FILLING
Filing is the systematic arrangement of business correspondence and records so that they may be obtained quickly when needed for reference.
Examples of office documents that require to be filed are:
- Letters and memoranda
- Business documents such as enquiries, quotations, orders, invoices, statements, receipts, etc.
- Accounting documents such as ledgers, stock record card, etc.
- Bulky documents such as magazines, newspapers, advertising material, etc.
- Reference books and other source of information
PURPOSE OF FILING
- To preserve records for future reference
- To gather related documents together in one suitable file
- To protect records against damage from fire, water, etc in order to keep them secure and in good condition
- To provide evidence in case of any dispute in a court of law
- To help find documents quickly when needed for reference
- To keep information away from unauthorized people
- To keep the office tidy
- The law requires that certain documents must be stored for a given period of time
THE FILING PROCESS
- Collecting – the papers to be filed are collected together in a filling tray or basket that is labeled.
- Inspecting – each paper or document is inspected of the release symbol or mark which indicates that it is ready for filing. The release symbol/mark may be the initials of the person sending that material for filing; the work ‘file’ or a letter F and the date, a line through the text; or any other previously agreed mark.
- Indexing – an appropriate caption or name under which the paper will be filed is selected.
- Cross referencing – if a document can be filed under more than one heading a cross-reference sheet is prepared.
- Coding – every paper or document is marked, i.e. circling or underlining with a coloured felt pen the relevant word to indicate/show how it has been indexed.
- Sorting – documents going to the same folder/drawer are placed together to avoid time being wasted by having to return to the same file or drawer repeatedly.
- Filing – documents are stored in the correct file folders.
ESSENTIAL QUALITIES OF A GOOD FILING SYSTEM
- Simplicity – the system should be simple to understand and operate
- Accessibility – the cabinets must be conveniently situated and the files within the cabinets easy to locate
- Elasticity – capable of expansion, if required to suit the changing needs of business
- Compactness – should occupy the minimum of space because modern office space is costly
- Economy – it must not be costly. There should be minimum cost of its installation and operation
- Capable of safeguarding documents against damage by fire, water, dust and maintaining confidentiality of the information
- Classification – it must employ the most appropriate method of classification
- Cross-reference – this is needed so that a document that may be found under different headings can be easily located
- Out-guides – an ‘out-guide’ system should be incorporated. It indicates the documents which have been withdrawn and the person or department withdrawing them.
- Retention – the system should allow records to be retained or discarded on the basis of their usefulness
FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN CHOOSING FILING EQUIPMENT
- The number and size of records involved – the equipment should accommodate all the records
- Space available – this is the area available in the office to place the equipment
- Cost of the equipment – the firm should be able to afford the equipment without having to incur heavy expenses
- Prevention of theft and fraud – equipment should be lockable to safeguard the documents
- The degree of protection of documents that is required against loss through damage by fire or water and deterioration through dust
- The likely future expansion – need for a filing equipment which will accommodate records if they increase in future
- Frequency and speed of retrieval – it should be easy to insert, locate and extract documents from the equipment with less time and effort
TYPES OF FILING EQUIPMENT
- File folders
- File covers
- Filing cabinets
FILE FOLDERS
These are mainly of three types:
- Manila paper folder
- Plastic folders
- Envelope or wallet folders
FILE COVERS
They include:
- Box files – these are files made in the shape of boxes with spring clips fitted to hold the papers firmly. They are used for storing bulky documents which cannot be punched e.g. pamphlets and brochures
- Lever-arch files – these files have two arches shaped metal rods which open and close by lowering a lever. Single sheets of documents can be removed and inserted. The file stands on its bottom edge and is labeled on the spine. A hole on the spine allows the insertion of a finger to draw the file from the shelf
- Ring binders – these are files made of hard covers and have two or more rings which open to allow the insertion and removal of documents. They are useful for documents that require constant updating
- Concertina file – this is a file containing lettered or numbered pockets connected together and expand when more documents are inserted. They are used or documents and papers kept for temporary periods waiting processing like petty cash vouchers and such documents which do not need to be punched e.g. certificates. They are particularly useful as bring-forward systems or ‘tickler’ files.
- Multipart files – these are files consisting of a few (usually seven or nine) manila dividers fastened together to form one comprehensive file for unpunched papers. The dividers are tabbed for quick reference and are held together by elastic across the corners.
