QUSTION ONE
Examine four roles of external communication system in an organization
- Communication about Price
Companies communicate the price of their products and services by using advertisements in print media and on television, radio and the Internet. Offers, such as buy-one-get-one free tactics, typically increase sales. Other incentives such as bonus points or coupons help generate customer loyalty by getting consumers to buy products at a reduced price. Additionally, companies send email messages to offer discounted prices, free samples and joint promotions with other companies using vouchers and financing deals.
- Communication with Channels
By communicating with customers through direct marketing channels, distributors or business partners, companies enable sales, and delivery of their goods and services in ways that end up providing companies target partners and suppliers with offers of reduced prices using communication mechanisms such as brochures, functional specifications and selling guides, Through external communication documents such as requests for proposals or statements of work, companies set up business relationships allowing them to prosper in a complex, global marketplace.
- promotion literature
Companies promote their products by communicating the benefits and features in printed product or service literature. Functional specifications, reference manuals and other product documentation enable customers to decide if the product meets their needs. Literature also convinces potential customers that products provide, a return on investment and an affordable total cost of ownership. Promotional literature tends to include attractive photos, text and descriptive language to describe product or service details. Using logos and slogans to build up their brand recognition, companies develop a market, presence.
- Product Training and Support
Companies present their, products at trade shows and events to demonstrate their personal or business use. They conduct framing courses to show people how to use product functions and certify personnel in product usage. Companies offer instructor-led training, virtual events using Web conferencing software and self-paced courses to meet the needs of busy professionals, during training events, instructors and company representatives give presentations and communicate with participants to learn about individual needs. Additionally, companies conduct surveys using online questionnaires to get feedback on product usage and requirements for new product development.
QUSTION TWO
Poor communication is one of the contributing factors to low productivity in organizations.
Assess four communication problems which are likely to be encountered at the work place and recommend measures that could be employed to minimize the problem
- Language Barriers
A diverse workplace has several benefits to a business, such as a variety of solutions to company issues and insight into international markets during expansion. But the language barrier that can sometimes occur in a diverse workplace, or any workplace, may become a communication problem. There might be language barriers between people of different ethnic backgrounds; people of different ages and people with different levels of industry experience. Any language barrier is going to slow communication or create .misunderstandings that makes communication ineffective.
While communicating within the organization it’s important to communicate in an official language that everyone can understand. This will minimize language barriers at the workplace.
- Personal Issues
Effective communication in a workplace is based on professional correspondence designed to assist in the daily operation of the company or the continued growth of the organization. When, employees allow personal issues to affect company communication, a communication problem, develops, that could take a long time to track down and resolve. People who refuse to communicate based on a. personal disagreement are damaging the company’s, ability to do business and slowing the growth of the organization.
So as to reduce communication problems at the workplace, it’s important that personal issues are resolved so that employees are able to communicate effectively.
- Lack of Feedback
One way communication can become an ineffective way to exchange information throughout the company. Employees and managerial staff should provide feedback at all times to improve the quality of information disseminated and the manner in which the information is delivered. For example, if a department tends to send out information in a format confusing to other people in the company, then that department needs to be informed of its communication problems immediately or else the information coming from that group will always pose a communication challenge.
- New Hires
Companies that at do not include communication training in their new-hire orientation programs will be forced to struggle with new hires who are forced to learn proper communication procedures by a process of hit and miss.
When new employees are brought into the organization, they need to receive a comprehensive introduction into the proper ways to communicate, throughout the organization.
Outline four factors that might affect an audience’s accurate reception of information
- Focusing on a personal agenda
When we spend our listening time formulating our next response, we cannot be fully attentive to what the speaker is saying.
- Experiencing information overload
Too much simulation or information can make it very difficult to listen with full-attention. Try to focus on the relevant information, and the central points that are being conveyed.
- Criticizing the speaker
Do not be distracted by critical evaluations of the speaker. Focus on what they are saying – the message – rather than the messenger,
- Getting distracted by emotional noise
We react emotionally to certain words, concepts and ideas to a myriad of other cues from Speakers (appearance, non-verbal cues) make a conscious effort to quiet your own emotional reactions so that you can listen properly.
- Getting distracted by external “noise”
Audible noise may be extremely distracting. Some things can be minimized e.g., turn down the ringer on your phone, and the email beep on the computer while meeting with someone. Other noises may be unavoidable .e.g. construction, other-people. Also, there may be figurative “‘noise” from the external environment, such as distracting, or inappropriate decor in a room, or environmental, conditions such as the room being too hot or cold
- Experiencing physical difficulty
Feeling physically unwell or experiencing pain can make it very difficult to listen effectively. You may wish to communicate that this is not reschedule the discussion. Otherwise, you may just need to concentrate even more, on the task of listening.
