CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR/INDIVIDUAL BUYER BEHAVIOUR.
This is the behavior exhibited by consumers in planning,purchasing and using economic goods and services.the concern of a marketer is what causes the act of a purchase or a non-purchase.marketers are therefore concerned with the whowhat how and why and when of consumer behavior.
Consumer market refers to all the individulas and households who purchase goods and services for personal use.
Organization market/behavior refers to when the goods or services bought are for production,own use or resale e.g. government agencies,manufacurers and the wholesalers.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ORGANISATION MARKET/BEHAVIOUR.
- Demand is organizational.
- Volume of transaction is higher
- Few customers are involved
- Usually concentrated in a particular location and not dispersed like consumers.
- Direct distribution is used as opposed to indirect method.
- Professional nature of buying is used.
- Complex negotiations are involved.
- Personal selling promotion is used.
- Buying is influenced by multiple actors ieinitiators,deciders,final users and gate keepers(controls information) ie personal secretaries and technical personnel.
REASONS FOR STUDYING CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR.
- The way a buyer behaves dictates a companys marketing production and other strategies which has a great impact on success or failure of the business.
- Consumer behavior is a major component of the marketing concept/customer focus ie a firm should create a marketing mix that satisfies consumer needs and wants given the changes in their behavior.
- By gaining a better understanding of factors that affect consumer behavior,a marketer is better placed to predict how consumers will respond to the firms total marketing strategies
- Exposure to external stimulus such as advertising has been known to activate the desired response in customers.
- It helps a company to be continually profitable in business.
- Understanding consumer behavior decreases the level of risks especially in launching of the new products.
- Consumer benefit by knowing their own consumption pattern ie they are able to understand why they behave the way they do.
- As scholars, it helps us understand why consumers act in a certain consumption way.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR.
There are four main factors that usually influence consumer behavior ranging from;
- Cultural factors.
- Social factors
- Personal factors
- Psychological/physiological factors.
1.CULTURAL FACTORS.
It consists of;
- Society culture-culture is the set of basic values, perceptions ,beleifs,norms and behviour learnt by a member of the society from families and other important institutions. Culture influences activities people enganging what is material comfort achievement and success.Marketers should always try to identify cultural shifts inorder to discover new products that may be demanded.
- Sub-cultures-this consists of smaller cultures that provides more specific identification and socialization for its members.they include nationalities ie Kenyans vsUgandans,racial groups ie black vswhite,religious groups iemuslimsvsChristians,geographical regions ie western vs eastern etc.many sub-cultures make up important market segments and marketers often design products and marketing programs tailored to the needs of this segments.
- Social class-these are the social stratification within a society.they are relatively permanent with members sharing similar values,intrests and behavior e.g. the upper class,middle class and lower classes.marketers are interested in social class because people within a give social class tend to have similar buying behavior and they show distinct product and planned preferences in areas such as clothing,homefurnishing,leisure activities etc.
2.SOCIAL FACTORS.
There are three components here ie.
1.Reference groups-a group refers to two or more people who interact to accomplish individual or mutual goals.groups have an influence on ones attitude and behavior.they are categorized as;
- Primary group-this have regular but informal interctions e.g. friends,co workers etc.
- Secondary groups-they are more formal but have less regular interactions e.g. religious groups,professional associations etc.
- Aspirational groups-this refers to many kinds of membership groups iescout,ymca and they may hope to join other aspirational groups.
- Membership groups-this is one which a person actually belongs including fraternities,sororities(society of female university/college students),social clubs and family.
- A dissociative group-this is one that a person wishes to maintain a distant from because of differences in values/behaviours.
Reference groups create pressure to conform to certain behavior and lifestyles.a marketer concern is to identify the reference group and target them with a specific marketing programme.
2.Family- this is the most influential social group because through it one acquires orientation towards religion,politics,sportclub,education-ie when parents are book readers the children usually ends up doing the same,selfworth and buying behavior e.g. when making expensive purchases,a husband will influence the wife and vice versa.
3.Role and status-this describes the position a person holds in the society to which he/she belongs.a role consists of the activities people are expected to perform according to the people around them.each role carries a status which reflects the general esteem given to the role by the societ e.g. an mp,achief,manager etc.it also influences the club or organization that one belongs.
