 UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2012/2013
UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2012/2013
THIRD YEAR EXAMINATION FOR THE BACHELOR OF
SCIENCE IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
BIT 4201 ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
DATE: DECEMBER, 2012 TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS: Answer Question ONE and any other TWO
QUESTION ONE
a) Outline two specific laws of Software Evolution as formulated by Lehman and
discuss the empirical evidence supporting the validity of each law. (4 Marks)
b) For each of the key phases of the software development life cycle, discuss the key
features and practices that distinguish the Extreme Programming approach to
software development from traditional software development. (6 Marks)
c) Discuss the importance of the following activities in software engineering
(8 Marks)
i. Project Management:
ii. Risk management:
iii. Configuration Management:
iv. Quality management:
d) Using relevant examples discuss the levels and types of requirements (3 Marks)
e) Discuss the advantages of using formal specification languages (5 Marks)
f) Identifying and considering the needs of all of the different stakeholders can help
prevent software product requirements from being overlooked. Explain (4 Marks)
QUESTION TWO
a) Why is random testing insufficient even for relatively small programs? (2 Marks)
b) Unit testing is the process of testing a single program unit (e.g. a procedure) in
isolation from the rest of the program. How would you go about choosing test
cases for unit testing? (4 Marks)
c) Integration testing can be tacked top-down or bottom-up. Describe each of these
strategies. Why is integration testing harder than unit testing? (4 Marks)
d) Explain the purpose of each of the following. What types of error is each likely to
find?
i. Endurance testing
ii. Recoverability testing
iii. Regression testing
(6 Marks)
e) The company you work for develops internet applications. To reduce time to
market, the company is considering dispensing altogether with integration testing.
Instead, the company plans to rely on Beta testing, in which free trial versions of
new software will be sent to existing, trusted customers to try out, with the
agreement that they will report any problems they encounter. What are the
advantages and disadvantages of this approach? (4 Marks)
QUESTION THREE
a) Zave defines Requirements Engineering as “the branch of software engineering
concerned with the real-world goals for, functions of, and constraints on software
systems [and] the relationship of these factors to precise specifications of software
behaviour, and to their evolution over time and across software families”. Why is
Requirements Engineering considered to be the most important part of software
engineering? (4 Marks)
b) Requirements should state what a system should do, without stating how it should
do it. Why is this distinction useful? (2 Marks)
c) Structured Analysis proceeds by modelling the current physical system,
abstracting a model of the current logical system, and then modelling the new
logical system. What are the advantages and disadvantages of building these three
separate models? What representations are used for
each of these models? (4 Marks)
d) Explain why each of the following is an important property of a software
specification, and explain how it can be achieved when writing specifications:
(6 Marks)
i. validity;
ii. traceability;
iii. verifiability.
e) Project managers sometimes regard work put into writing high quality
specifications as “gold plating”, and claim that it is unnecessary as it doesn’t
contribute to producing program code. Under what circumstances is this view
sensible, and under what circumstances is it foolish? (4 Marks)
QUESTION FOUR
The following class diagram relates to an advertising agency that invoices their customers
for the screening on television of adverts that the agency has created for them.
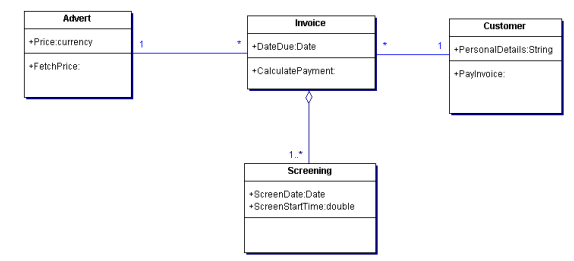
When a customer wishes to make payment they initiate the following collaborations
between objects:-
The Customer>PayInvoice method is triggered.
The PayInvoice method triggers the Invoice>CalculatePayment method.
The CalculatePayment method gets details of each Screening and triggers
Advert>FetchPrice to find out the price of each screening.
a) Represent the collaborations described above in a sequence diagram. (5 Marks)
b) Represent the collaborations above in a UML collaboration diagram. (5 Marks)
c) Why does UML support both sequence and communication diagrams? (5 Marks)
d) How should we cross-check sequence and communication diagrams against other
UML models? (5 Marks)
QUESTION FIVE
a) A software architecture describes a high-level design view of a software system.
What are the advantages of explicitly describing the architecture independently
from the implementation? (5 Marks)
b) Pipe-and-filer architectures treat a task as a series of processing steps, such that
the output of one step forms the input of the next step. Give an example of a pipeand-filter system and describe the advantages and disadvantages of this style?
(5 Marks)
c) Object oriented architectures can be difficult to develop because each object
needs to know which other objects exist and how to call their methods. This
limitation can be overcome using implicit invocation. Describe how an implicit
invocation scheme works, and give two examples of its use. (5 Marks)
d) An architectural description language (ADL) is a general purpose language for
Describing software architectures. What kinds of basic components and basic
connectors would you expect an ADL to provide? What advantages are there in
using an ADL? (5 Marks)
