
UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS: 2017/2018
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN
INFORMATION COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
BCT 1305 SEMICONDUCTOR AND DIGITAL LOGIC
FULL TIME/PART TIME
DATE: DECEMBER, 2017 TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS: Answer Question One & ANY OTHER TWO questions.
QUESTION ONE [30 MARKS]
a) Name the gates in the diagrams below. For each give the truth table. [10 Marks]
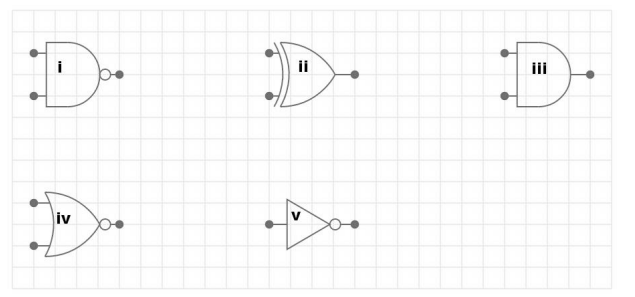
b) Using diagrams explain the difference between N-type and P-type Semiconductors[6 Marks]
c) Describe the difference between a logic gate and a flip-flop. Give a symbol for each
[4 Marks]
d) Give the symbols for the XNOR and NAND gates [2 Marks]
e) Give the difference between the semiconductor and conductor materials [2 Marks]
f) Define the terms below
i. doping
ii. p-n junction
iii. forward bias
iv. free electrons [4 Marks]
QUESTION TWO
a) Define the terms digital and analogue. Clearly show the difference. Neat waveform diagrams
may be used [6
Marks]
b) Perform the following number conversions [8 Marks]
i. 34.6710 = _______________2
ii. 2B.3E16 = ______________2
iii. 10010.10112 = __________8
iv. 26.78 = ________________2
c) List two applications of computer systems [2 Marks]
d) Give two advantages of digital transmission over the cheaper analogue transmission
[2 Marks]
QUESTION THREE
a) Define the following as used with digital logic [4 Marks]
i. Sequential logic
ii. Counter
iii. Register
iv. Multiplexer
b) Using D-flipflops construct a 4-bit register [4 Marks]
c) Name two main types of counters [2 Marks]
d) Give the circuit and operation of a comparator circuit [6 Marks]
e) Give any two number codes and their use [4 Marks]
QUESTION FOUR
a) Define the term combination logic [2 Marks]
b) Minimise the following logic expressions using the K-map [9 Marks]
i. F(ABC) = m(0,1,2,5,7) Ʃ
ii. F(ABCD) = m(0,1,3,4,6,7,8,10,12,13,15) Ʃ
iii. F(ABC) = m(1,3,5,6,7) Ʃ
c) Apart from data storage give three other application of register circuits. Illustrate each with a
block diagram [6 Marks]
QUESTION FIVE
a) Given the truth tables below, minimise the output using a k-map and give the outputs X and Z.
Draw the circuits. [10 Marks]
A B C X Z
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 1
1 1 1 1 0
b) Give the difference between combinational and sequential logic [3 Marks]
c) A circuit compares two bits A and B, and gives two outputs X{A>B} and Y{A<B}. Draw the
truth table and the logic circuit [7 Marks]