FILE CABINETS
These include:
- Lateral cabinets – these have filing pockets suspended side by side along the shelves of the cabinet. Files are kept in their vertical positions in these suspended filing pockets.
- Vertical cabinets – these cabinets have drawers in which files are kept in their vertical position. The cabinets are made of steel or wood and have special locking devices and are used for sorting documents like files, foolscaps, paper, etc.
- Horizontal cabinets – these cabinets have wide shallow drawers to store large documents such as maps, plans, drawings. The documents are store or filed flat in the cabinet drawers one on top of the other.
- Circular rotary cabinets – in these cabinets’ files are kept in pockets around a central vertical pillar.
METHODS OF FILING
VERTICAL FILING METHOD
This is a method of storing files by placing them on their spines one behind the other in drawers of vertical filing cabinets. The identification titles are place at the top edge of the files which are normally visible.
Advantages
- Economical – the folders are cheap and many folders can be accommodated by a single filing cabinet. Hence there is saving in terms of money as well as space.
- Ready reference – it is easy to locate a file by reading the identification titles on the files.
- Elasticity – filing cabinets drawers can accommodate a large number of folders.
- Safety and security – cabinets offer protection of files against damage by fire, water or dust and they can be locked to provide security to confidential documents.
- Universal application – vertical filing has proved useful in preserving all types of papers/documents. g. orders, invoices, letters, quotations, tenders, etc. can be filed with a great ease and preserved without difficulty.
- Adaptability – vertical filing can be easily adapted to all types of classification. The folders can be arranged alphabetically, numerically, geographically, subject-wise or on some other basis according to the needs of an individual office.
Disadvantages
- It causes fatigue since the filing clerk has to keep on pulling out the drawers.
- Cabinets must be place in a spacious room to allow for the drawers to be opened and give room for the filing clerk.
- Only one person has access to the cabinet.
- A folder can quite easily become hidden at the bottom of the drawer underneath the other folder.
HORIZONTAL FILING METHOD
This is a method of storing files in a horizontal or flat position, one top of another on shelves or in drawers.
Used for storing maps, photographs, drawings and charts too large to be stored in the standard filing cabinet.
Advantages
- It takes less space than vertical method
- It is ideal for large documents such as maps, plans, drawings, photographs, charts, etc
Disadvantages
- It is difficult to extract files if the file needed is at the center or bottom of the pile
- It is difficult to replace files in their correct position
- It is more tiresome since the clerk has to keep on removing and replacing both the wanted and unwanted file
SUSPENSION FILING METHOD
In this method a drawer is fitted with metal rods from which filing pockets are suspended vertically and folders are place inside the pockets. Each pocket displays a card showing the name of the folder in that particular pocket.
Advantages
- It prevents files from wear and tear
- It does ensure that files are kept upright thus making reference easier
- No files can collect underneath other files
- More filing pockets can be added for the insertion of new files
- It is easy to replace files in correct pockets as the pockets are overlapped to give a flat top which carries a title strip protected by a plastic cover.
Disadvantages
- The suspended filing system is more costly.
LATERAL FILING METHOD
This is a method whereby files are placed side by side on a shelf or cupboards.
Advantages
- Saves floor space as shelves may be built up to ceiling height if necessary
- Causes less fatigue as there is no pulling of drawers
- A large number of files can be viewed at one time which saves time in location of folder
- The method is highly elastic and offers an almost unlimited scope for expansion
- Saving in equipment costs when compared to vertical and suspension filing
Disadvantages
- It is difficult to read identification on folders compared to vertical filling
- Files may become dusty because of the large opening
- Location of files from a height can be a hazard
FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN CHOOSING A METHOD OF CLASSIFICATION
- Size – what is the size of the system that is the quantity and variety of documents to be filed, g. numerical classification is the best suited
- Simplicity of the system – which is the simplest system? Alphabetical classification is the simplest and easiest method to understand
- Accuracy – the system must ensure that there is no misfiling. In this respect, the numerical classification gives precision
- Speed – speed of reference is a very important factor. Some mixed or compound classification can ensure this
- Elasticity – the system must be elastic to give a scope for expansion numerical expansion for example serves this purpose well
- Convenience – which can be the most convenient method of reference
METHODS OF CLASSIFICATION
ALPHABETICAL
This method refers to the filing of documents according to the names of individuals or organizations in alphabetical order.
Advantages
- It is simple to understand and operate
- Related documents are grouped/kept together making it a convenient method when locating document for one person, subject or organization.
