
2018 Agriculture Paper 2
SECTION A (30 marks)
1. State six characteristics of a good breeding stock.(3 marks)
- Young;
- Healthy;
- Prolific;
- High performer/yielder;
- Free from physical deformities;
- Fertile;
- Proper body conformation;
- Adapted to local conditions;
- Good mothering ability;
2. State four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment.(2 marks)
- Ensure efficiency;
- Make them durable;
- Reduce replacement costs;
- Avoid injury to the user;
3. State four reasons why a calf should be fed on colostrum.(2 marks)
- Highly digestible;
- Highly nutritious;
- Contains antibodies which boost immunity; Has laxative effect;
- Highly palatable;
4. Give two reasons for growing grass around a fish pond.(1 marks)
- Stabilize the banks;
- Attract insects which lay eggs that hatch into larvae for fish food;
5. Name four systems of poultry rearing. (2 marks)
- Free range;
- Deep litter;
- Fold;
- Battery cage;
6. State three advantages of conterriporary comparison method of selecting breeding stock.(1½ marks)
- It is possible to compare animals of different age groups;
- Eliminates differences due to environmental factors;
- It is possible to compare bulls of different artificial insemination centres; It is accurate;
7. Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock breeding:
(a) close breeding (½ mark)
- Close breeding:- Breeding of closely related animals;(b) line breeding (½ mark)
- Line breeding:- Mating of distantly related animals that share a common ancestry;(c) out crossing (½ mark)
- (c) Out crossing:- Mating of unrelated animals within the same breed;(d) cross breeding (½ mark)
- Cross breeding:- Mating of two animals of different breeds;
8. State four livestock rearing practices undertaken in a crush to control parasites and diseases.(2 marks)
- Vaccination;
- Deworming;
- Hoof trimming;
- Spraying;
- Dehorning;
- Treatment/injection;
9. Name the dairy cattle breed that
(a) produces the highest milk yield in kilograms (½ mark)
(a) – Friesian;
(b) is fawn/brown coloured with white colour on the face, legs below knees and hocks, tail switch and flanks (½ mark)
- – Guernsey;(c) is most suitable for marginal areas with poor pastures. (½ mark)
- Jersey;
10. Distinguish between each of the following breeding practices:
(a) clutching and ringing (1 mark)
(a) Crutching:- Cutting of wool around the external reproductive organ of a female sheep to facilitate mating while
Ringing:- Trimming of wool around the sheath of the penis in rams to facilitate mating;
(b) tupping and serving (1 mark)
(b) Tapping:- Act of mating in goats and sheep;
Serving:- Act of mating in cattle and pigs;
11. What is a predisposing factor of a disease?(1 mark)
Conditions which lead to the animal contracting a disease
12. State four candling qualities of good eggs for incubation. (2 marks)
- Fertile (has germinal disk; black spot);
- Free from blood spots; Large air space;
- Free of hair cracks;
- Free of excessively porous shell; Free of broken shells;
13. Apart from the roof, name four other parts of a building that can be constructed using wood. (2 marks)
- Floor;
- Ceiling;
- Door;
- Windows
14. State four symptoms of internal parasite infestation in livestock. (2 mark)
- Starring coat;
- Eggs and parasites seen in faeces;
- General emaciation; Diarrhoea;
- Pot-bellies; Anaemia; Anorexia;
- Dehydration/pale mucosa
15. State the functional difference between the following:
(a) cross-cut saw and rip saw (1 mark)
- Rip saw: – cuts along the grain of wood.
- Cross-cut saw — cuts across the grain of wood;
(b) wood chisel and cold chisel (1 marks)
- Wood chisel — cutting grooves/chopping rough wood surface;
- Cold chisel — cutting thick sheets of metal.
16. Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock health:
(a) predisposing factor (1 mark)
- Conditions inside or outside the animal body which make it to contract a disease;
(b) incubation period (1 mark)
- Is the duration between the time of infection and the time the first symptoms show up;
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
17. The diagram below shows a livestock parasite.
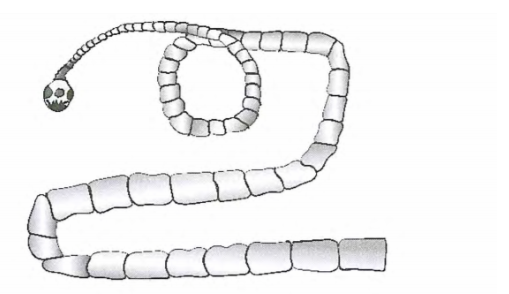
- (a) Identify the parasite.(1 mark)
- Tapeworm(b) Explain how the parasite is passed from(i) livestock to human beings(1 mark)
- Ingestion of bladder worm;
(ii) human beings to livestock(1 mark)
- Ingestion of eggs (proglottids) passed in human faeces during grazing/feeding;
(c) Explain two control measures for the parasite in a zero grazing unit.(2 mark)
- Use of antihelmintics/deworming to kill endo-parasites;
- Proper hygiene in the unit;
- Proper use of latrines to prevent contamination by infected faeces;
- Proper cooking of meat to destroy bladder worms;
- Use of clean feed, feeders, water and watchers to prevent contamination;
18. The diagram below illustrates a tractor drawn implement.
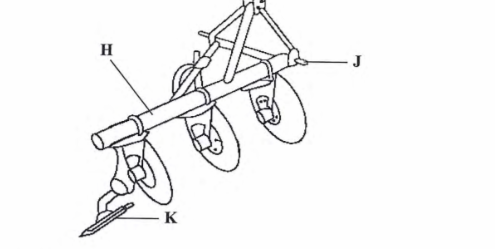
- (a) Identify the implement (1 mark)
- Disc plough(b) Name the part labelled H and I(1 mark)H – Beam;
I – Lower link attachment point;
(c) State one function of the part labelled K(1 mark)
Counteracts the thrust by the discs to balance the plough;/helps to adjust the depth of ploughing;
(d) Explain why the implement is suitable for ploughing areas with hidden stones. (1 mark)
The discs are able to roll over obstacles;
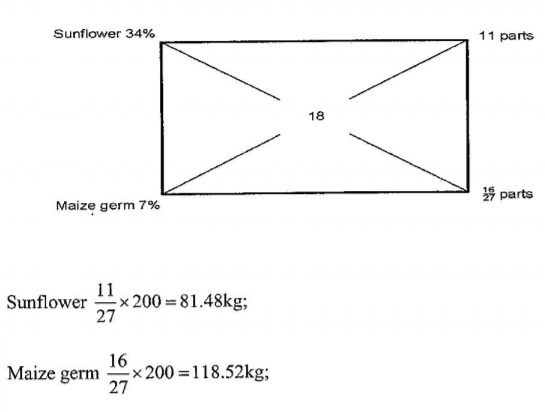
19. A farmer is required to prepare 200 kg of dairy meal containing 18% digestible crude protein (DCP).
Using the Pearson’s Square Method, calculate the quantity of sunflower seed cake (34% DCP) and maize germ (7% DCP) the farmer requires for the dairy meal. (5 marks)
20. The diagram below represents a practice of identifying livestock on a farm.
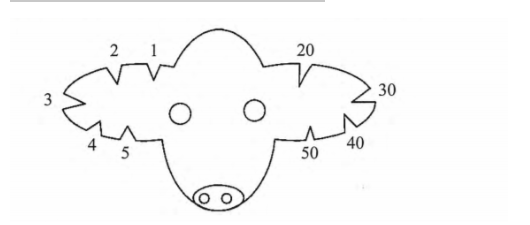
- (a) ldentify the practice(1 mark)Ear notching;(b) Determine the number that identifies the animal represented by the illustration (1 mark)
155
(c) Draw a diagram of the animal identified by the number 148 on the farm. (1 mark)

- (d) Give two reasons why this method of identification is discouraged in livestock rearing. (2 marks)
- The notching is painful to the animal;
- Notched wounds cause secondary infections;SECTION C (40 marks)Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 23.
