MASOMO MSINGI PUBLISHERS APP – Click to download and access all our soft copy materials
Below is sample of our COMPANY LAW Revised Notes.
You can buy in SOFT COPY (at our Masomo Msingi Publishers mobile app) or in HARD COPY (We deliver)
Call | Text | WhatsApp 0728 776 317 or E-mail info@masomomsingi.com
TOPIC 1
NATURE AND CLASSIFICATION OF COMPANIES
Introduction
A company can be defined as an association of people who contribute resources into a business and in return acquire shares or ownership of the business and they share out the profit that is generated by the business.
A company is considered to be a legal person and therefore the persons who have created it are always considered to be separate from that company.
In Kenya majority of companies are registered governed by the Companies Act 2015.
CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPANY
- Legal personality: A registered company is considered to be a legal person that is separate from the person who formed it. The concept of legal personality was explained in the case of reference salomon vs salomon co lts 1897. In this case salomon had converted his sole trade business into a company where he was a majority shareholder together with his family members. He had also given the company a loan that was not secured by the company’s assets making him a secured creditor. When the company went into liquidation the other creditors argued that Salomon should not be paid as a secured creditor before them because according to them he and the company were the same. The court held that Salomon and the company were separate and according to the court once a company is registered it becomes a separate legal person different from its owners.
- Limited liability: The liability of members of the company is limited up to the extent of any amount that remains unpaid on the shares that are taken by the members. Therefore, where the member has fully paid for his shares he cannot be called upon to contribute to the debts of the company if the company is unable to pay its debts.
- Ownership of the property: A registered company can acquire and own property under its registered name .Such property does not belong to the members or shareholders. This was explained in the case of Macaura vs Northern Assurance Co Ltd 1925. In this case Macaura had converted his timber business into a company. He took an insurance cover to protect the timber against fire. However, the policy was registered in his own name. When the timber was destroyed by fire Macaura made claim for compensation but the insurance company refused arguing that Macaura had no insurable interest on the timber . When he sued the company the court held that Macaura could not be compensated because the property he insured belonged to the company. The court explained that companies’ properties do not belong to the members
- Capacity to Contract: A registered company can enter into legally binding contracts with other parties in order to pursue its objectives.
- Capacity to sue or be sued: a registered company can sue another party to protect its interest and can also be sued if it fails to fulfill its obligations.
- Perpetual succession: The Company’s life is not affected by the death of its members. If a member dies the company continues to exist.
- Common Seal: A registered company can acquire a common seal that can be used as an official signature of the company.
- Borrowing Power: A registered company can borrow finances from lenders to finance its operations.
- Management: Registered companies are usually managed by trained personnel that are able to provide professional services to the company.
- Transfer of Shares: Shares of a registered company can be transferred from one member to another.
Disadvantages of a company
- It’s expensive: Registration of a company involves costs, including legal fees.
- Complicated procedures: A lot of procedures are involved in formation and running the company.
- Publicity/lack of confidentiality: A company is subject to undue publicity i.e. such documents must be delivered to the registrar and are open to public scrutiny.
- High taxation: companies pay corporation tax at 30% for local companies and 37.5% for foreign companies which is relatively high compared to an income tax paid by individual partners.
- Participation in the management: shareholders other than those who are directors are not involved in the day to day management of the company
- Doctrine of ultra vires: Any act done beyond articles of association is null and void i.e. beyond powers.
TYPES OF COMPANIES
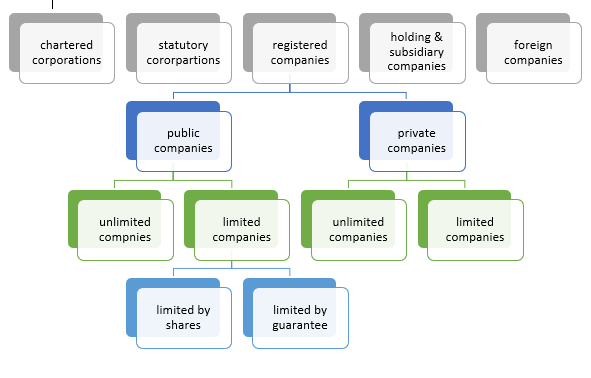
- Chartered corporations
- These are corporations created by a charter that is granted by the president.
- Only private universities are created through charter in Kenya.
- Under university’s act, the president is empowered to grant a charter to any private university intending to be set up to benefit the country.
- The charter must set out the name, membership and also the powers and functions of the universities e.g. mount Kenya University.
- Statutory corporations
- They are created by an Act of parliament or an order of the president in accordance with the state corporations Act.
- These are government corporations especially parastatals.
- The Act creating the corporation gives it a name, management structure and also prescribes the objects i.e. Kenya pipeline, Kasneb, NSSF, NHIF, Central Bank etc.
- Registered corporations
- Are created in accordance with the provisions of companies Act.
- Certain documents must be delivered to the registrar of companies for registration i.e. MOA and AOA. Examples include public and private companies.
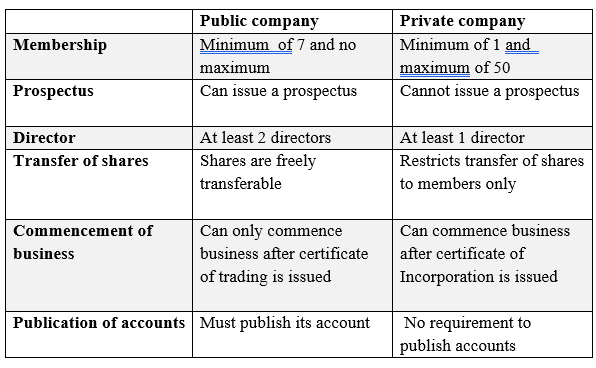
Public company
This is a company with the following features:
- Must have a minimum of 7 members and no. maximum.
- Must have at least 2 directors.
- Its shares must be freely transferable.
- It must have a statutory meeting i.e. first AGM within 3 months of formation for companies that were created before 2015.
- Must publish annual accounts.
- After acquiring certificate of incorporation, it must go ahead and acquire certificate of trading to commence business.
- It must have a company secretary.
N/B: A public company is required to include at the end of its name the words-public limited company (PLC) e.g. Safaricom PLC
Private company
A private company is a company with the following features.
- Members are a minimum of 1 and max of 50 persons excluding employees.
- It requires at least 1 director.
- Restricts the right to transfer its shares.
- It prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for its shares i.e. doesn’t issue a prospectus.
- Not mandatory to publish its accounts.
- Required to have a Company secretary if it has a share capital of 5million.
N/B: A private company must include the word limited or Ltd at the end of its name.
A public and private company may be classified under;
- Companies Limited by shares
It refers to a company which the liability of members is limited to the amount unpaid on the shares held by them.
2. Companies Ltd by guarantee
A company Limited by Guarantee if:
- it does not have a share capital;
- The liability of its members is limited by the company’s articles to the amount that the members undertake, by those articles, to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its liquidation; and
- Its certificate of incorporation states that it is a company limited by guarantee.
Companies Limited by Guarantee in Kenya are mainly registered for the purpose of operating non-profit organizations that require a legal personality.
3. Unlimited companies
These are companies where member’s liability is unlimited.
Such members may lose their private assets, in case the company is declared insolvent.
DISTINCTION BETWEEN COMPANIES AND OTHER FORMS OF BUSINESS ASSOCIATIONS SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPS, PARTNERSHIPS AND COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES
Difference between Public Company and private company