4.PERSONAL FACTORS.
There are several variables here;
- Age and life cycle stage-buying is shaped by our age and the stage of the family life cycle e.g. young,singles and old will purchase different products from married couples with children.
- Occupation-blue collar workers tend to buy more work clothes while white collar workers will buy expensive suits.
- Lifestyle-this are the activities,intrests and opinions which potray the whole person.they are influenced by our hobbies and intrests.
- Personality and self concept-personality refers to the unique psychological characteristics that lead to relatively consistent and lasting responses to ones own environment.it includes self confidence,sociability,dominance,aggressiveness etc.personality is useful for analyzing consumer behavior for certain products e.g. heavy coffee drinkers are said to be very social.
This concept is well understood using the concept of the johari window ie
| How we see ourselves | How others see us |
| How we want to be seen | Ideal self-dream |
4.Psychological/physiological factors.
- Motivation-a person has many needs at any given time some of which are biological e.g. hunger and thirst while others are psychological arising from the need for recognition,self esteem or belonging(maslows hierarchy of needs).
A need becomes a motive when it is driven to a sufficient level of intensity.it directs a person to seek satisfaction through a product or service.marketers must therefore uncover the deeper motives of consumers.
- Perception-a persons actions are influenced by his/her perception of the situation.perception is a process by which people correct ,organize and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world.peopleform different perceptions of the same stimulus because of the perceptual process.it involves;
- Selective attention-this is the tendency to scream out most of information to which they are exposed.
- Selective retention-this is the tendency of people to retain information that supports their attitudes and beleifs.
- Selective distortion(change)-this is the tendency of people to interpret information in a way that will support what they already believe.
- Learning-this describes changes in an individuals behavior arising from experience.the learning concept calls for a marketer to build up demand for a product by associating it with strong rives and providing positive reinforcement.
- Beleifs-this is a descriptive thought that a person has about something which may be based on knowledge,opinion,faith or emotional attitude.a marketer will be interested in beleifs that people formulate about specific products and services that if the beleifs are wrong and prevent purchase,a marketer will launch a campgain to correct them.
- Attitudes-they describe a persons relatively consistent favourable or unfavourableevaluation,feelings and tendancies towards an object or idea.it gives rise to liking or disliking things,moving towards or away from products.attitudes are difficult to change and a marketer should therefore try to fit his/her products into existing positive atitudes of consumers.
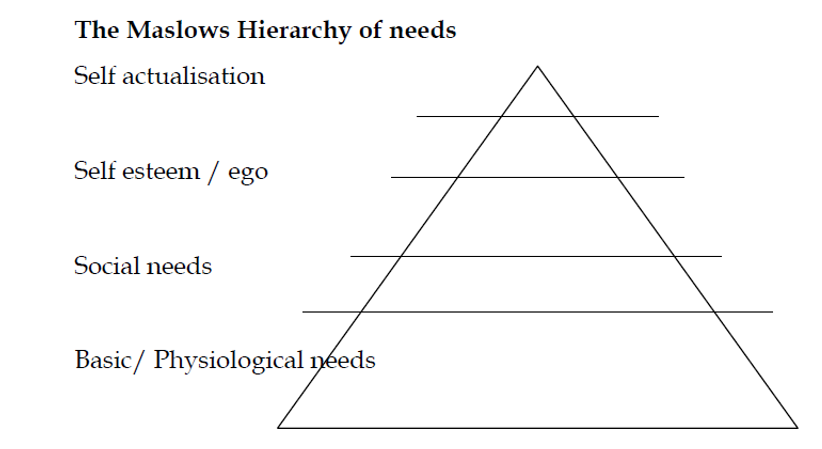
This concept is well understood using the concept of the maslows hierachy of needs which is is a triangular representation.
- Self actualization needs;self development
- Esteem needs;selesteem;recognition;status
- Social needs;sense of belonging,love
- Safety needs;security protection.
- Physiological needs;hunger,thirst.
According to maslow;human needs are arranged in a hierarchy. Starving people will take little interest in latest happenings in the art world. A person tries to satisfy the most important need first when that need is satisfied,it will stop being a motivator and the person will then try to satisfy the next most important need.
