 UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2013/2014
UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2013/2014
ORDINARY EXAMINATION FOR THE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
BIT 2103 PRINCIPLES OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
DATE: APRIL, 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS: Answer Question ONE and any other TWO
QUESTION ONE
a) . Using your own words, give a definition of “Artificial Intelligence” [2 Marks]
b). Briefly explain three objectives of studying artificial intelligence [3 Marks]
c) Translate the following sentences into predicate logic
i) No one likes brussel sprouts [2 Marks]
ii) John likes everyone who is tall. [2 Marks]
d). Give three limitations of using rules as a technique for representing knowledge.
[3 Marks]
e) . Answer the following questions by indicating whether the statements are True (T) or
False (F). [4 Marks]
a) “Two primary school children, Dennis and Sarut are playing the Tic-tac-toe game.
Dennis makes the first move (starts the game).”The minimum number of moves
Sarut could make is 2 for Dennis to win the game.
b) Depth-first search is often slower than Breadth-first search.
c) Draughts (checkers) and Scrabble are both deterministic games.
d) A rational intelligent agent acts in such a way as to minimize its expected value of
performance measure given the percept sequence to date.
f) . Consider the search tree shown below where each circle represents a node
corresponding to a state in the search space. The estimated cost (i.e. h function) for
finding a solution from a node is shown in its circle. The two nodes with h = 0 are goal
states and the other terminal nodes are dead-ends. (I.e. states that can never reach a goal).
Actual link costs are marked on the links between the nodes. Thus the path cost (i.e. g
function) of a node is equal to the sum of the link costs from the root to that node.
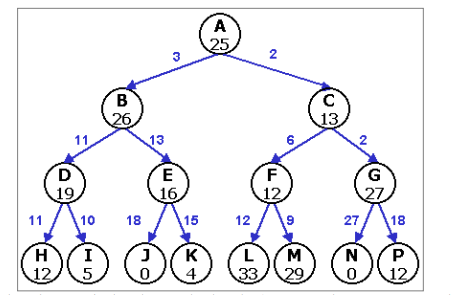
i). Using the depth-first search algorithm, give the path to goal state. What is the path
cost? [4 Marks]
ii). Using the greedy search algorithm to find the path to goal state .what is its path
cost? [3 Marks]
g). Show the truth value of the following propositional calculus sentences [3 Marks]
i). (P Q ) R ; where P and R have truth value F, and Q has truth value T
ii). (P Q) (P R) ; where P, Q and R have truth value T
h).Describe the meaning of the term “inference engine ” [2 Marks]
i).State and explain any two knowledge representation schemes. Give an example for
each case [4 Marks]
QUESTION TWO
a) Explain the meaning of the following terms [6 Marks]
i) Intrapersonal intelligence
ii) Forward chaining
iii) Backward chaining
b) State and explain five elements of defining a search problem in artificial intelligence.
[5 Marks]
c) Explain one application of artificial intelligence business enterprises Give one example
[3 Marks]
d). Consider the MIN-MAX game tree given below. (To answer this question you will
have to draw two neat sketches of the tree on your answer sheet)
i). Fill in the utility function values at each node (the blank circles) in the MIN-MAX
tree below, and mark the first move path, from the root node (initial state) with a thick
line. [2 Marks]
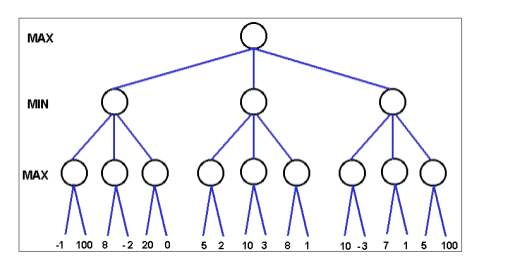
ii). Cross out the branches that are pruned by pruning. How many nodes did you not
have to visit with pruning (count the leaf nodes as well)? Show all intermediate
values at each node as they get updated. [4 Marks]
QUESTION THREE
(a) Explain the meaning of the term “knowledge representation”. [2 Marks]
(b).Briefly explain two assumptions of knowledge representation. Give one example for
each assumption [4 Marks]
(c) State and explain any three methods of acquiring knowledge [3 Marks]
(d)Use the following two figures of an 8 tile puzzle game. to define its search problem
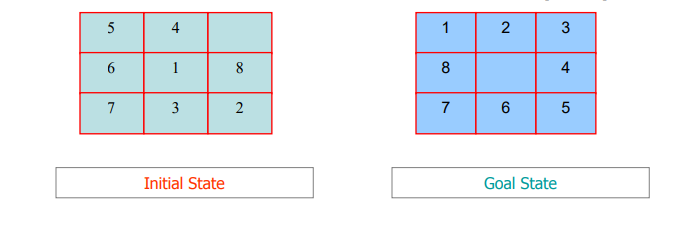
[7 Marks]
QUESTION FOUR
a) Outline four differences between an agent and other software. [4 Marks]
b) State and explain four types of agent’s environments [4 Marks]
c) Briefly explain two types of mobile agents. Give one example for each type
[2 Marks]
d) Describe the two principles of The Alpha-Beta values that are used during pruning
in min max algorithm [2 Marks]
e) You are given an expert system with several rules pertaining to the interpersonal
skills of a job applicant
R1: if the applicant answers questions in straight forward manner then she is easy to
converse with
R2: If the applicant seems honest then she answers in straight forward manner.
R3: If the applicant has item on her resume that are found to be untrue then she does not
have honest.
R4: If the applicant is able to arrange an appointment with the executive assistant then
she is able to strike up a conversation with the executive assistant.
R5: IF the applicant strikes up a conversation with the executive assistant and the
applicant is easy to converse with then she is amiable.
R6: If the applicant has adequate interpersonal skills. Then we will offer her the job.
Solve the following problems:
5 4
6 1 8
7 3 2
1 2 3
8 4
7 6 5
Initial State Goal State
i) Assume that the applicant does not have any items or her resume that are found to be
untrue and that she is able to arrange an appointment with the executive assistant. Run a
forward chain analysis to find out whether we will offer her a job. [2 Marks]
ii) It is known that the applicant answers questions in straight forward manner. Run
backward chain analysis to find out whether we will offer a job to the applicant.
[2 Marks]
iii) We have just discovered that the applicant was able to arrange an appointment with
the executive assistant. It is also known that she is honest. Doesnt she have interpersonal
skills? [2 Marks]
QUESTION FIVE
a) Describe the meaning of the term ‘expert system’ in the context of artificial
intelligence [2 Marks]
b) Outline any four benefits of implementing explanation facility in expert systems?
[4 Marks]
c) Use examples to describe any three applications of expert systems [3 Marks]
d) Draw a well labled structure of an expert system. [4 Marks]
e) Explain the function of each part of an expert system drawn in (d) [7 Marks]
