INTRODUCTION
People at all levels of the enterprise must constantly make decision and solve problems. Decision making and problem solving are important parts of a manager job. Decision may be of nature:
- How profit should be invested
- Which employee should be assigned a particular task
Whether the problem is larger or small, it is usually the manager who has to confront it , and decide what to take.
Types of Problem and Decision
Managers will make different types of decision under different circumstance and the information available when making a decision will vary.
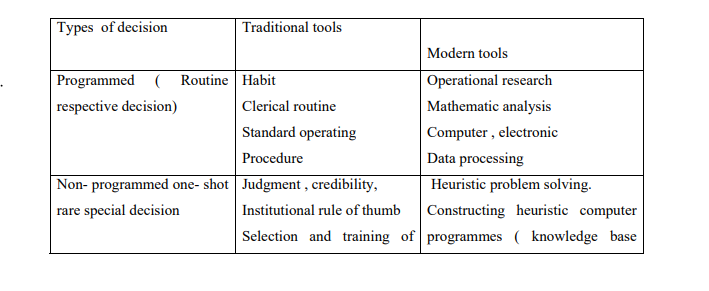
- Programmed
Programmed decision are those that are made in accordance with some habit , rule or procedure . Every organization has written or unwritten policies that simplify decision making in recurring situation . Programmed decisions are used for dealing with complex as well as with uncomplicated issues. If a problem recurs and if its component elements can be defined, predicted and analyzed, then it may be a candidate for programmed decision making. Programmed decision limits the decision maker’s freedom because the organization rather than the individuals decide what to do.
However, the policies, rules and procedure of which we make decision makers of the time needed to work out new solution to every problem, then allow the decision maker to devote attention to other important activities.
- Non- programmed decision are those that deal with unusual or unique problem ; problems which have not come up often enough to be covered by a\a policy or it is so important that it deserves special treatment , it must be handled
by a non –programmed decision e.g. decisions on: - Allocation of resources
- Society relation
- Falling product lines
Most management training programs try to improve a manager ability to make nonprogrammed decision – usually by trying to teach them to make decision reasonably.
TOOLS FOR DECISION MAKING
The following is a summary of decision and the traditional and modern tools used.
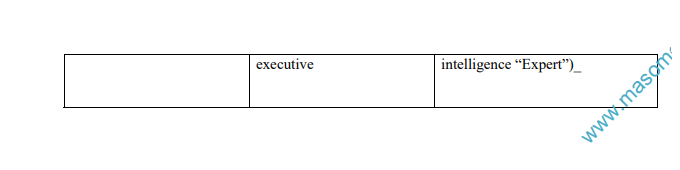 THE DECISION MAKING PROCESS
THE DECISION MAKING PROCESS
It involves six basic steps
Step1: define the problem as an idea to be acted upon
This step involves an accurate assessment of the problem so that management does not treat mere symptoms. This step should result in a statement of the desired results
Step 2: Develop alternative solution
Alternative are the possible course of action, only one of which may ultimately be chosen is need to have as many alternative as possible
Step 3: Gather information pertinent to alternative
Once alternative have been identified the next step in decision making is to collect information. The main information for decision making are existing rules , procedure available facts , research , feasibility studies , simulation , opinion of advisers , experience ,
public and forecast
Step 4: consider constraints and evaluate problems
At this step the manger eliminates some alternative because of constraints. Constraints may be either from external e.g. custom organization charters , limited money and personnel , organization policies , procedure , rules , higher level managers , laws and political consideration , the public competitors actions, labour unions , the education of potential employees , society and economy . The most common method of evaluation include: risk analysis, cost benefit analysis decision trees
Step 5: Alternative Selection
This step involves selection of alternative from those that have been proposed and not eliminated. It is the most difficult and managers should take into account the effects of the decision.
Step: 6 follow –up
Involves implementation of the decision reached in step 5 above. It requires that the appropriate action be carried out. It may involve appropriating funds, assigning personnel, hiring new personnel, erring for work space, or purchase of equipment real estate supplies or inventory