- It is a direct method of filing as there is no need for an index. It is self-indexing i.e. the first letter will tell you where the documents is located
- A miscellaneous folder can be opened up to place miscellaneous papers i.e. papers or correspondence which are very small in amount and do not warrant the need to open an individual folder.
Disadvantages
- It is cumbersome in a large filing system as it takes longer to find papers
- There is congestion under common names
- It is difficult to estimate space requirements under different letters of the alphabet e.g. how many Hs, how many Ps
- Possibility of documents being filed under more than one letter, so necessitating cross-referencing
RULES OF ALPHABETICAL FILING
- File according to the initial letter of the surname and each subsequent letter e.g. Parker E. H., Parkinson M.W., Parsons N.V.
- If the surnames are the same, file by initials e.g. Opio A.K., Opio D.E., Opio O.D.
- A surname alone precedes a surname with an initial and a surname with an initial precedes a surname with a first name e.g. Wilkinson, Wilkinson H.J., Wilkinson Albert J, Wilkinson Albert John
- Consider the surnames prefix as part of the surname whether joined to it or not e.g. Da Costa, De Bie, La Barne, O’Connor
- Treat names beginning with M, Mc, Mac as if they were spelt Mac and file according to the first letter after the prefix e.g. McDonald, Maclntyre, M’mahon
- Names beginning with ‘St’ prefix are treated as if they were spelt ‘Saint’ e.g. St George, Saint Mary.
- Titles are ignored e.g. Kamau S.K. (Dr), Ottishubo A.M. (Mrs) and other titles such as Col., Capt. etc.
- Treat any number in a name as if it were written in full e.g. The 51 Restaurant – fifty one Restaurant (The)
- When filing hyphenated names, ignore the hyphen and treat whole name as one word e.g. Davies-Phillips, Davies-Roberts
- If the surname, first names are identical file according to towns e.g. Otieno Charles, Kisumu, Otieno Charles, Mombasa
- When ‘the’ is the first word in a firms, organization or company name, it is ignored e.g. The East Africa Road Services Co. Ltd is filed as East African Road Services (The)
- File an organization name consisting of initials before whole words e.g. AA Duplicating Co. Ltd, A-Z Enquiry services Ltd, Abbey Court Hotel
- File under surname if the firm’s name has a first name e.g Ernest William Co. Ltd is filed as Williams Ernest Co Ltd
- Firms whose names consist of initials should be filed before firms whose names are written in full e.g. UCJ Engineering Co. Ltd, Lamb’s Furniture Co Ltd but if the initials full word is known, file normally e.g. AA refers to Automobile Association, RAC refers to Royal Automobile Club etc
- File government departments and ministries under the key words e.g Ministry of Defence is filed as Defence, Ministry of or Agriculture, Ministry of, Education, Ministry of, Trade and Industry, Department of etc
- If you have a lot of correspondence with several different local authorities these would be filed under the name of the local authority and subdivide according to the name of the departments e.g. Education Department, Dar es Salaam City, Water Department, Dar es Salaam City
- When an organization has several names, the first name is treated as the surname e.g. Ngare, Murora & Apondi Advocates is filed. Under Ngare or Messers Mohammed and Mwangi under Mohammed
NB: Letters are always filed under the names of the organizations and not under the name of the person who signs the letter
QUESTION
Identify the first indexing unit in the following names and arrange the names in alphabetical order
Eunice Wekesa Retailers
Uasin-Gishu Manufacturers Ltd
Otieno McOwiti
The House of leather
St Thomas Academy
Dominic Obara
Department of Environmental Resources
Ngare, Murora & Apondi Advocates
Sir Maximillan Amukobole
498 Supermarket
- Amukobole Maximum (Sir)
- Environment Resources, Department of
- 498 Supermarket
- House of leather (The)
- Obara Dominic
- McOwiti Otieno
- Ngare, Murora & Apondi Advocates
- St Thomas Academy
- Uasin-Gishu Manufacturers Ltd
- Wekesa Eunice Retailers
GEOGRAPHICAL CLASSIFICATION
This method refers to the filing of documents according to their geographical locations e.g. countries, counties, districts, cities or towns. This method is applicable in those departments of an organization such as Sales or Transport which are concerned with geographical areas.
