment of incentives should be established through scientific work study free from bias and
- Guaranteed minimum wage should be guaranteed to every worker irrespective of his
- Simplicity – the incentive plan should be easy to understand and simple to operate so that a worker can calculate his own earnings.
- Equitable the plan should provide equal opportunity to all workers to earn incentive pay .
- Economical – The plan should not be very costly in operation.
- Flexibility There should be scope for making changes in the scheme to rectify errors and to take care of changes in technology, markets demand.
- Prompt payment – The time gap between actual performance and incentive payment should be a small as possible.
- Adequate incentive – Incentive payments under the scheme should be large enough to motivate the worker .
Types of wage incentives
- Individual incentive plans
- Group incentive plans
- Plans wide incentive plans
Under individual incentive plans, earning are related directly to the performance of the individual workers.
Group incentive schemes earning of a group are related to the performance of the group as a whole. In plant wide schemes, performance of the factory as a whole is used as the basis for calculating earning of workers
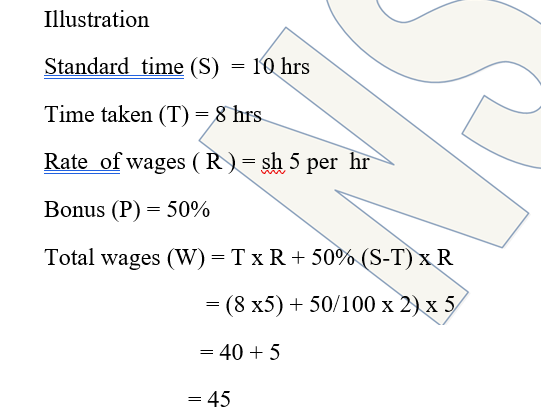
Halsey Weir plan
Under this plan a standard time is fixed on the basis of past performance records. A worker who completes his job within or more than the standard time is paid a guaranteed time wage. The bonus is calculated on the basis time rate.
Merits
- The plan is simple to understand a worker can easily calculate his earnings.
- Both the employer and the worker get equal
- A guaranteed minimum wage to every worker provides s a sense of security.
- The plan encourages the worker to be efficiency
Demerits
- Standard based on past performance may not be scientific and fair.
- Workers get only half of the benefit of their
- Much clerical work is involved because records of time saved and bonus earned has to be kept.
Rowan plan.
Under this method a minimum time wage is guaranteed to every worker . a standard time is determined in advance.
Illustration
Lets us use the data given under halsey we plan
Total wages = T xR + (TxR x time saved
Standard time
- 8 x 5 + (8 x5x2/10)
- 40 + 8
- Shs 48
Merits
The guarantee of minimum wage gives a feeling of security.
Both the employer and the worker share the benefit of time saved.
The efficient workers get bonus or a diminishing rate if they save more than 50% of the standard time
Demerits
The plan is difficult to understand for an average workers.
Efficient workers are discouraged to save more than half of the standard time.
Emersion efficiency plan
Under this plan standard time for the job is determined sciencetifically and a minimum time wage is guaranteed to all workers. Efficiency is measured by comparing the actual time taken with the standard time
Illustration
Standard time(S) = 10 hrs
Time taken ( T) = 8 hrs
Time wage (R ) sh 5 per hr
Bonus = 10 % up to 75 % efficiency
= 20% for 75% – 100%
= 30 % beyond 100%
Total wages = (TxR0 + Percentage by bonus x R xR)
In this case, the efficiency is = 10/ 8 x 100 = 125
Therefore , bonus at 30%is payable
Total wage = (8x 5) + 30/100 ( 8×5)
= 40 + 12
= shs 52
Worker A = Time taken 16 hrs bonus Nil
Worker B = Time taken 14 hrs Bonus = 1/10 x 14 x 5
“ C = Time taken 10hrs Bonus = 2/10 x 10x 5
” D = Time taken 8 hrs Bonus = 3/10 x 8 x5
Merits
- It provides a sense of security to all workers .