QUSTION THREE
In relation to communication barriers, explain the following terms
Abstracting
An abstract is a condensation of something. When we communicate, we unconsciously resort to ‘abstracting’, i.e., keeping to the essentials. We eliminate what we decide to be superfluous. But the receiver may not be competent enough to understand what we have eliminated. Abstracting is necessary for good and effective communication but it should not be done in certain demanding situations. If done it becomes a barrier. When you are instructing a lay and illiterate person about cleaning the house you have to tell literally to remove cobwebs, sweep, dust and mop. Abstracting at this situation may not prove to be useful. The worker may not understand that you want every step and process to be gone through. But when you give the job to an agency you can simply say, I want the house “thoroughly cleaned”. They share your perception about the job. Good abstracting can remove barriers in communication caused by unnecessary words and details. In a communication ‘process, if the participants have different levels of perception will be a barrier to communication.
Slanting
Slanting is a barrier to communication. A slanted report is judgmental. News reporters are asked to report news and not give them a slant. A small crowd or a large crowd’ is generally slanted expressions giving only relative meanings. Instead, if you say a gathering of about five thousand people you avoid slanting. Communication should also be unaffected by inferences and assumptions. Most inferences and all assumptions are highly subjective. They tend to become barriers if they form the basis of a message or information.
Built in resistance
It is a possible psychological block which is emotional in nature. For example, you might be emotionally blocked if you are announcing a new policy you know will be unpopular, giving-the first major presentation on your job or writing to someone you dislike. The people with whom you are communicating are also subject to emotional blocks, they may feel indifferent or hostile towards you or your subject or be biased against you perhaps because of your youth sex, race, relatives, friends or even clothes or against your subject perhaps because they think its illogical.
Environmental stress
It is a possible psychological block which is emotional in nature. For example, you might be emotionally blocked if you are announcing a new policy you know will be unpopular, giving-the first major presentation on your job or writing to someone you dislike. The people with whom you are communicating are also subject to emotional blocks, they may feel indifferent or hostile towards you or your subject or be biased against you perhaps because of your youth sex, race, relatives, friends or even clothes or against your subject perhaps because they think its illogical.
Distortion
Distortion refers to the loss of meaning of the message in handling. This largely occurs in the encoding and decoding stages of communication.
QUESTION FOUR
Using an appropriate diagram describe Berlo’s SMCR model of communication
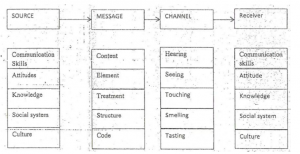
While the Aristotle model of communication puts the speaker in the central position and suggests that the speaker is the one who drives the entire communication, the Berlo’s model of \ communication takes into account the emotional aspect of the message. Berlo’s model of communication operates on the SMCR model
In-the SMCR model
S – Source
M – Message
C – Channel
R-Receiver
Let us now study all the factors in detail:
S – Source
The source in other words also called the sender is the one from whom the thought originates. He is the one who transfers the information to the receiver after carefully putting his thoughts into words.
How does the source or the sender transfer his ‘information to the recipient?
It is done with the help of communication skills, attitude, knowledge, social system and culture
- Communication Skills
An individual must possess excellent communication skills to make his communication effective and create an impact among the listeners. The speaker must know where to take pauses, where to repeat the sentences, how to speak a particular sentence, how to pronounce a word and so on. The speaker must not go on and on. He should also make a point to cross check with the recipients and listen to their queries as well. An individual must take care of his accent while communicating. A bad accent leads to a boring conversation.
- Attitude
It is rightly said that if one has the right attitude, the whole world is at his feet. There is actually no stopping for the person if he has right attitude. A person might be a very, good speaker butt if he doesn’t have the right attitude, He would never emerge as a winner. The sender must have the right attitude to create a long lasting impression on the listeners. An individual might be an MBA from a reputed institute, but he would be lost in the crowd without the right attitude.
- Knowledge
Here knowledge is not related to the educational qualification of the speaker or the number of degrees he has in his portfolio. Knowledge is actually the clarity of the information which the speaker wants to convey to the second party .One must be thorough in what he is speaking with complete in-depth knowledge of the subject.-Remember questions can pop up anytime and you have to be ready with your answers. You need to be totally familiar with what you are speaking. Before delivering any speech, read as much you can and prepare the subject completely without ignoring even the smallest detail.
- Social System
Imagine a politician delivering a speech where he proposes to construct a temple in a Muslim dominated area. What would be the reaction of the listeners? They would obviously be not interested. Was there any problem in the communication skills of the leader or he didn’t have the right attitude? The displeasure of the listeners was simply because the speaker ignored the social set up of the place where he was communicating. He forgot the sentiments, cultural beliefs, religious feelings of the second party. Had it been a Hindu dominated society, his speech would have been very impressive
- Culture
Culture refers to the cultural background of the community or the listeners where the speaker is communicating or delivering his speech.