Advantages
- Speedy location is possible as documents relating to one particular area are all together
- Suitable for companies that have several branches spread over different parts of the world or county e.g. oil companies or commercial bank
- It has an element of direct filing
Disadvantages
- Weak knowledge of geography on the part of filing personnel can cause errors
- When regional boundaries are changed the filing also needs to be changed
- There may be need for an index
SUBJECT CLASSIFICATION
This method refers to the filing of documents according to the subject matter of each document e.g. it is easier for a buyer of typewriters to have a file with the correspondence on typewriters than have to look at separate files depending on the names of the people involved.
Advantages
- All documents referring to a particular subject matter are kept together in one place for easy reference
- The files can easily be expanded or contracted by simply adding or subtracting old ones
- Can be more confidential than using individual’s names
NUMERICAL CLASSIFICATION
This method refers to the filing of documents according to numerical sequence/order
Advantages
- Each new file is given the next number and placed behind the last file in the system thus has unlimited expansion
- There is less likelihood of folders being misfiled, since people tend to be more accurate in placing numbers in order than in arranging things alphabetically
- A missing number or one out of place, would soon be spotted in a system of numerical filing and misplacement could therefore be speedily rectified
- The card index that must be made to connect the names with the numbers can be used for other purpose e.g. addresses and telephone number
- Customers’ file can be quoted on letters as part of the reference, i.e. after the dictator/typist initials, a customer’s reference might be SJP/NJS/2591. When this is quoted on his reply, there is no problem at all in referring to his file.
Advantages
- No direct access; need to consult an index causing delay in finding a folder
- Possibility of transporting figures resulting to errors in filing
- It is not easy to arrange files for miscellaneous papers
- It involves a lot of work both in setting up and operating it
TERMINAL DIGIT
In this classification method numbers are broken into pairs and read from right to left. For example, 680761 would be the terminal digit and read in pairs as 68 07 61. This number means that 68 is the file drawer, 07 guide card number and 61 the folder number. The next folder number would be 62
Advantages
- It speeds up location of documents in a large system
- Distributes the filing through several drawers so overcoming crowding
- Capable of varied interpretation in different circumstances e.g. the number groupings could be different from one system to another
- High degree of accuracy is possible
- Easy to add new files
- Easy to identify a misplaced file
Disadvantages
- It is more complex to learn and operate
- Requires special training
- Needs an index
ALPHA-NUMERICAL CLASSIFICATION
The method of classification is a combination of numerical sequence and alphabetical order. Blocks of numbers are assigned topics arranged in alphabetical order and then the topics are su-divided alphabetically and numerically.
For example:
48 Post Office
48.1 Parcel Services
48.2 Telegraph Services
49 Production
49.1 Control
49.2 Experimental
49.3 Market Surveys
Advantages
- File groups are preconceived to meet specific needs
Disadvantages
- Requires an index
- Flexible is very limited
- Training filing clerk is essential
CHRONOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
In this classification documents are filed in order of their dates. Most papers are placed in files in date order, with the latest paper on top and the oldest at the back of the file. Therefore, chronological filing is not often used as a basic system, but is the normal method of filing
Advantages
- It is useful where a date has special significance over all else
- It is an essential aspect of most other systems
- It is easy to understand
- It provides for unlimited scope of expansion
Disadvantages
- It is not always suitable
- Incoming letters are usually to be separated from outgoing ones
ORGANIZATION OF THE FILING SYSTEM
CENTRALIZED FILING SYSTEM
In this system files of an organization are kept in one location often called the registry than in separate departments
Advantages
- Specialized staff can be trained to handle the filing work which improves efficiency and reduces cost
- Economical use of space and filing equipment
- Files are more complete because the correspondence of different departments about the same subjects filed together
- A standardized system of filing can be established throughout the organization
- Strict procedures for the requisition and return of files can be set up and these may reduce the number of files mislaid as well as deterring people from asking for files unnecessarily
- Safety and security measures are more easily incorporated since files can be locked in the room during the night and closely supervised during the day
- More effective supervision is possible as a supervisor can be put in charge of the whole filing system to ensure that all the filing clerks know their work and can do it effectively
- It minimizes duplication of records as it could be when each department keeps its own files
- It becomes feasible to consider expensive filing techniques e.g. microfilming or electronic filing
Disadvantages
- Lack of specialized knowledge concerning a particular by the filing staff can result in misfiling
- The more files stored, there may be delay in making files available which wastes time
- Inconvenience can be caused if one department retains files for long periods when they are needed elsewhere
- Restricts the opportunity for junior staff in different departments to learn about filling in order to replace staff in case of emergencies
- Some of the correspondence may not be suited to the particular system use
DEPARTMENTAL FILING
This is where each department keeps or files its own documents
Advantages
- Departmental records are more readily available for a quick reference which saves time
- The type of filing system may be employed which is most suitable for the correspondence with which the department deals. E.g. an export department would generally use a geographical system, whereas an advertising department would find subject filing more useful
- Departmental staff have a specialized/better knowledge of the work of the department and thus are able to file the records more accurately
- The filing system is not so large and therefore, is easier to handle
- It is more suitable for confidential files as they are not open to every member of the filing department
- It does not need a specialist staff for filing and this reduces staff/labor costs
- Departmental code letters may be used in correspondence and on file titles for easy recognition e.g. ‘S’ for sales department, ‘A’ for accounts department
Disadvantages
- There is increased capital costs and waste of space since each department requires its own filing cabinets
- Where the same information is dealt with in more than one department additional copies of documents may have to be made hence resulting to duplication
- There is usually less control of the withdrawal and return of folders as there is usually no specific person in charge of the files which in turn leads to files being mislaid and difficulty in locating files quickly
- There is tendency for each department to treat its files as if they are for the department only and hence be unwilling to lend them to other departments if needed.