- It is fair as the rate of bonus is related to the level of efficiency .
- It encourages healthy completion among
- Bonus begins at 67 percent efficiency which is within the reach of many workers.
Demerits
- There is little incentive after 100 percent efficiency level
- Employer may fix the standard/time at a low level making it impossible for most of the workers to earn
- The system may create jealousy and disunity among efficient and inefficient workers.
Bandeaux plan
Under this method , standard time for the job is sex scenically and it is expressed in terms of B for instance a standard time of 200B means the job should be completed within 200 minutes.
Total wages = S x R x 75% of R (S-T)
Illustration
Standard time (S) = 240BS (4 hrs)
Actual Time taken (T) = 180 BS ( 3 hrs)
Rate of wages ( R ) = sh 0.5 per B hr
Total wages = 240 x 0.50 + 75/100 x 0.5 (240 -180)
= 120 + 75 x 30
100
= 120 + 24.5
= 144.5
= sh 144.5
Merits
- Minimum wages are guaranteed to all workers .
- The foreman is motivated to increase productivity as one fourth of the value of time saved is paid to him.
- This plan is suitable in factories wherein a worker is expected to perform different types of jobs.
- Efficiency of different sections/workers in the factory can be compared.
Demerits
Workers may resent sharing the bonus with foremen.
Calculations involved are complicated.
Much clerical work is involved.
Taylor’s different piece rate plan
Under this system , standard task is established through time and motion study. Two piece rate are laid down, the lower rate for those workers who fail to complete the standard task within allocated time and higher rate for those who completed the task within or less than allocation time.
Illustration
Suppose the standard output is 50 units per day. The piece rate fixed are shs 2 and sh 1.50 per unit . Three workers A,B and C produce 40, 50 and 60 units respectively during a day. Their total wages will be as follows.
Worker A : 40 x shs 1.50 = sh 60
B : 50 x sh 2.00 = sh 100
C : 60 x sh 2.00 = 120
In this way an efficient workers is penalized as he gets a lower rate per unit.
Merit
- It provides sufficient incentive to efficient
- Inefficient workers are penalized but encouraged to reach the
- Use of time and motion help to improve and standardized work
- Workers have not to share the reward with the foreman
Demerits
- There is no guarantee of minimum wage to
- The land is harsh to workers who are just below the standard.
- It treats workers as machines not human being .
Group incentive plans
Under this scheme bonus is calculated for a group of workers and the total amount is distributed among the group members in preparation to the wages earned by each.
Advantages of group incentives plan
- Individual members of the group who occupy jobs requiring special care and attention have not to bear the whole loss of slow
- Charges of favoritism in the assignment of tough and easy jobs are not likely to
- The skilled and experienced workers are motivated to help and train inexperienced and new members .
- All these factors create teamwork and co-operative spirit in the group.
Profit Sharing Profit sharing is an important supplement to wages and good financial incentive . Profit sharing is an arrangement by which employees receives in addition to wages a share fixed in advance in the profits of the enterprise.
Advantages of profit sharing
- It help in improving productivity and to reduce cost because workers have a strike in the profitability of the
- It creates a sense of responsibility among employees.
- It helps in building up a stable and contented workforce
- Industrial climate is improved due to mutual co-operation between employer and employees for increasing the net profits.
- It helps to increase the earnings and standard of living of
- It contributes to social justice through a more equitable distribution of profit among employer and employee.
- It is a step towards industrial democracy because workers are treated as partners in industry.
Limitation of profit sharing
- Profit sharing does not ensure regular income to employees. The share in profits is payable only when the profit exceeds as a specified
- All workers are given the same amount and distinction is med between efficient and inefficient
- A share in profit is payable at long interviewers after the final accounts of the company are prepared.
- The determination of profit and its distribution may become a bone of contention between employer and employees.