M-Message
When an individual converts his thoughts into words, a-message is created. The process is also called Encoding
Any message further comprises of the following elements:
- content
One cannot show his grey matter to others to let him know what he is drinking. A thought has to be put words and content has to be prepared. Content is actually the matter or the script of the conversation. It is simpler words, the backbone of any communication.
For example Ted to Jenny. “I am really exhausted today; let’s plan for the movie tomorrow evening”.
Whatever Ted has communicated with Jenny is actually, the content of the message. It is very important for the speaker to carefully choose the words and take good care of the content of the speech. The content has to be sensible, accurate, crisp, related to the thought to hit the listeners bang, on and create an immediate impact.
- Element. .
It has been observed that speech alone cannot bring a difference in the communication. Keep on constantly speaking and the listeners will definitely lose Interest after some time. The speech must be coupled with lots of hand movements, gestures, postures, facial expressions, body movements to capture attention of the listeners and make the speech impressive. Hand movements, gestures, postures, facial expressions, body movements, gestures all come under the elements of the message.
- Treatment
Treatment is actually the way one treats his message and is conveys to the listeners. One must understand the importance of the message and must know how to handle it if a boss wants to fire any of his employees; he has to be authoritative and can’t express his message in a casual way. This is referred t o as the treatment of the message. One must understand how to present his message so that the message is conveyed in the most accurate form.
- Structure
A message cannot be expressed in one go. It .has to be properly structured in order to convey the message in the most desired form
- Code
Enter a wrong code and the locks will never open, enter a wrong password, you will not be able to open your email account. In the same way the code has to be correct in the communication. Your body movements, your language, your expressions, your gestures are actually the codes of the message and to and have to be accurate otherwise the message gets distorted and the recipient will never be able to decode the correct information.
C-Channel
Channel actually refers to the medium how the information flows from the sender to the receiver.
How does one know what the other person is speaking? Through Hearing
How does one know whether the pasta he has ordered is made in white sauce or not? Through tasting
How does one know that there is a diversion ahead or it’s a no car parking zone-? Through seeing
How will an individual come, to know that the food is fresh or stale? How do we find out the fragrance of a perfume? – Through smelling;
How will you find out whether the milk is hot or not? – Through touching.
All the five senses are the channels which help human beings to communicate with each other.
R – Receiver
When the message reaches the receiver, he tries to understand what the listener actually wants to convey and then responds accordingly. This is also called as decoding.
The receiver should be on the same platform as the speaker for-smooth flow of information and better understanding of the message. He should possess good communication ‘skills to understand what, the speaker is trying to convey. He should have the right attitude to understand the message in a positive way-. His knowledge should also beat par with the listener and must-know about the subject. He should also be from the same social and cultural background just like the speaker.
There are several loopholes in the Berlo’s model of communication.-According to the berlo’s model of communication, the speaker and the listener must be on a common ground for smooth conversion, which is sometimes not practical in the real scenario.
QUSTION FIVE
Highlight six methods of upward communication in an enterprise
- The grievance procedure
‘The grievance procedure enables employees to appeal to management and seek redressal of their grievances. It enables employees to bring their work-related problems to the notice of top management and protest against the arbitrary .actions of their immediate superior. Peer review boards accept grievances from employees, hear the arguments of both parties, and then arrive at a decision. The parties concerned .are then bound by these decisions. –
- Open-door policy
This is an organizational policy that allows employees to approach managers at any time and discuss their problems with them. Most of the times, this policy is hot actually implemented in organizations.
- Complaints and suggestions boxes
In some convenient places in the offer or the factory complaints and suggestions boxes are installed. The employees are encouraged to, drop their complaints or suggestion if any, in to these boxes. These boxes are opened at regular intervals and the inform gathered scrutinized
- Social gathering
Social gathering are frequently-arranged in different departments. These gatherings offer a very informal atmosphere in which all employees shed the inhibitions and. feel free to talk about their problems.
- Direct correspondence
Sometimes the manager may directly write to an employee and ask him to communicate with him.
- Reports
Employees may be required to submit reports about the progress of their work a regular intervals
- Counseling
In some organization workers are encouraged to seek the counsel of their superiors on their personal problems. As they feel encouraged to talk about themselves freely, they provide the managers with valuable information.
QUSTION SIX
the modern enterprise draws employees from various cultural backgrounds In relation to the above statement
identify three factors that contribute to communication breakdown across culture
- Cognitive constraints
- Behaviour constraints
- Emotional constraints
explain how the factors identified in (a) (i) above affect communication with employees across different cultures
Cognitive constraints- These are the frames of reference or world views that provide a backdrop that all new information is compared to or inserted into.