TYPES OF BUYING DECISIONS FOR CONSUMERS AND ORGANISATIONAL MARKETS.
- Habitual buying behavior-this occurs under conditions of low consumer involvement and little significant brand difference e.g. salt. Consumers have little involvement in this product category. They simply go to store and reach a Consumers appear to have low involvement with most low cost frequently purchased products.
- Variety seeking buying behavior-consumers undertake this in situations characterized by low consumer involvement but significant perceived brand differences. Consumers often do a lot of brand switching e.g. when buying cookies a consumer may hold some beleifs,choose a cookie brand without much evaluation and then evaluate the brand during consumption but next time,the consumer might pick another brand out of boredrom or simply to try something different. This also arises even during the incidences of purchasing a computer software enabling a website you have used to recognize you on visiting again.
- Dissonance(lack of harmony/agreement between things) –reducing buying behavior. Consumers are highly involved with an expensive,infrequent,or risky purchase but see little difference among brands.ie carpeting.buyers shop around to learn what is available,but buy relatively quickly,responding to price or purchase convenience.afterpurchase,consumers experience post purchase dissonance(after sale discomfort)when they notice certain disadvantages of carpet or her favourable things about brand not purchased.
- Complex buying behavior-highly involved in a purchase and perceive significant differences among brands. Consumers may be highly involved when product is expensive,risky,purchasedinferequently and highly self-expressive.ie a personal computer buyer will consider the variables below,processor,matrixscreen,gb,R.A.M,memory etc.
- New tasks-a business buying situation in which the buyer purchases a product or service for the first time.
- Straight rebuy- a business buying situation in which the buyer routinely re-orders something without any modifications.based on past buying satisfaction ie mainly done by purchasing department.
- Modified rebuy-a business buying situation in which the buyer wants to modify product specifications,price,terms or suppliers ie better offers.
ROLE PLAYERS IN THE BUYING DECISION PROCESS/CONSUMER BUYING ROLES.
This refers to the people involved in buying decision and the roles each person plays.they help a marketer to fine tune(know when to target) marketing effort.the decision making units in consumer buying involves.
- Initiator-this is the person who first suggests or thinks of the idea of buying a particular product or service.
- Influener-this is the person whose views or advice influence the buying decision.
- Decider-this is the person who actively makes the buying decision on what to buy,when or where to buy.
- Buyer-this is the person who makes the actual purchase.
- User-this is the person who consumes/uses the product/service.
CONSUMER ADOPTER CATEGORIES.
- Innovators-this are the first 2.5% of the buyers who adopt new products.they comprise of the young,netter educated and consumers who have higher incomes.they are more willing to take risks.
- Early adopters-these are the next 13.5% of buyers and are guided by respect and are the opinion leaders in the communities.they adopt new ideas early but carefully e.g. preachers,musicians etc.
- Early majority-these are the deliberate consumers.they are the leaders but are careful in what they purchase.they represent 34% of the buyers.
- Late majority-these are the skeptical or suspicious buyers.theyadopt an innovation only after the early majority has tried it.They represent 34% of buyers.
- Laggards-these are the traditionalist or conservative people.theyare suspicious of changes and adopt an innovation only when it has become something of a tradition itself. They represent 16 % of the buyers.
THE CONSUMER BUYING DECISION PROCESS/DECISION MAKING PROCESS.
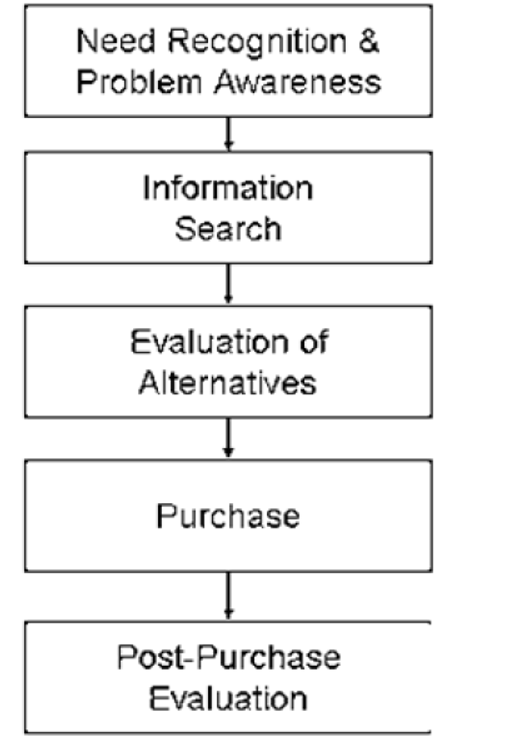
The consumer buying decision starts long before the actual purchase and continues long after.for routine purchase some of the stages are skipped but for non-routine purchases a consumer will go through the below five stages ie non routine purchaser.
