TOPIC 5 : ORDERING PROCEDURE
This is a set by step process of acquisition of goods , services and works as recommended by PPDA (2005)
A: IMPORTANCE OF FOLLOWING PURCHASE PROCEDURES
- Ensure public organisations get value for money
- Enhance transparency and accountability
- Ensure efficiency and effectiveness
- Promote competition and ensures that competitors are treated fairly by use of competitive procurement methods
- Promotes integrity and fairness of procurement procedures
- Restore public confidence in procurement process
- Build public trust to stakeholders
- Facilitate promotion of local industry and economic development
- To ensure that goods and service are obtained at the right price, right quality, right quantity, from right source and delivered at the right place.
- Conformance to PPDA 2005
- Government /organizational policies
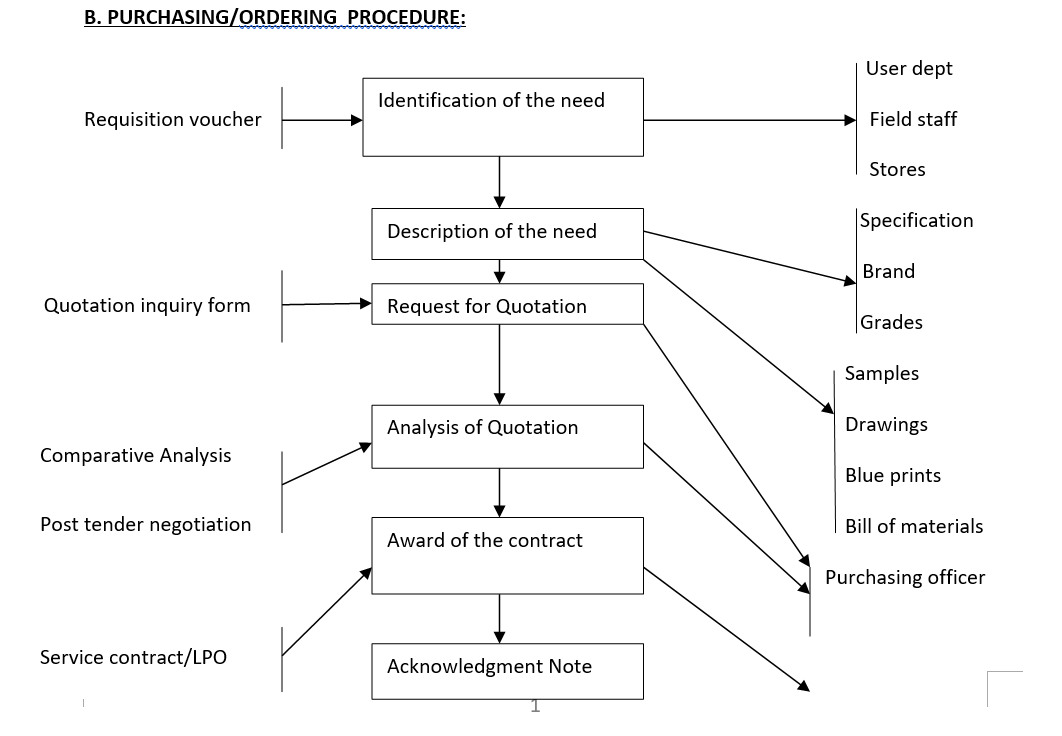
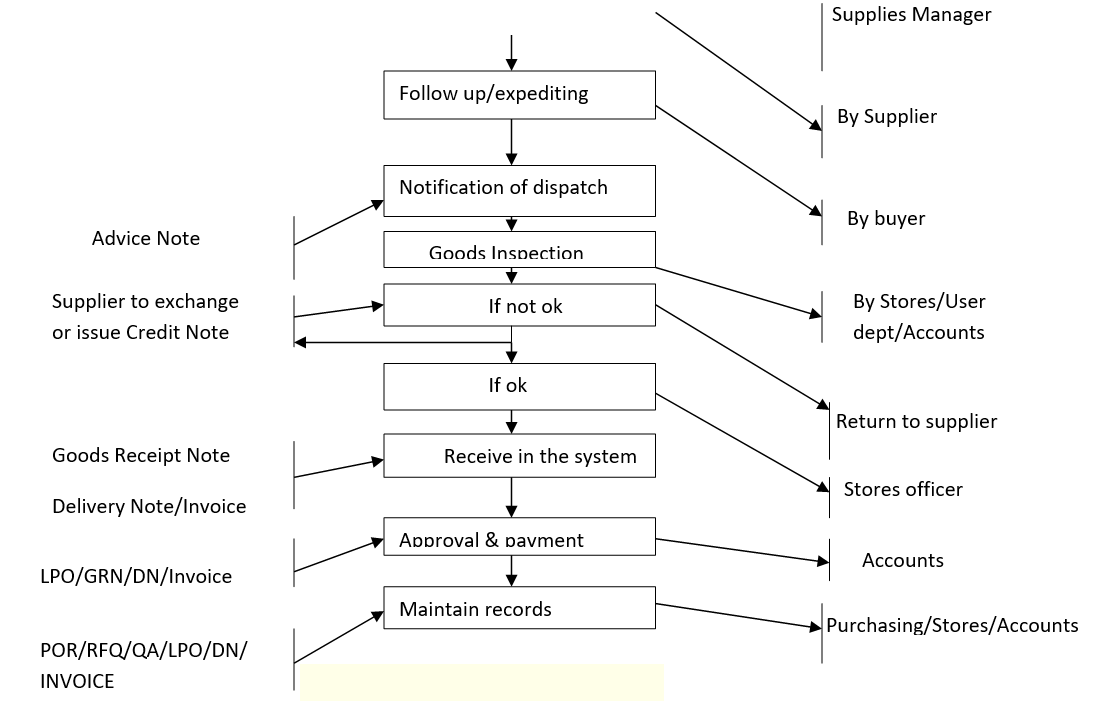
It is worthwhile to note that successful purchasing organisations follow a purchasing cycle or process to ensure that the important elements are not overlooked. Each material or service be procured, will require a different level of activity and priority. To this extent therefore, the purchasing function need to ensure that all the prescribed steps of purchasing are performed and executed.