- There is lack of specialized filing staff. If specialized staff is employed in each department, it would add to the cost of running the office.
CROSS-REFERENCING
It is required in order to locate documents which have been filed elsewhere because of:
- A firm or person changing their names
- A firm or company uses more than one name
- The correspondence being sought is under more than one name
- The firm is known by its initials
- Foreign names are difficult to decide what is the first indexing unit
A cross-reference sheet is made out, to direct a person to where a document is file
INDEXING
An index helps in locating the files needed or it is a methods used for making reference to records filed. Some indexes tell us where to find further information on the subject we have looked for.
Many systems of filing depend on an index, for example, geographical, numerical and subject classifications. However, files arranged in alphabetical sequence do not need an index since individual files can be located and identified immediately
The following are the main types of index namely
- Page index
- Card index
- loose or vertical card index
- visible card index
- strip index
- rotary index
- edge-punched cards
- visible loose-leaf books
PAGE INDEX
This is the type of index which is similar to the one at the end of a book where subject matter is alphabetically classified and then relevant page numbers are given against each heading or subheading.
Advantages
- it is very simple and easy to operate
- can be easily understood
- cheap method – very little equipment needed to put the method in operation
- it facilitates easy reference
- it is durable
Disadvantages
- Inflexible – if more of a subject matter is to be added there may not be sufficient space
- When looking up for a subject matter one has go through the whole page
CARD INDEX
- Vertical (loose) card index
Cards are stored vertically in drawers in alphabetical order
Advantages
- Additional cards can be inserted in correct order at any place
- Index cards of ‘dead’ files are removed easily
- Guide cards may be used to divide the index into sections
- Cards can be removed to add or enter information
- Capable of indefinite expansion as the number of drawers can be increased as desired
Disadvantages
- The cards are loose and can be mislaid
- If the drawer is upset all cards fall out and it takes considerable time to put them all back correctly
- Cards become worn out through constant handling
- The drawer containing the cards is heavy
Application/Use
- Libraries
- Hospitals
- Credit records
- Staff records
- Visible card index
Cards are held or housed in flat trays in such a way that they overlap each other, the title of each clearly visible. The trays can be put horizontally into cabinets.
Advantages
- Provides a quick reference as a number of cards can be seen at a glance
- Transparent plastic covers can be lifted over the exposed portions of the cards to protect from dust or dirt
- Trays can be locked in metal cabinet to safeguard confidential information
- Colour markets can be affixed to the visible portion cards to focus attention to vital facts
- New cards can be inserted and old ones can be removed
- Entries can be made on the cards without removing them from the cabinet
Disadvantages
- No convenient where may records are involved
- It is necessary to train staff for visible card index
- The filing equipment is quite costly
Application/use
- Personal records
- Stock control
- Credit control
- Customer information
ROTARY INDEX
Cards are fixed to the center of a wheel which is easily rotated to bring the required card in view.
Advantages
- Rotary equipment is useful for housing large number of cards
- Saves space
- Assists in speedy reference as information can be extracted from the records much more quickly
- Insertion of new cards and removal of unwanted cards is very easy
EDGE-PUNCHED CARDS
The cards have a series of punched holes round the edges which represent an item of the information. To select the information from the cards a steel needle is passed through a particular position and some cards fall out and leave the other in position and the information is decoded.