- Need recognition;
This is the first stage in which the consumer recognizes that they have a problem or need.the consumer senses a difference between his/her present state and some future desired state.the need can be triggered by internal stimuli ie normal needs such as hunger or thirst or psychological needs such as self esteem.the rise to a level higher enough to become a drive.the needs can also be triggered by external stimuli e.g. Wilson watching a tv advert on a mobile phone.a marketer should carry out a research to find what brought about this need.wilson may have felt the need for good quality music and thought of buying a mobile phone after seeing the advert.
By gathering such information the marketer can identify factors that triggered interest in the product and develop marketing programmes that involves these factors.
- Information search.
Depending on the consumers drive to purchase the product he/she may undertake any information search related to the need.information search may be;
- Heightened attention(alertness).-in this case,Wilson became more receptive to any information about mobilephones e.g. through advertisement orlistening to friends who own the mobile phone.
- Active information search(actively searching information)-wilson looks for reading material on mobile phones,asks friends to give her more information or visit outlets that sells the phones to enquire for more information.sources of information includes;
- Personal sources-this is the most effective source and it includes family,friends,colleagues etc.
- Commercial sources-this includes adverts,salespeople,displaysetc.they give the most information about the product.
- Public sources-this includes the mass media,tv,radio and newspapers.
- Experiments-this involves handling,examining and using the product.the information obtained increases consumers awareness and help the consumer to drop certain brands from consideration.marketers must therefore design awareness programmes through the sources of information consumer use and importance of each source to the consumer.
- Evaluation of alternatives-this is the stage in which consumer uses the information obtained to evaluate alternative brands.this is based on fact that:
- The consumer is trying to satisfy a need e.g. music and is therefore looking for certain benefits from the product.
- The consumer sees the product as a bundle of attribute for Wilson,this could be music,internet,calling reliability and price of the mobile phone.
- The consumer attaches different degrees of importance to different attributes based on their unique needs.
- Consumers develop a set of brand belief about where each brand stands on each attribute.This makes up the brand image.
- Consumers arrive at attitudes towards the various brands through an attribute evaluation procedure.marketers should study consumers to find out how they evaluate various brands therefore takes step to influence the buyers decision.
- Purchase decision.
This is the stage in which the consumer actually buys the product. The consumer will purchase the most preferred brand. Two factors will influence the purchase decision.
- Attitude of others-This is the extent to which another person attitude reduces ones prefereedalternative.This depends on the intensity of the other persons negative attitude,how close the person is to the consumer and the consumers motivation to comply with the other persons wishes/issues.
- Unexpected situation factors that may come to change the purchase decision-this may be a change in income,price increases etc.this may make a consumer modify,postpone or avoid the purchase decision based on the perceived risk.in executing a purchase decision the consumer may make up to five purchase subdivision ie
- Brand decision e.g. nokia,motorolla and Samsung.
- Vendor decision e.g. safaricomairteletc (where to buy).
- Quantity (do I buy one or two).
- Timing-e.g. at the age of 18 years
- Payment methods e.g. loan
- Post purchase decision.
This will depend on satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the product.it is defined by the relationship between consumers expectation and the products perceived performance. Claims made about the product must truthfully represent the product likely performance. A marketer will be interested in satisfaction or dissatisfaction of the consumer because a dissatisfied consumer may or return the product.
They may seek information to confirm the products high value or may take public action by complaining to the government or other authorities. They can also dispose off the product,rent it out or convert it to serve another purpose.
Satisfied consumers on the other hand are likely to bring more business to the community.