Behaviour constraints-Each culture has its own rules about proper behaviour which affect verbal and nonverbal communication. Whether one looks the other person in the eye-or not; whether one says what one means overtly or talks around the issue; how close the people stand to each other when they are talking–all of these and many more are rules of politeness which differ from culture to culture.
Emotional constraints- Different cultures regulate the display of emotion differently. Some cultures get very emotional when they are debating an issue. They yell, they cry, they exhibit their anger, fear, frustration, and other feelings openly. Other cultures try to keep their emotions hidden, exhibiting or sharing only the “rational” or factual aspects of the situation.
describe six characteristics of effective feedback on employees performance in an enterprise
- given with the goal of improvement
- timely
- honest
- respectful
- clear
- issue specific
- supportive
- motivating
- action-oriented
- Solution-oriented.
QUSTION SEVEN
Analyze the cause of barriers to lateral communication
Lateral communication or horizontal communication is communication between different individuals and. departments, or organisms on the same organizational level. Some of the barriers to lateral communication are;
Territoriality
Territoriality often occurs when members of an organization “control task-related activity within a defined and fixed sectional area and as a result regard other involvement of that area as territorial encroachment” “Departments value their turf and strive to protect it This problem may be compounded through interdepartmental rivalries that arise from win/lose competition for rewards and resources”
Rivalry
Rivalry within organizations occurs for example when the different levels of an organization fail “to cooperate with one another”
Specialization
Specialization is a problem that often happens when organizations do not have uniformity within departments, causing communication difficulties. Specialization can occur with procedures or vocabulary used by Afferent departments. For example when “differ .at specialties use the same terms in different ways,” this can create confusion and miscommunication. When this occurs organizations have trouble functioning properly and do not run smoothly.
Lack of Motivation
“Horizontal communication often fails simply because organization members are unwilling to expend the additional effort that it requires.” “Horizontal communication may require contact with people in units that are well removed from our own. The channels and rules of interaction may be unclear. We do not really know these people
QUSTION EIGHT
State six benefits and four limitations of downward communication
- Gives specific direction about the job being entrusted to a subordinate
The decision fallen at managerial levels are transmitted to states in the form of directives so an action may be initiated.
- Explains the policies and organizational procedures
A clear understanding of policies given to the lower state, wider perspectives so that they can grasp and relay their role more meaningfully
- Apprises the subordinates of their performance:
If the performance of the subordinates is objectively assessed and the assessment communicated to him in a considerate tone, it will definitely promote efficiency. Appreciation to good work will raise his morale and strengthen his dedication pointing out has shortcomings will enable him to overcome them.
- Gives information about the rational of the jobsite
To explain to a subordinate the significance of the job assigned to him and why he has been entrusted with it. The importance of the objective of downward communication has only been recognize
- Enhances objectivity of the organization
- Encourages efficiency in work performances
limitations of downward communication
- Under – Communication and over communication
Downward communication is often made by either under communication or over communication i.e. A superior may either talk too little or too much about a job under communication may also involve incomplete instructions, which will inevitably lead to unsatisfactory performance over communication or talking too much, on the other hand may lead to the leakage of confidential information.
- Delay: The lines of communication in downward communication being very long transmitting information to the lowest worker in time – consuming process. By the time information reaches him it may have lost much of as significance, or it may have caused damaging delay
- Loss of information: Unless the communication is fully written, it is not likely to be transmitted downwards in it’s entirely. A part of it is almost contains to be lost.
- Distortion in long lines of communication, information is not only distorted. Exaggerating making under statements giving unconscious taints to facts are a part of human nature.
- Built – in resistance
- Downward communication causes of too much authority flow. The subordinates do not get any opportunity of participating in the decision making process they are expected to receive policy.
identify circumstances under which
oral communication will be preferable to written communication
- Where faster communication is required: Two or more people talking can deliver a message, discuss an issue, reach an agreement, or ask a question and receive an answer much more quickly than they could using written communication.
- Where immediate feedback is expected: When the receiver does not understand a message, he or she can ask for clarification right away.
- Where a message should be conveyed in an emotional way: When people communicate orally, the message consists of more than the spoken words. A nonverbal message accompanies every oral communication. Facial expressions, body movements, gestures, tone of voice, rate of speech, and voice inflection all add meaning to the words actually spoken. These nonverbal components help the receiver interpret the emotional significance of the message.
- Where human relationships should be established: Through oral communication, people working together are able to develop team spirit and a sense of mutual responsibility. By communicating with each other orally, people are able to improve each other’s morale.
written communication will be preferable to oral communication
Where no facial expression is required during conveying the message
– Where no bodily movement is required for effective conveying of the message
– When one does not want to make a face to face discussion.
– Where it is necessary to edit the message before its sent to the receiver.
– Where a permanent record of the message is required.