- During periods of prosperity, workers may start considering the share in profit as a permanent
Directing
Directing is the process of motivating, activating , leading and supervising people. Directing includes all those activities by which a manager influence the action s of subordinates,
It involves getting others to act after all preparation has been made. Directing is the heart of the management process because it is concerned with initiating action.
Controlling
It implies checking verifying and regulation to ensure that everything occurs in co formality with the plans adopted and the instruction issued . Such monitoring helps to minimize the gap between desired results and actual performance.
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
Performance appraisal is the process of assessing the performance and progress of an employee or of group of employees on given job and his potential for future development.
Characteristics of performance appraisal.
- Performance appraisal is a process consisting of a series of steps.
- It is a systematic examination of an employee’s strength and weakness in term of the job.
- It is a scientific or objective study formal procedures are used in this study.
- It is an ongoing or continuous process where in the evaluation are arranged periodically according to a definite plan.
- The main purpose of performance appraisal is to secure information necessary for making objective and correct decision on employees.
Objectives of performance appraisal
- To provide feedback to employees so that they come to know where they stand and can improve their job performance.
- To provide a valid database for personnel decisions concerning placement pay, promotion, transfer punishment.
- To diagnose the strength and weakness of individual so as to identify further training needs.
- To provide coaching, counseling, career planning and motivation to subordinates.
- To develop positive superior subordinates relations and thereby reduce grievance.
- To facilitate research in personnel management.
- To test the effectiveness of recruitment, selection, placement and induction programmers.
Uses of performance appraisal
- It provides valuable information for personnel demotions, transfer and determination.
- It helps to judge the effectiveness recruitment, selection, placement and orientation systems of the organization.
- It is useful in analysis training and development needs. These needs can be assessed because performance appraisal reveals people who require further training tore move tier
- Performance appraisal can be used to improve performance through appropriate feedback, working and counseling to employees.
- Performance appraisal facilitates human resource planning, career planning and succession planning.
- It promotes positive work environment which contribute s to productivity.
- It competitive spirit is created and employees are motivates to improve their performance.
Process of performance appraisal
- Establishing performance standards- The appraisal process begins with the setting up of criteria to be used for appraising the performance of the employees. The criteria are specified with the help of job analysis which reveals contents of a job. This criteria should be clear, objective, and in writing.
- Communicating the standards – The performance e standard specified in the first step are communicated and explained to the expected of them. The standards should be conveyed to the evaluators should be conveyed to the standards should be obtained.
- Measuring performance – Once the performance standards are specified and accepted the next stage is the measurement of actual performance. This requires choosing the rights techniques of measurements, identifying the internal and external factors influencing performance and collecting information on results achieved.
- Comparing the actual with the standard
Actual performance is compared with the predetermined performance standards. Such comparisons will reveal the deviation which may be positive or negative. Positive deviation occurs when the actual performance exceeds the standards.
- Discussing the appraisal
The results of the appraisal are communicated to and discussed with the employees. Along wish the deviation the reasons behind them are also analyzed and discussed. Such discussion will enable an employee to know his weakness and strengths
- Taking corrective action- Through mutual discussion with employees, the steps required to improve performance are identified and initiated. Training coaching, counseling etc are examples of corrective actions that help to improve performance.
Problems in performance Appraisal
-
- Errors in Rating – Performance appraisal may not be valid indicator of performance and potential of employees due to the following types of errors.
- Halo effects – It is the tendency to rate an employee consistently high or low on the basis of overall impression..
- Stereotyping – This implies performing a mental picture of persons on the basis of his age, sex, caste or religion.
- Central tendency – It means assigning average rating to all the employees in order to avoid commitment or involvement.
- Constant Error- some evaluators tend to be in assessing performance.
- Personal bias – Performance appraisal may become invalid because the rater dislikes an employee.
- Spill over effects – This arises when sat performance affects assessment of present performance.
- Lack of reliability – Reliability implies stability and consistency in the measurement. Lack of consistence over time and among different raters may reduce the reliability of performance appraisal.
- Incompetence- Raters may fail to evaluate performance accurately due to lack of knowledge and experience.