Advantages
- Speed of retrieval of information
- Accuracy i.e. elimination of errors
- Versatility – can be used for a variety of purposes
Disadvantages
- Costly to small organizations
- Difficulty in preparing cards
Application/use
- Vehicle records
- Estate agents
- Client records
- Sales analysis
STRIP INDEX
Strips of the paper are supplied in a sheet. They are separated by perforated lines. The strips are typed on and then separated and fitted into a frame and the frame can be placed in a holder on the desk top or desk stand or mounted on the wall.
Advantages
- Strips are available in a variety of colors and signals can be used
- Additions, alterations and removals can be made without difficulty
- Information can be clearly seen as the strip exposes all the details in view
- It is very suitable for providing a list of brief items that must be available for frequent reference e.g. names and addresses, telephone numbers, account numbers, etc
Disadvantages
- Each item of information is limited to one line entry
Application/use
- Telephone numbers
- Account numbers
- Addresses
VISIBLE LOOSE-LEAF BOOKS
The sheets or pages of the book are smaller in size than the cover of the book. They have holes punched at the edge so that they fit into the prongs of the loose-leaf book in such a way that they overlap each other exposing the titles.
Advantages
- Pages can be inserted and/or extracted easily without interfering with the continuity of the records
- The books can be locked away when not in use
- Less expensive than the ordinary visible record card
- Gives speed in reference and speed in posting information
- Are flexible and provide facilities for expansion
Disadvantages
- Not convenient where may records are involved
- Ring holes sometimes get torn when in frequent use so holes have to be reinforced
- If the loose-leaf book contains valuable or confidential information pages may get lost
FOLLOW UP SYSTEMS or CHARGE OUT SYSTEMS
These are systems or procedures to account for records that have been taken out of the filing system
- Use of substitution card
It is placed in the original folder to indicate that an individual paper is borrowed from a file. It gives details of the document taken out, date of removal and the name of the borrower.
- Use of an absent card (also known as an out guide/out card or tracer)
When a file is taken out of the office an out card of or absent card should be inserted in the place where the file is normally kept. Some out cards have a frame into which can be fitted a card giving details of the location of the missing folder; a pocket on the reverse side houses papers which accumulate for filing whilst the file is absent.
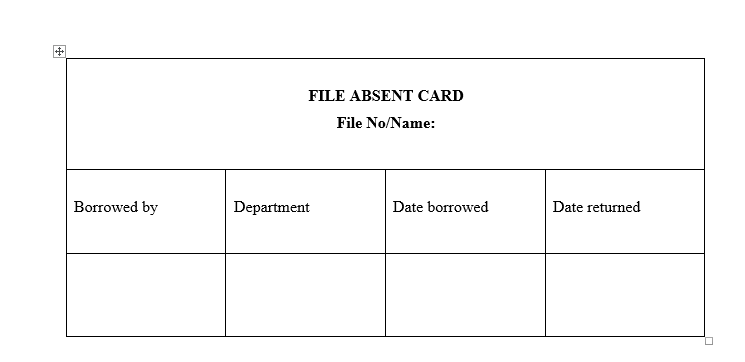
- Use of absent folder – which should be a different colour from the normal file folder to make it stand out, can be inserted in place of the file to be removed. Into this placed form showing the name or number of the removed file and who has it. The absent folder can be used for placing papers in whilst the file is out.
- Use a file register – use to record the date of borrowing, the name of the file, the name of the borrower and the department of office where he works. The date on which the file is returned can be entered in the last column. The person responsible for the files should make a daily check through the ‘Returned’ column and follow-up any files which have been out for an unreasonable length of time.
- Tickler file
- It is a reminder system where file folders or concertina files are used. In the tickler file, file folders or a concertina file sections are labelled January to December. In each file folder or concertina file sections divider cards or sheets of stiff paper labelled 1-31 to divide the days of the month.
- A form is then prepared indicating the name of the file, some means of identifying the particular documents wanted, the date they are to be returned and the name of the person borrowing
- The form is placed in the file folder or concertina file sections behind the divider card for the day of the month when the file or documents are to be returned
- Therefore, a tickler file enables a filing clerk to follow-up a file or documents borrowed and ensure they are returned on the due date because he has to go through the ticker file every morning
RETENTION OF RECORDS
- If correspondence is retained unnecessarily, files become bulky, occupy valuable space in cabinets and make the retrieval of documents more difficult. For this reason it is necessary for a file retention policy to be agreed by the organization i.e. the length of period records are retained by an organization.