Authority and controls:
Authority: This is the power to determine, adjudicate, or settle issues/disputes in any social set up. Authority assigned to a particular person or position holder must correspond with responsibilities articulated in various levels of authority. In acquisition of goods/ service the aspect of authority is evident since various persons have the autonomy to initiate or order goods/services for the companies. For instance, stores staff, field staff as well as unit leaders of various departments have the right to initiate purchasing through raising purchase order requisitions. Purchasing officers on the other hand have a leeway to order goods for the company.
Control: This is the power or influence applied in a working environment in order to complete successful task. Basically, the purchasing function has the power to regulate the aspect buying goods for the company. If a purchasing officer realizes that the requisition forwarded to him by the stores/field staff/user departments entails order of goods which are plenty in the stores, he is entitled to re sent back the requisition to the originator. This attribute to some extent ensures that the company purchase what is needed and not what the originator of the requisition want.
Documentation in Purchasing:
- Requisition:
The stores staff/field staff or user department(s) initiates purchasing through preparation requisitions. Requisitions entail the code number of materials, description of the materials, quantity to order as well as the reason for ordering.
- Local Purchase order:
A purchase order (PO) is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller will provide to the buyer. Sending a PO to a supplier constitutes a legal offer to buy products or services. Acceptance of a PO by a seller usually forms a one-off contract between the buyer and seller, so no contract exists until the PO is accepted.
Reasons why companies use LPOs.
- They allow buyers to clearly and explicitly communicate their intentions to sellers and protect the seller in the event of a buyer’s refusal to pay for goods or services.
- Sets out in writing the items ordered
- Sets out the prices of the items ordered
- Sets out the manner of delivery
- Shows the terms of payment e.g. by cheque or cash
- Evidences the person who signed it and therefore this shows the person to take responsibility for it
- Allows the receiving department something to check against when the goods arrive
- Allows the paying department something to check against before making payment
- Request for quotation (RFQ):
This is a document sent by the buyer to the supplier requesting the supplier to quote the prices accordingly. It is important to note that the RFQ should have clear information pertaining the items to be purchased. This should involve correct contacts of the supplier, ideal specifications and also the quantity to be purchased. The document can be accompanied by other documents such as drawings, any additional information which enables the supplier to quote as per the buyer’s request.
- Quotation enquiry:
Formal statement of promise (submitted usually in response to a request for quotation) by potential supplier to supply the goods or services required by a buyer, at specified prices, and w ithin a specified period. It may also contain terms of sale and payment, and warranties. Acceptance of quotation by the buyer constitutes an agreement binding on both parties.
- Consignment note:
This is a document prepared by a consignor (Supplier) and countersigned by the carrier as a proof of receipt of consignment for delivery at the destination. This document evidences the receipt of the goods an attribute which shows the truthfulness of the actual delivery of the consignment from the consignor to the consignee. The document is generally used as an alternative to bill of lading (especially in inland transport), it is generally neither a contract of carriage nor a negotiable instrument.
- Goods receipt note (GRN):
This is a document used to record the inward entry of any goods received at the premises of the organization. The document normally consist of the details of Quantity Received, Quantity Rejected and Quantity Accepted, Supplier name and Purchase order number. The practice of preparing GRNs is important as it promotes proper inventory control and restricts the unwanted, unauthorized entry of goods in the organization. The GRN preparation is a part of effective Inventory Control Management.
- Advice note:
This is a note sent to a customer (Buyer) by a supplier of goods to advise him that an order has been fulfilled. The advice note may either accompany the goods or be sent separately. Also an advice note notifies the buyer that goods have been dispatched or are ready for collection. Copies of the advice note may be sent to relevant departments e.g. purchasing and stores
Other documents in purchasing
- Quotation analysis
- Delivery Note
- Invoice
- Credit Note
Management of purchasing records:
Management of records is the practise of maintaining the records of an organisation from the time they are created up to their eventual disposal. The practise of records management involve planning, organising, controlling and most importantly provision of authority to the ideal people who should access the records in question. Purchasing records are concerned with the storage of information. This information can be filled manually or through computer system. Computerization enables vast amounts of information to be stored, obviates duplication and ensures efficient retrieval of data. The distinct ways in which purchasing records may be managed entail:
- Filing of the records
- Updating of the records
- Archiving of the records
- Provision of security for the records
- Classification of the records
- Provision of tracking mechanism for easy retrieval of records
- Disposal of records