- Negative approach- Performance appraisal loses most of its value when the focus of management is on punishment rather than on development of employees.
- Multiple objective- Raters may get confused due to too many objectives or unclear objectives of performance appraisal.
- Resistance – Trade unions may resist performance appraisal on the ground that is involves discrimination among its members.
- Lack of knowledge – The staff appraising performance of employees might not be trained and experience enough to make correct appraisal
Essential of an effective performance appraisal system.
- Mutual trust – an atmosphere of mutual trust and confidence should be created in the organization before introducing the appraisal system.
- Clear objective – the objectives and uses of performance appraisal should be made clear and specific. The objectives should be relevant, timely and open.
- Standardization- Well defined performance factors and criteria should be developed. These factors as well as appraisal form procedures and techniques should be standardized.
- Training – Evaluators should be given training in philosophy and techniques of appraisal.
- Job relatedness- the evaluators should focus attention on job related behavior and performance of employees.
- Documentation- The raters should be required to justify their ratings. Documentation will encourage evaluators to make conscious effort minimizing personal biases.
- Feed back and participation- Arrangement should be made to communicate the rating to both employees and the raters.
- Individual difference – While designing the appraisal system, individual difference in organization should be recognized. Organization differs in terms of size, nature needs and environment.
- Post appraisal interview – After appraisal interview with the employee should be arranged. It is necessary tossup feedback to know the difficulties under which the employer work and identify their training needs.
Methods of performance appraisal
1. Confidential Report- This is a traditional form of appraisal used in most government organization. A confidential report is a report prepared by the employees immediately supervisors/superior. It covers the strength and weaknesses, main achievement and failure personality and behavior of the employees. It involves a lot of subjectivity because appraisal is based on impression rather than on data.
2. Free form or essay method- Under this method evaluators writes a short essay on the employees performance on the basis of overall impression.
3. Straight ranking method
In this technique, the evaluator assigns ranks to all employees in the same work units doing the same job. Employees are ranked from the best to the poorest on the basis of overall performance.
4. Paired comparison method
This is a modified form of man to man ranking. Herein employees are compared with all the others impair at a time.
5. Forced distribution method
In these techniques the rater is required to distribute his rating in the shorn of a normal frequency distribution. The purpose is to eliminate the rater’s bias of central tendency.
6. Graphic rating scales
It is a numerical scale indicating different degrees of a particular taint. The rater is given a printed form for each employee to be rated. The form contains several characteristics relating to the personality and performance of employee.
7. Checklist method
A check list is alit of statement that describes the characteristics and performance of employee on the job. The rater checks to indicate if the behavior of an employee is positive or negative to each statement.
Critical incidents method.
In this method the supervisor keeps a written records of critical either good or bad event and how different employees behaved during such events. The rating of an employee depends on his positive /negative behavior during these events.
Group appraisal method
Under this method a group of evaluators assesses employees. This group consists of immediate supervisors of the employee. The group determines the standards of performance for the job, measures actual performance on the employee.
Field review method
In this method, a training officer from the personnel department interviews line supervisor to evaluate their respective subordinate. The interviewer prepares in advance the questions tobe asked; by answering these questions a supervisor gives his opinion about the level of performance.
Importance of keeping records for implementation purpose.
- Account of programs kept in an orderly way. To measure the progress of the concern or to find our certain other facts , a history of the firm is needed . the past record , history of the project , recount the dealings.
- Proper study of the position of the project . the preserved record are the contributory factors without which a good proper study of the position of the firm cannot be made and statement cannot be prepared.
- Comparison of project. past record make it easy and possible to compare the performance of one period with that of another period by comparison , one can know there is progress or not.
- Policy making. Past record , events , progress etc are very necessary to decide future policies and lans . in the absence of record the policies and plans may not be successful.
- Legal requirement. Certain records are to be kept for a number of years from the legal point of view.
- Evidence . records are good evidence in the court of law, in the case of suit.