21. (a) Describe how natural incubation is set up and managed.(8 mark)
- Provide the broody hen with a nesting box which should be spacious to allow movement of the hen;
- Provide nesting material in the nesting box to maintain warmth;
- Provide the broody hen with 10 — 15 eggs; Keep the nest in a dry; and well-ventilated area;
- Provide the hen with balanced feed and water;
- Dust the hen with appropriate insecticides to control external parasites;
- Allow the hen to go out at least once to exercise and feed;
- Do not disturb the hen when the eggs start hatching;(b) Describe the management of growers in poultry rearing.(5 mark)
- Provide adequate floor space, feeders, and waterers;
- Provide litter on the floor up to 15cm deep; Provide growers mash adlib;
- Provide plenty fresh water;
- Dust the birds with appropriate insecticides to control external parasites; Keep the litter dry to avoid dampness;
- Provide grit or oyster shells towards the end of growers stage/at 12 weeks;
- Gradually introduce layers’ mash from the 16th week until it completely replaces growers’ mash at 18th — 19th week.(c) Describe seven possible sources of power on a farm.(7 mark)
- Human power:- Working directly or utilizing their capacity of organization;
- Animal power e.g. donkeys, oxen camels for cultivation and transportation;
- Wind power e.g. for winnowing, pumping water and turning turbines; Water power e.g. driving turbines to produce HEP driving maize grinding mills and pumping water; Biomass e.g. Biogas, wood or charcoal;
- Solar radiation in photosynthesis, drying crops, generate electricity, etc; Electric power from geothermal, hydropower and nuclear stations, battery;
- Fossil fuel:- petroleum, coal, natural gas, etc;
- Tractor:- Bums petrol or diesel to produce power which is transmitted and used in different ways
;22. (a) Describe pneumonia disease under the following sub-headings:
(i) causal organism(1 mark)
Bacteria/virus/HycopIasma mycoides,
Dust and worms in the lungs;
(ii) animals affected(2 mark)
- Calves;
- kids;
- lambs;
- piglets;
- poultry;
(iii) predisposing factors(2 mark)
- Poor ventilation;
- Overcrowding;
- Age
- young animals;
- Diarrhoea and other illnesses;
(iv) symptoms(5 mark)
Dullness;
- Loss of appetite;
- Starring coat;
- Emaciation;
- Rapid breathing;
- Fluctuating body temperature; Nasal mucous discharge;
- If chest is pressed, animal starts coughing
(v) control measures.(3 mark)
- Keep young animals in warm houses;
- Proper sanitation;
- Isolation;
- Treatment using antibiotics;
(b) Explain seven housing requirements for a calf.(7 mark)
- Concrete/slatted floor to facilitate cleaning;
- Spacious to allow exercise, feeding and watering;
- Single housing to prevent licking of one another/ skin infections and spread of worms;
- Well lit to facilitate synthesis of vitamin D;
- Well drained to prevent dampness which predisposes the calf to infections;
- Free from draughts: Solid on the wind ward side to prevent entry of cold winds;
- Leak proof to avoid dampness/wetness which encourages infections;23. (a) State five signs of heat in cattle.(5 mark)
- Restlessness;
- Mounting others and stands still when mounted;
- Slight rise in temperature; Slight drop in milk yield;
- Vulva swells and becomes reddish;
- Clear or slimy mucus discharge from vagina; Frequent mowing;
(b) State five advantages a spray race has over a plunge dip.(5 mark)
- Suitable for pregnant and sick animals;
- Animals do not swallow the acaricide wash; Spraying is faster;
- It is less laborious;
- Acaricide wash is not wasted as it is recycled
(c) Give five reasons for maintaining livestock healthy.(5 mark)
- Healthy animals grow fast and mature early;
- Animals give a longer productive life;
- Produce good quality products;
- Give maximum production/performance; Prevent spread of diseases;
- Healthy animals are economical to keep;
- (d) Explain five factors that determine the amount of food eaten by a livestock animal. (5 marks)
- Body size or weight of the animal; large animals eat more food;
- Environmental conditions where the animals is; animals in cold areas require more food;
- Physiological condition of the animal; lactating animals require more food;
- Level of production:- High producers also require more food;
- Purpose for which the animal is kept; animal kept as a pet requires less food than the one kept for production or performance;