Factors to consider in records retention
- Some documents have to be retained for legal requirements e.g. memorandum and articles of association, auditors reports
- Other documents are assets and there might be non-existence of alternative documents e.g. title deeds
- Other documents have a set number of years they are supposed to be retained e.g. contract of employment 7 years after the employee leaves, bank statements 6 years etc
- The need to retain documents for auditing purposes
- Space available – if there is enough space or a room set aside to store the documents
- Future need – if the records will be needed in future for reference
- Are there copies elsewhere? Both copies need not be kept
- The possible need for documents to be produced in their original form as evidence in a court of law
- How often and quickly the documents needed or required
- Cost – if the cost of holding these records is low then they are retained
NB: When records become inactive, they should either be destroyed or transferred to reserve storage. These inactive documents which become out of date and are no longer required are said to be dead files which should be stored away in a store room.
If records are to be destroyed, a shredding machine is used. It cuts paper into very thin strips making them unreadable to maintain confidentiality.
MICRO FILMING
- This is the processing of photocopying record to reproduce them as miniature films. To view documents which have been microfilmed, a machines called a ‘ viewer’ or ‘reader’ is used, which projects the film onto a screen for reading
- The images are stored on a roll of film, sheets of microfiche, aperture card or jacket
- Microfiche – this is a rectangular sheet of microfilm which holds 98 micro-images. A micro image is an A4 sized document reduced in size 24 times
- Aperture image – an individual microfilm (35mm or 70mm), is mounted into an aperture of a punched card
- Jacket – this is a transparent folder (a channeled plastic carrier) for storing strips of microfilm.
Advantages of microfilming
- There is saving in filing equipment as well as floor space
- Safety can be ensured by storing original documents in say a bank and using film for daily reference
- Film is more durable than paper and provide a much more permanent record
- If information has to be sent by expensive air-mail, microfilming can reduce postage costs substantially
- It is not possible to misfile or misplace microfilmed records as it could be with loose papers in a folder
- The film can be enlarged on to paper, thus providing quick and accurate duplicate copies of the original documents
- Where constant reference to microfilmed records is required thousands of microfilm records can be accommodated in a desk thus saving the movement of staff filing cabinet
Disadvantages
- Where reference is required, it may be relatively slow since the film has to be viewed through a reader
- Once the information has been recorded in a film, it is difficult to make alterations and this can be a problem when there is need to make corrections or make insertions to store information
- The equipment required for microfilming is relatively costly and could only be used economically in an organization where very large quantities of documents are kept on file
- There is a great loss in case of one film is lost as one film will be keeping so many documents
- In case of poor processing with stale chemicals, the film may be unreadable
- On many microfilm readers location of a particular film may be difficult, causing further delay and frustration
- Unless carefully chosen, the reduction ration of some documents can be so extreme to make it difficult to read on the reader
- Records in coloured paper are sometimes difficult to reproduce
COMPUTERISED/ELECTRONIC FILING
- Computers are increasingly being used for storing records
- Data may be stored in the following ways:
- Flopping disks or diskette – we have 8 inch, 51/4 inch, 3inch floppy disks. They are used with personal computers
- Magnetic tape – this may be reel-to-real cassette or cartridge
- Hard disks – store and provide relatively quick access to large amounts of data
- Todays, computers typically come with a hard disk that contains several billion bytes (gigabytes) of storage
- Optical disks – it is a compact disk or CD. CD has replace floppy disks
- USB flash drives – it includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface. USB flash drives are removable and rewritable and physically much smaller than a floppy disk
- Print out of a computer data – commonly referred to as hard copy
Advantages of computerized filing
- Speed and ease of access to information
- Maintain files automatically – and new records, update existing ones and amend instantly as required
- There is saving in office floor space
- Reduced paperwork
- Greater security by using pass words
- Files are not removed when access is made to them
- Records can be displayed on the screen
- Information from records can be printed
- Durability of words – records have a higher lifespan
Disadvantages
- Cost of acquiring equipment
- Time taken to input data and verify it using a keyboard
- Cost and time taken to print out copies when it is necessary to work away from the terminal
- The danger of an operator accidentally erasing data from the memory of a computer
- The need for backup copies
- The problems incurred when there is a power cut or a system breakdown, information cannot be accessed leading to stoppage of operations
ADVANTAGES OF ICT DEVICES FOR STORAGE OF RECORDS OR OF USING ELECTRONIC FILING SYSTEM
- The devices require little office space
- Various storage devices can be used that one can choose from
- Provides long-term storage
- The devices are portable; hence one is able to carry a lot of information or documents
- Provides for backup, that is, one can store the same information in different devices at different locations for safety.
