This essentially should incorporate current as well potential businesses. The analysis should address the following two issues:
- What businesses will the organization be in?
- How will the organization allocate its resources among the businesses?
These two issues give rise to the following fundamental strategy challenges:
- How attractive is the group of businesses the organization is in?
- If the organization retains its current businesses, how good is its performance outlook in the future?
- How can the organization strengthen its business portfolio?
Models of Portfolio Analysis
Business portfolio models or matrices are a technique for categorizing businesses and ranking them on the basis of attractiveness. Portfolio analysis enables the organization to identify the strategic options that can help in strengthening its business portfolio in order to enhance performance. The following matrices are among the most popularly used portfolio models.
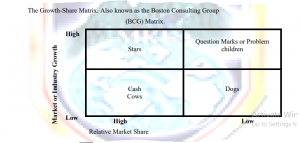
1.Market or industry growth refers to the rate at which industry sales are growing.
2.Relative market share refers to the ratio of the organization‘s market share to that of the biggest rival in the industry.
3.In this 2 x 2 matrix, various businesses are plotted accordingly depending on their market growth and the organization‘s relative market share
Which categories of businesses as represented by quadrants of the matrix, would require the following strategies?
Investment
Divestment
Liquidation
Growth
Joint venture
Strategic alliances
The matrix suggests the following strategy prescriptions or options:
1.Stars
- Best businesses in portfolio
- Strong businesses in good markets
- Businesses generating and using a lot of cash
- Strategy should defend and grow such businesses
2.Question Marks
- Heavy net cash users
- Need cash from other businesses
- Today‘s question marks are likely to be tomorrow‘s stars
- These businesses need investment and growth strategies
3.Cash cows
- Cash-rich businesses
- The cash can be used to develop businesses with better future prospects e.g.
4.Question marks.
- These businesses need strategies that will maintain them so that the organization can continue to ‗milk‘ them for cash.
5. Dogs
- Weak businesses in low growth markets.
- Such businesses need strategies that will drain them for cash.
- Eventually divestment and liquidation strategies are needed.
- Proceeds of liquidation may be used for strengthening other businesses.
6.The strategies that will be considered by the organization will depend on the strategic objectives to be achieved or the opportunities, threats, strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
For example:
Question marks
1.The opportunity to be exploited is high market growth rate for such businesses.
2.The weakness confronting the firm is low market share.
- Such businesses can be turned into stars by enhancing the organization‘s market share (possible strategic objective).
- One or more of the following are possible strategies:
1.Improving professional skills of sales force.
2.More aggressive advertising.- Improving the product.
3.Motivating channel members
4.Changing pricing strategy
- The entire portfolio should be in cash balance i.e. the need to balance between the cash generated and cash used.
Market Attractiveness – Business Strength Matrix. Also known by the following names:
- General Electric Matrix
- McKinsey Matrix
- 3 x 3 Matrix
- Nine Cell Matrix
- Multi-factor Matrix
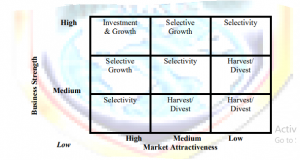
- The logic behind this matrix and the application of the matrix are similar to those of the BCG.
- Unlike the market growth dimension of the BCG model, the market attractiveness dimension of the GE model is a product of many factors.
- Similarly the business strength dimension of the GE model is a product of many factors unlike the relative market share dimension of the BCG model.
- The 3 x 3 matrix produces more refined analyses than the 2 x 2 BCG matrix.
What would be the strategy prescriptions of this model?
At this point every manager is expected to undertake a business strategic analysis. The basic question here is how to succeed in the market place. A choice has to be made among various strategy options. Strategy options must be chosen that will enhance the organization‘s competitive position. Therefore strategic analysis at business level is concerned with identifying and generating strategies that can help the business to develop a solid and sustainable competitive advantage. The strategies can be identified with the help of models, the relevant models depending on the strategic objectives to be achieved.

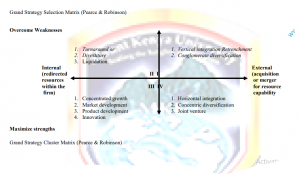
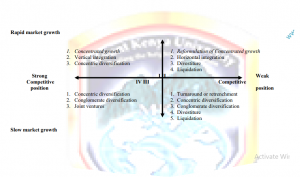
In the Strategic evaluation and choices, The strategic options generated during strategic analysis must be evaluated in order to select the best options. Strategy is aimed at achieving a firm‘s strategic objective. An objective can be achieved by doing a number of things, each being a strategy in itself. For example, British Airways‘ objective of having at least 70% of their professionally qualified in their jobs can be achieved through the following strategies:-
- Training employees on the job.
- Training employees off the job.
- Hiring only qualified people.
- Giving training grants or allowances to employees to enable them attend courses on their own.
- Poaching from other airlines.
The various strategy options for achieving an objective should be evaluated in order to choose the best one(s) among them. Some pertinent evaluation criteria are:
- Effectiveness in achieving the objective.
- Potential competitive advantage.
- Likely competitor responses.
- Benefits e.g. financial benefits.
- Cost
- Affordability
- Resources
- Ease of implementation
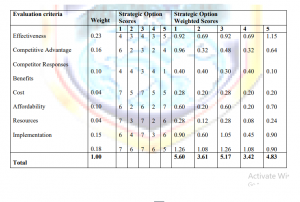
There are a number of ways the criteria can be used to evaluate strategic options. One such way is to assign weights to the criteria and compute weighted scores for the options as illustrated in the example below.
Example:
Objective: Professional qualifications
Strategic Options:
Training employees on the job = 1
Training employees off the job = 2
Hiring only qualified people = 3
Giving training grants and allowances = 4
Poaching from other airlines = 5
Rating Scale:
A seven-point scale where 1=Poor and 7=Very Good may be used to score the extent to which a strategic option suits an evaluation criterion
The weights and scores can be generated by any one of the following methods:
- Evaluator‘s judgment
- Brainstorming
- Jury of experts
- Empirical
- After the evaluation, the strategic option(s) with the highest weighted scores can be chosen for implementation. In this illustration, it could be the first strategic option only, or the first and third strategic options together.
Therefore, the best strategies for ensuring that employees would be professionally qualified as desired are:
- Training employees on the job.
- Hiring only qualified people.
- Current employees who were not qualified would be trained on the job, while ensuring that no one who is not qualified would be hired in future.
- If three strategies were needed or possible, the third strategy would be to poach from other airlines people who were already qualified and perhaps more experienced in the airline industry.
- According to the weighted scores, training employees off-the-job and giving training grants and allowances would be bad strategic options.