- Filed information is secure since it can only be accessed by persons with the necessary password where it has been used
- Easy and fast retrieval of documents
- Easy to operate
- The documents stored electronically can be accessed by people far away from where they are stored through the internet
Examples of storage devices – Compact discs, floppy discs, flash discs, hard disks, magnetic
Disadvantages
- Only suitable for areas with electricity
- Information cannot be accessed during power failure which may lead to stoppage of operations
- Information cannot be accessed during computer system breakdowns, which may lead to stoppage of operations
- Storage devices can be damaged easily if proper care is not taken leading to loss of stored information
- Information stored in computer hard discs can get damaged through the introduction of virus into the computer
- High technology methods may be used by criminals (hackers) to access confidential information stored in computer hard discs
GENERAL RULES FOR FILING/SAFEGUARDING AGAINST LOSS OF DOCUMENTS
- Ensure that all papers are passed or authorized for filing
- File neatly and methodically by sorting and grouping all correspondence before filing
- Ensure correspondence is placed in the correct file
- Place the correspondence in the files in the correct sequence of dates so that the most recent document is on top
- Avoid large bulky files. The old documents should be transferred to inactive files, inactive files are kept in boxes which are clearly labeled with the contents and dates and stored in a storeroom
- Do not remove individual papers from a file. If an individual paper must be removed, a note stating the date, name of correspondent and name of the person holding the paper should be placed in the file
- Provide cross-reference to enable to locate documents filed elsewhere
- If a file is temporarily removed complete an out card or absent card
- When there is insufficient correspondence from one source to justify opening an individual file place it in a “miscellaneous file”
- Always close filing cabinet drawer after use for reasons of safety and security
- Lock filing cabinets before leaving the office at night or for any length of time
- File daily and regularly so that the filing system is always up to date
- Seek guidance when in doubt concerning the filing of non-classified papers which is unclear
- Ensure proper training of filing clerks on filing
- Ensure one person has the ultimate responsibility for the filing of documents
- Use of the appropriate system of classification
- Ensure not too many people have access to the filing system as it is likely that documents will go astray or be misled when returned
- Ensure the registry is centrally located because if it is far away it leads in delay or failure to return documents
- Photocopying the originals and lending out copies
- Micro-filming where the original copies are kept as films
- Use of close-circuit television where the filing clerk displays the document on the screen and after the user finishes seeing it the filing clerk files it
REVISION QUESTIONS
- State three types of filing cabinets that may be used in an office
- Give three reasons why it is important to establish a follow-up method for records in a filing system.
- Outline three benefits of using a computerized system of keeping records in an organization or explain the reasons that have led to the increased use of computers to file records in organizations
- Outline the advantages of using a departmental filing system in an organization
- Explain four advantages of storing information on micro-film
- State four problems that may face an organization that doesn’t file its documents.
- Explain the measures that an Office Manager may take to minimize loss of files from the registry or explain five measures that may be taken in an office in order to minimize misfiling of records.
- Outline six reasons for filing documents
- Explain six reasons why an organization may decide to use a numerical filing system
- Outline the advantages of establishing a centralized filing system in an organization
- Mwanzo Company Limited is the process of setting up a filing system. Outline five factors that should be incorporated in the system in order to make it efficient or outline five indicators of an efficient filing system in an organization or outline the essentials of a good filing system.
- The Office Manager at Mawendo limited is reluctant to adapt alphabetical filing system. Explain five reasons that may account for this reluctance or Mega Limited intends to adapt the alphabetical system of classifying documents. Outline the shortcomings that may be associated with this system.
- Explain the factors that may influence the choice of a filing classification to be used by an organization
- Justify the necessity of records retention policy in an organization or outline the factors that may influence the retention period of documents in an organization
- Describe the suspension method of filing highlighting its advantages
- Explain the factors that may influence the choice of filing equipment to be used in an office
